
Police work is a demanding profession that often exposes officers to high levels of stress. The nature of their job requires them to face dangerous situations, make split-second decisions, and deal with the aftermath of traumatic events. As a result, police officers are more likely to experience chronic stress compared to individuals in other professions.
Stress has been shown to have detrimental effects on both physical and mental health. It can lead to the development of anxiety disorders and other psychological issues. Understanding the associations between stress, anxiety, and resiliency in the context of police work is crucial for promoting the well-being of these brave men and women who serve and protect our communities.
Research has found a strong correlation between stress and anxiety among police officers. The constant exposure to stressful situations can contribute to the development of anxiety symptoms, such as excessive worrying, restlessness, and irritability. This heightened state of anxiety can negatively impact an officer’s job performance and overall quality of life.
However, not all officers respond to stress and anxiety in the same way. Some individuals demonstrate remarkable resilience, which allows them to cope effectively with the challenges of police work. These resilient officers are better equipped to handle stress, adapt to changing circumstances, and maintain a positive outlook.
By exploring the link between stress, anxiety, and resiliency in police work, researchers hope to identify factors that contribute to officers’ ability to withstand the pressures of their profession. This knowledge can inform the development of targeted interventions and support systems to enhance the well-being of police officers and promote their long-term mental health.
The Impact of Stress on Police Officers
Police work can be extremely demanding and stressful, with officers regularly exposed to high-pressure situations and traumatic events. The associations between stress, anxiety, and resiliency in police work have been extensively studied, highlighting the significant impact that stress can have on the mental and physical well-being of police officers.
Chronic exposure to stressful situations can lead to increased levels of anxiety and can have detrimental effects on an officer’s overall health. The constant pressure to perform under challenging circumstances can contribute to the development of anxiety disorders and other mental health issues.
Furthermore, the nature of police work often involves witnessing or experiencing traumatic events, which can further exacerbate stress levels. These traumatic experiences can lead to symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and can have long-lasting effects on an officer’s mental health.
In addition to the psychological impact, stress can also take a toll on the physical well-being of police officers. The constant strain and pressure associated with police work can contribute to the development of physical health problems such as cardiovascular disease, obesity, and sleep disturbances.
Recognizing the impact of stress on police officers is crucial in order to develop strategies and interventions to support their mental and physical well-being. Implementing stress management programs, providing access to mental health resources, and promoting a culture of resiliency can help mitigate the negative effects of stress and improve the overall health and job satisfaction of police officers.
Physical and Emotional Effects of Stress

Police work is inherently stressful, and the effects of stress can have both physical and emotional impacts on police officers. The demands of the job, including long hours, exposure to traumatic events, and the need to make split-second decisions, can lead to chronic stress.
Chronic stress can manifest itself in a variety of ways. Physically, it can lead to fatigue, headaches, and muscle tension. Police officers may also experience gastrointestinal issues, such as stomachaches or irritable bowel syndrome, as a result of ongoing stress. Additionally, chronic stress can weaken the immune system, making officers more susceptible to illness and infections.
Emotionally, chronic stress can lead to anxiety, depression, and burnout. Police officers may find themselves constantly on edge, irritable, or experiencing mood swings. They may also have difficulty sleeping, which can further exacerbate the effects of stress.
It is important to note that not all police officers experience the same level of stress or exhibit the same physical and emotional effects. Resiliency, or the ability to bounce back from stress, can vary among individuals. Some officers may have strong coping mechanisms in place, allowing them to better manage stress and its effects. Others may struggle to cope, leading to a higher risk of developing stress-related conditions.
Research has shown associations between stress, resiliency, and job performance in police work. Understanding the physical and emotional effects of stress is crucial in developing strategies to support the well-being of police officers and promote their resiliency in the face of challenging work environments.
High-Risk Factors for Stress in Police Work

Police work is inherently stressful due to the nature of the job, which involves dealing with high-pressure situations, traumatic events, and constant exposure to violence and danger. The stress experienced by police officers can have significant negative effects on their mental and physical well-being, as well as their ability to perform their duties effectively.
Resiliency, or the ability to bounce back from stressful situations, plays a crucial role in mitigating the impact of stress on police officers. However, certain high-risk factors can make it more challenging for officers to maintain their resiliency and cope with the stress they face on a daily basis.
