In the fast-paced world of surgery, stress is an inevitable part of the job. Surgeons face immense pressure and high-stakes situations on a daily basis, which can take a toll on their mental and physical well-being. However, recent studies have shown that mindfulness-based stress resilience training could be a promising solution to help surgeons cope with the demands of their profession.
Mindfulness, a practice rooted in ancient Buddhist traditions, involves paying attention to the present moment with an open and non-judgmental attitude. It has gained popularity in recent years for its potential to reduce stress and improve overall well-being. In the context of surgery, formal mindfulness-based stress resilience training offers a structured approach to cultivating mindfulness skills specifically tailored to the unique challenges surgeons face.
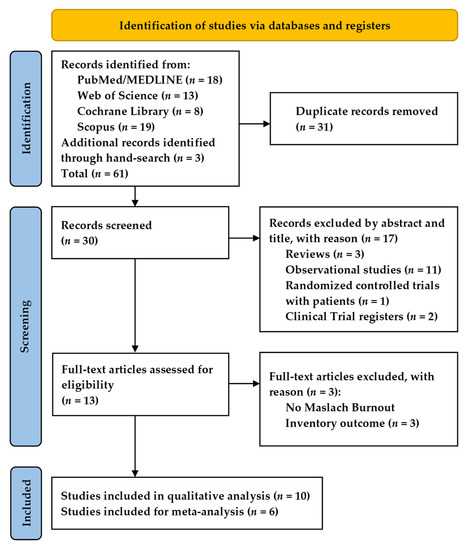
The feasibility of implementing formal mindfulness-based stress resilience training among surgeons is an area of active research. Preliminary studies have shown promising results, with participants reporting reduced stress levels, increased focus, and improved emotional regulation. These findings suggest that integrating mindfulness training into surgical education and practice could have profound benefits for both surgeons and their patients.
The Impact of Stress on Surgeons
Surgeons are highly trained professionals who perform complex and demanding surgical procedures. The nature of their work exposes them to high levels of stress, which can have a significant impact on their well-being and performance. Stress in surgery is often associated with long hours, high patient expectations, and the potential for adverse outcomes.
Research has shown that stress can have negative effects on surgeons, both physically and mentally. Physically, stress can lead to fatigue, sleep disturbances, and musculoskeletal disorders. Mentally, stress can contribute to burnout, depression, and anxiety. These effects can not only affect the surgeon’s quality of life but also impact patient safety and outcomes.
Formal mindfulness-based stress resilience training has emerged as a potential solution to address the impact of stress on surgeons. This training is based on the principles of mindfulness, which involve paying attention to the present moment without judgment. By cultivating mindfulness, surgeons can develop greater self-awareness and the ability to respond to stress in a more adaptive and resilient way.
Feasibility studies have demonstrated that formal mindfulness-based stress resilience training can be successfully implemented in surgical settings. Surgeons who have participated in such training have reported improved well-being, reduced stress levels, and enhanced performance. This training has the potential to equip surgeons with valuable tools and techniques to manage stress and improve their overall resilience.
| Physical Effects of Stress on Surgeons | Mental Effects of Stress on Surgeons |
|---|---|
| Fatigue | Burnout |
| Sleep disturbances | Depression |
| Musculoskeletal disorders | Anxiety |
Addressing the impact of stress on surgeons is crucial for the well-being of both the healthcare professionals and their patients. By implementing formal mindfulness-based stress resilience training, surgical departments can create a supportive and resilient work environment that promotes the physical and mental health of surgeons. Further research is needed to explore the long-term effects and sustainability of such training programs in surgery.
The Need for Stress Resilience Training

Stress is a common and significant issue among surgeons. The demanding nature of surgery, combined with long hours, high stakes, and intense pressure, can lead to high levels of stress and burnout. It is essential to address this issue to ensure the well-being and effectiveness of surgeons.
One potential approach to managing stress in surgery is through resilience training. Resilience refers to the ability to bounce back from adversity and maintain a sense of well-being. It involves developing skills and strategies to cope with stress and challenges effectively.
Mindfulness-based stress resilience training is a promising method for enhancing surgeons’ resilience. Mindfulness involves paying attention to the present moment in a non-judgmental way. It can help surgeons become more aware of their thoughts, emotions, and physical sensations, allowing them to respond to stressors in a more adaptive manner.
Feasibility studies have shown that mindfulness-based stress resilience training can be successfully implemented in various settings, including healthcare. It has been found to reduce stress, improve well-being, and enhance performance among healthcare professionals.
Given the high levels of stress experienced by surgeons and the potential benefits of resilience training, there is a clear need for formal mindfulness-based stress resilience training programs in surgery. Such programs could help surgeons develop the skills and strategies necessary to manage stress effectively and maintain their well-being and effectiveness in the demanding surgical environment.
By addressing the need for stress resilience training, healthcare institutions can support the mental health and professional growth of their surgeons, ultimately benefiting both the individual surgeons and the patients they serve.
Benefits of Mindfulness-Based Stress Resilience Training