- Excessive workload: Police officers often work long hours, including night shifts and weekends, which can lead to chronic fatigue and increased stress levels. The demanding nature of the job, with its high workload and pressure to meet performance targets, can make it difficult for officers to find time for self-care and relaxation.
- Lack of support: Police officers may feel isolated and unsupported, both within their own organization and in the broader community. They may face criticism and hostility from the public, which can erode their sense of trust and increase their anxiety and stress levels. A lack of support from colleagues and superiors can also contribute to feelings of burnout and emotional exhaustion.
- Traumatic incidents: Police officers are frequently exposed to traumatic incidents, such as accidents, violence, and death. Witnessing and dealing with these events can have a profound impact on their mental health and well-being. The constant exposure to trauma can increase the risk of developing post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and other anxiety disorders.
- Organizational factors: The organizational culture and policies within police departments can contribute to stress and anxiety among officers. A lack of clear communication, inadequate training, and ineffective leadership can create a hostile work environment and increase job-related stress. Additionally, the stigma surrounding mental health issues within law enforcement can prevent officers from seeking help and support when they need it most.
Understanding the high-risk factors for stress in police work is essential for developing effective strategies to support officers and promote their resiliency. By addressing these factors and implementing measures to reduce stress and anxiety, police departments can create a healthier and more supportive work environment for their officers.
The Connection between Stress and Anxiety
Stress and anxiety are closely intertwined in the context of police work. The demanding nature of the job can often lead to high levels of stress, which in turn can contribute to the development of anxiety. Police officers face numerous stressors on a daily basis, including exposure to traumatic events, long hours, and the pressure to make split-second decisions that can have life-altering consequences.
Resiliency plays a crucial role in how individuals respond to stress and anxiety in the workplace. Those with higher levels of resiliency are better able to cope with the challenges and demands of police work, reducing their susceptibility to anxiety. Resilient individuals are more likely to bounce back from stressful situations, adapt to change, and maintain a positive mindset.
Research has shown that there are significant associations between stress and anxiety in police officers. High levels of stress have been found to increase the likelihood of developing anxiety disorders, such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). These disorders can have a profound impact on an officer’s well-being and ability to perform their duties effectively.
It is important for police departments to recognize the connection between stress and anxiety and implement strategies to support the mental health and resiliency of their officers. This can include providing access to counseling services, offering stress management training, and promoting a culture of open communication and support.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Stress and anxiety are closely linked in police work. |
| Resiliency plays a crucial role in how individuals respond to stress and anxiety. |
| High levels of stress increase the likelihood of developing anxiety disorders. |
| Police departments should prioritize the mental health and resiliency of their officers. |
Understanding Anxiety Disorders

Anxiety disorders are a common mental health condition that can significantly impact police work and overall well-being. Police work is inherently stressful, and the demands of the job can contribute to the development and exacerbation of anxiety disorders.
Anxiety disorders are characterized by excessive and persistent worry, fear, and apprehension. Individuals with anxiety disorders may experience physical symptoms such as increased heart rate, difficulty breathing, and sweating. These symptoms can interfere with an individual’s ability to perform their duties effectively and may lead to a decrease in job performance and overall resiliency.
There are several different types of anxiety disorders that can affect police officers, including generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). GAD is characterized by excessive worry and anxiety about everyday situations, while panic disorder is characterized by recurrent panic attacks. PTSD can develop after exposure to a traumatic event and is often marked by intrusive thoughts, nightmares, and hyperarousal.
The associations between police work and anxiety disorders are complex. The high-stress nature of police work can contribute to the development of anxiety disorders, but individuals with pre-existing anxiety disorders may also be more drawn to careers in law enforcement. Additionally, the exposure to traumatic events and the constant threat of danger can exacerbate symptoms of anxiety disorders in police officers.
Resiliency plays a crucial role in managing anxiety disorders in police work. Resilient individuals are better able to cope with stress and adversity, and may be less likely to develop anxiety disorders or experience severe symptoms. Building resiliency can involve developing healthy coping mechanisms, seeking support from colleagues and mental health professionals, and engaging in self-care practices such as exercise and relaxation techniques.
Understanding anxiety disorders and their associations with police work is essential for promoting the well-being and resiliency of law enforcement officers. By recognizing the signs and symptoms of anxiety disorders and providing appropriate support and resources, police departments can help to mitigate the impact of anxiety on officers’ mental health and job performance.
Prevalence of Anxiety among Police Officers
Anxiety is a common mental health issue that affects individuals in various professions, including police officers. The demanding nature of police work, with its exposure to high levels of stress and trauma, can contribute to the development of anxiety disorders.
Studies have shown that police officers are at a higher risk of experiencing anxiety compared to the general population. The prevalence of anxiety among police officers can be attributed to several factors, including the chronic exposure to stressful situations and the need to constantly make split-second decisions that can have life-altering consequences.
The associations between stress and anxiety in police work are well-documented. The constant pressure to perform at a high level, coupled with the inherent dangers of the job, can lead to chronic stress, which, in turn, increases the likelihood of developing anxiety disorders.
However, it is important to note that not all police officers experience anxiety to the same extent. Resiliency plays a crucial role in mitigating the negative effects of stress and anxiety. Police officers who possess higher levels of resiliency are better equipped to cope with the demands of their work and are less likely to develop anxiety disorders.
Efforts to address the prevalence of anxiety among police officers should focus on promoting resiliency and providing adequate support systems. This can include implementing stress management programs, offering mental health resources, and fostering a supportive work environment that encourages open communication about mental health concerns.
In conclusion, the prevalence of anxiety among police officers is a significant issue that warrants attention. By understanding the factors contributing to anxiety and promoting resiliency, steps can be taken to improve the mental well-being of police officers and enhance their overall job performance.
The Role of Resiliency in Police Work
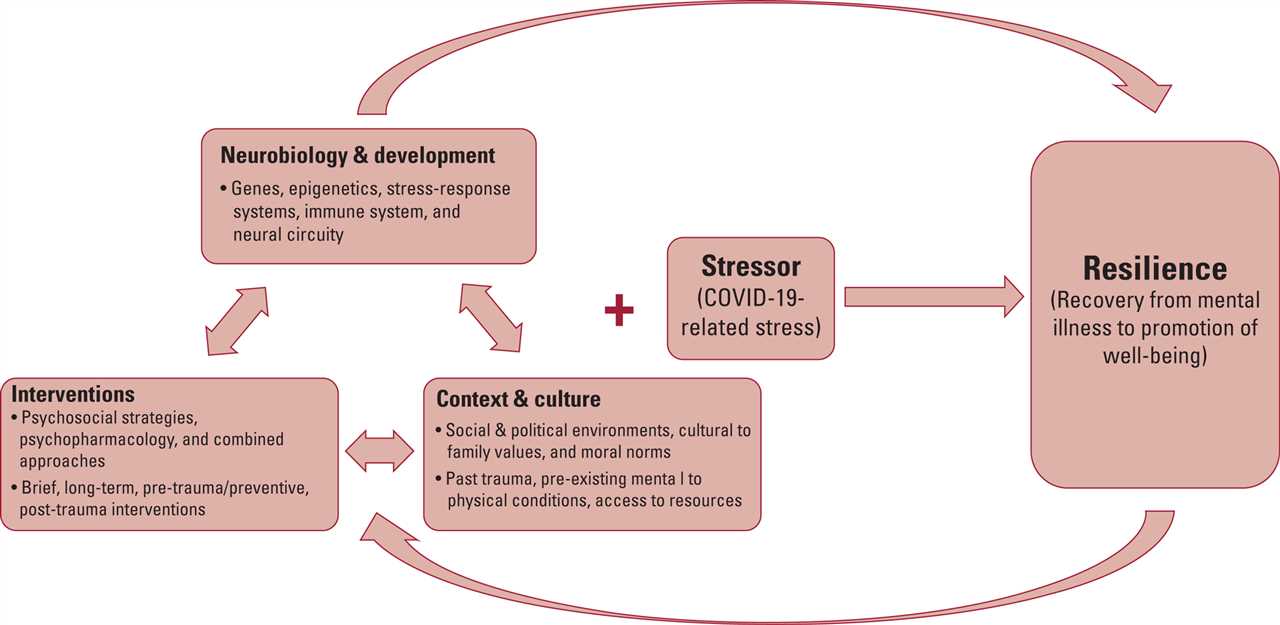
Resiliency plays a crucial role in the demanding and high-stress environment of police work. It refers to an individual’s ability to bounce back from difficult situations, adapt to change, and maintain a positive mindset despite the challenges they face.
Police work is inherently stressful, with officers often exposed to traumatic events, violence, and constant pressure to maintain public safety. The ability to effectively cope with these stressors is essential for their well-being and job performance.