Mindfulness-Based Stress Resilience Training (MBSRT) offers numerous benefits for surgeons facing high levels of stress in their profession. The formal training program focuses on enhancing resilience and reducing stress through mindfulness practices.
1. Stress Reduction: MBSRT equips surgeons with techniques to manage stress effectively. The training helps them cultivate a sense of calmness and equanimity, enabling them to navigate the high-pressure environment of surgery with greater ease.
2. Improved Focus and Concentration: MBSRT enhances surgeons’ ability to stay focused and present during complex surgical procedures. By training their minds to stay in the present moment, surgeons can minimize distractions and make more accurate decisions, leading to improved surgical outcomes.
3. Enhanced Emotional Well-being: Surgeons often face emotional challenges due to the nature of their work. MBSRT teaches them how to acknowledge and regulate their emotions, promoting greater emotional well-being and resilience in the face of difficult situations.
4. Increased Self-Compassion: MBSRT encourages surgeons to develop self-compassion and self-care practices. By being kind and understanding towards themselves, surgeons can better cope with the demanding nature of their profession, reducing burnout and promoting overall well-being.
5. Improved Communication and Collaboration: MBSRT emphasizes the importance of mindful communication and collaboration within surgical teams. Surgeons who undergo this training are better able to listen actively, communicate clearly, and work harmoniously with their colleagues, leading to improved patient outcomes.
6. Feasibility and Adaptability: MBSRT is a feasible and adaptable training program that can be easily integrated into surgeons’ busy schedules. The formal structure of the training allows for systematic skill development, ensuring that surgeons can experience the full benefits of mindfulness practice.
In conclusion, Mindfulness-Based Stress Resilience Training offers a range of benefits for surgeons, including stress reduction, improved focus and concentration, enhanced emotional well-being, increased self-compassion, improved communication and collaboration, and feasibility and adaptability. By incorporating mindfulness practices into their daily lives, surgeons can enhance their resilience and well-being, ultimately leading to improved patient care.
Enhanced Emotional Well-being

The formal mindfulness-based stress resilience training for surgeons has shown promising results in enhancing emotional well-being. Surgeons often face high levels of stress and burnout due to the demanding nature of their profession. The mindfulness training aims to provide them with the tools and techniques to effectively manage stress and improve their emotional well-being.
This training is specifically designed for surgeons and incorporates mindfulness practices that are tailored to their unique needs and challenges. Surgeons are taught how to cultivate present-moment awareness, non-judgmental acceptance, and self-compassion, which are essential for managing stress and promoting emotional well-being.
The feasibility of implementing mindfulness-based stress resilience training in the surgery field has been demonstrated through pilot studies and preliminary research. Surgeons who have participated in these programs have reported significant improvements in their ability to cope with stress, reduce burnout, and enhance their emotional well-being.
By integrating mindfulness into their daily lives, surgeons can develop a greater sense of self-awareness, emotional regulation, and resilience. This can lead to improved job satisfaction, better patient care, and reduced risk of burnout and mental health issues.
In conclusion, the formal mindfulness-based stress resilience training holds great potential for enhancing the emotional well-being of surgeons. By providing them with the necessary skills and practices, this training can help surgeons navigate the demanding and stressful environment of surgery with greater ease and resilience.
Improved Cognitive Functioning

Surgeons face high levels of stress and pressure in their daily work, which can have a negative impact on their cognitive functioning. However, formal mindfulness-based stress resilience training has shown promise in improving cognitive functioning among surgeons.
The practice of mindfulness, which involves paying attention to the present moment without judgment, has been found to enhance cognitive abilities such as attention, working memory, and decision-making. By training surgeons in mindfulness techniques, they can learn to better regulate their attention, reduce distractions, and make more effective decisions in the operating room.
Research has shown that surgeons who undergo formal mindfulness-based stress resilience training experience improvements in their cognitive functioning. They are better able to stay focused during surgery, make more accurate judgments, and have improved working memory capacity. This not only benefits the surgeons themselves but also has potential positive effects on patient outcomes.
Furthermore, the benefits of improved cognitive functioning extend beyond the operating room. Surgeons who have undergone mindfulness training report better cognitive performance in their daily lives, including improved concentration and problem-solving skills. This can have a significant impact on their overall well-being and job satisfaction.
In conclusion, formal mindfulness-based stress resilience training has the potential to improve cognitive functioning among surgeons. By enhancing attention, working memory, and decision-making abilities, surgeons can better navigate the high-stress environment of surgery and improve their overall performance. Further research is needed to explore the long-term effects of mindfulness training on cognitive functioning among surgeons and its impact on patient outcomes.

I am Patrina de Silva, a psychologist and mental health blogger in Sri Lanka. After obtaining psychology degrees from the University of Colombo and Monash University, I returned home to work as a counselor while also starting the popular blog “Pressy but Happy” to provide advice on psychological issues. Over the past decade, my empathetic articles have made my blog a leading mental health resource in the country. In addition to writing, I maintain a private therapy practice, frequently volunteer counseling time, and conduct seminars, driven by my passion for destigmatizing mental illness and educating the public on the mind-body connection. I strive to be an influential voice in my field through my compassionate approach.