Studies have shown that individuals with higher levels of resiliency are better equipped to handle the stress and demands of police work. They are more likely to maintain a sense of control, remain calm under pressure, and make sound decisions in challenging situations.
Furthermore, resiliency is associated with better mental health outcomes for police officers. It acts as a protective factor against the development of anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Officers who possess higher levels of resiliency are less likely to experience the negative psychological effects often associated with their profession.
Resiliency is not only beneficial for individual officers but also for the overall functioning of police departments. It contributes to higher job satisfaction, improved teamwork, and greater organizational effectiveness. Officers who are resilient are better able to support and assist their colleagues, fostering a positive work environment.
Developing and enhancing resiliency skills should be a priority in police training and ongoing professional development. This can be done through stress management programs, psychological support services, and resilience-building exercises. By investing in the well-being and resiliency of police officers, organizations can ensure their long-term success and effectiveness.
In conclusion, resiliency plays a critical role in police work by enabling officers to effectively navigate the stress and challenges they face. It is associated with better mental health outcomes, improved job performance, and a positive work environment. By recognizing and promoting the importance of resiliency, police departments can support the well-being and success of their officers.
Defining Resiliency and its Importance
Resiliency is a crucial trait for individuals working in high-stress occupations such as the police force. It refers to the ability to bounce back and recover from adversity, challenges, and traumatic experiences. In the context of police work, resiliency is the capacity to effectively cope with the constant exposure to anxiety and stress.
Police work is inherently demanding, with officers facing a wide range of stressors on a daily basis. These stressors can include dealing with dangerous situations, witnessing violence, managing conflicts, and facing the constant threat of harm. As a result, police officers are at a higher risk of developing anxiety and stress-related disorders.
Understanding and cultivating resiliency is essential for police officers to maintain their mental well-being and perform their duties effectively. Resiliency allows officers to adapt and thrive in the face of adversity, enabling them to remain focused, make sound decisions, and maintain positive relationships with colleagues and the community they serve.
By developing resiliency, police officers can better manage the challenges and pressures that come with their work. They are more likely to maintain good mental health, reduce the risk of burnout, and experience greater job satisfaction. Moreover, resiliency can also contribute to improved overall well-being and life satisfaction.
Research has shown associations between resiliency and various positive outcomes, including lower levels of anxiety and stress, better coping skills, and improved overall psychological functioning. By recognizing the importance of resiliency and implementing strategies to enhance it, police organizations can support the well-being and performance of their officers.
In conclusion, resiliency plays a crucial role in the lives of police officers, helping them effectively navigate the challenges and stressors of their work. By understanding and cultivating resiliency, police officers can maintain their mental well-being, reduce the risk of anxiety and stress-related disorders, and ultimately enhance their performance and satisfaction in their roles.
Building Resiliency in Police Officers

Resiliency is a crucial trait for police officers to develop and maintain in order to effectively cope with the high levels of stress and anxiety that are inherent in their line of work. The associations between stress, anxiety, and resiliency in police work have been extensively studied, and it is clear that building resiliency is essential for promoting the well-being and mental health of police officers.
One effective way to build resiliency in police officers is through comprehensive training programs that focus on stress management techniques, emotional regulation, and coping strategies. These programs can provide officers with the necessary tools and skills to effectively manage and reduce stress and anxiety in their daily work.
Additionally, creating a supportive and inclusive work environment is crucial for building resiliency in police officers. This can be achieved through fostering open communication, promoting teamwork and collaboration, and providing access to resources and support networks. By creating a positive work culture, officers are more likely to feel supported and empowered, which can enhance their resiliency.
Furthermore, implementing regular wellness initiatives can also contribute to building resiliency in police officers. These initiatives can include physical fitness programs, mindfulness and meditation practices, and access to mental health services. By prioritizing officer well-being and providing opportunities for self-care, police departments can help officers better manage stress and anxiety, ultimately enhancing their resiliency.
In conclusion, building resiliency in police officers is crucial for their well-being and mental health. By implementing comprehensive training programs, fostering a supportive work environment, and prioritizing officer wellness, police departments can effectively promote resiliency and help officers cope with the stress and anxiety associated with their work.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Resiliency is essential for police officers to cope with stress and anxiety. |
| Comprehensive training programs can provide officers with tools to manage stress. |
| A supportive work environment promotes resiliency. |
| Wellness initiatives contribute to building resiliency. |
Strategies for Managing Stress and Anxiety
Resiliency in police work is closely associated with the ability to effectively manage stress and anxiety. Law enforcement professionals face unique challenges and high levels of stress in their daily work, which can take a toll on their mental and emotional well-being. Here are some strategies that can help police officers and other law enforcement personnel cope with stress and anxiety:
1. Recognize and acknowledge stress: The first step in managing stress is to recognize and acknowledge its presence. This involves being aware of the physical and emotional signs of stress and understanding how it affects your overall well-being.
2. Practice self-care: Taking care of your physical, mental, and emotional health is crucial for managing stress. Engage in activities that you enjoy, get enough sleep, eat a balanced diet, and make time for relaxation and self-reflection.
3. Build a support network: Surround yourself with supportive colleagues, friends, and family members who understand the unique challenges of police work. Having a strong support network can provide emotional support and help you navigate through stressful situations.
4. Develop healthy coping mechanisms: Find healthy ways to cope with stress and anxiety, such as exercise, meditation, deep breathing, or engaging in hobbies and interests outside of work. Avoid unhealthy coping mechanisms, such as excessive alcohol or drug use.
5. Seek professional help: If stress and anxiety become overwhelming and start affecting your daily life, don’t hesitate to seek professional help. Mental health professionals can provide guidance and support tailored to your specific needs.
6. Practice stress management techniques: Learn and practice stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, time management, and problem-solving skills. These techniques can help you effectively manage stress and prevent it from becoming overwhelming.
7. Prioritize and set boundaries: Prioritize your tasks and responsibilities, and set clear boundaries between work and personal life. Avoid overcommitting yourself and learn to say no when necessary. Creating a healthy work-life balance is essential for managing stress.
8. Stay connected: Stay connected with your colleagues and the law enforcement community. Participate in peer support programs or join professional associations that provide resources and support for managing stress and anxiety.
By implementing these strategies, police officers and other law enforcement personnel can better manage the stress and anxiety associated with their work, enhancing their resilience and overall well-being.
Stress Reduction Techniques for Police Officers
Police work can be incredibly demanding and stressful, with officers often facing high-pressure situations and witnessing traumatic events on a regular basis. This constant exposure to stress can have a significant impact on their mental and physical well-being. However, there are several techniques that police officers can use to reduce stress and promote resiliency in their work.
One effective stress reduction technique is mindfulness meditation. This practice involves focusing one’s attention on the present moment, acknowledging and accepting one’s thoughts and feelings without judgment. Research has shown that regular mindfulness meditation can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being. Police officers can benefit from incorporating mindfulness meditation into their daily routines, whether it’s through guided meditation apps or attending mindfulness training programs.
Another technique that can help police officers manage stress is physical exercise. Engaging in regular physical activity not only improves physical fitness but also releases endorphins, which are natural mood boosters. Exercise can help reduce anxiety and depression, increase self-confidence, and improve sleep quality. Police departments can support their officers by providing access to fitness facilities or organizing group exercise activities.
Developing a strong support network is also crucial for stress reduction and resiliency. Police officers can benefit from connecting with colleagues who understand the unique challenges of their work. Sharing experiences, discussing coping strategies, and offering emotional support can help officers feel less isolated and more supported. Police departments can facilitate these connections by organizing peer support groups or providing access to counseling services.
In addition to these techniques, it’s important for police officers to prioritize self-care. This includes getting enough sleep, eating a balanced diet, and engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation. Taking breaks and setting boundaries between work and personal life are also essential for managing stress and preventing burnout.
By incorporating these stress reduction techniques into their daily routines, police officers can better cope with the demands of their work and improve their overall well-being. The associations between stress, anxiety, and resiliency in police work can be mitigated through the implementation of these strategies, ultimately leading to a healthier and more resilient police force.

I am Patrina de Silva, a psychologist and mental health blogger in Sri Lanka. After obtaining psychology degrees from the University of Colombo and Monash University, I returned home to work as a counselor while also starting the popular blog “Pressy but Happy” to provide advice on psychological issues. Over the past decade, my empathetic articles have made my blog a leading mental health resource in the country. In addition to writing, I maintain a private therapy practice, frequently volunteer counseling time, and conduct seminars, driven by my passion for destigmatizing mental illness and educating the public on the mind-body connection. I strive to be an influential voice in my field through my compassionate approach.
