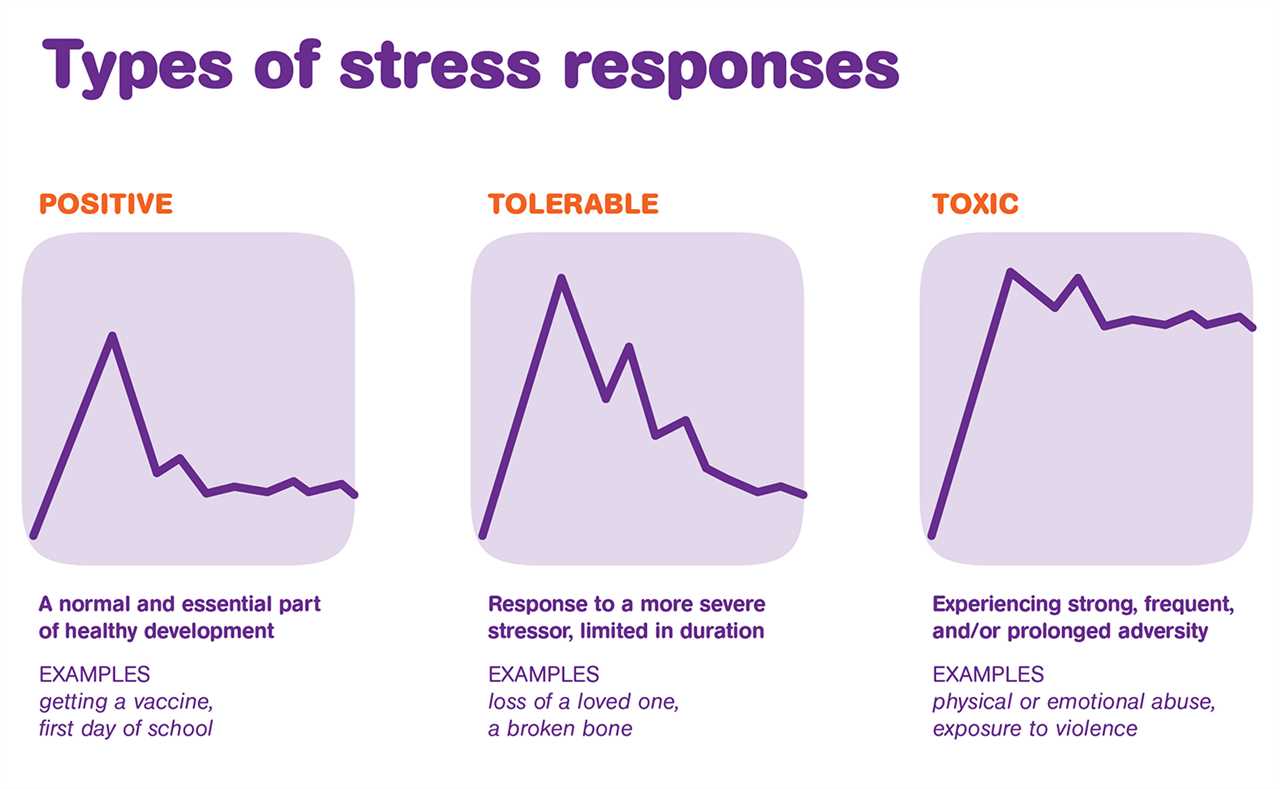
In today’s fast-paced world, stress has become an inevitable part of our lives. From work demands to personal responsibilities, we are constantly bombarded with various stressors that can have a profound impact on our well-being. One particular type of stress that has gained significant attention is toxic stress. Unlike normal stress, toxic stress refers to prolonged exposure to adverse experiences, such as abuse, neglect, or chronic illness, which can have detrimental effects on both our physical and mental health.
To better understand the long-term consequences of toxic stress, researchers have developed a chart that examines the impact of time on resilience. This chart compares the duration of exposure to toxic stress with an individual’s ability to bounce back and recover from adversity. The findings from this chart shed light on the importance of early intervention and support for individuals who have experienced toxic stress.
According to the chart, individuals who have experienced toxic stress for a shorter duration tend to demonstrate higher levels of resilience. This suggests that the sooner we can identify and address toxic stressors, the better chance we have of mitigating their negative impact on our well-being. Additionally, the chart highlights the importance of ongoing support and interventions, even after the removal of the toxic stressor, as individuals may continue to struggle with the long-lasting effects.
Resilience, the ability to adapt and bounce back from adversity, plays a crucial role in mitigating the effects of toxic stress. The chart emphasizes the need for resilience-building interventions, such as therapy, support groups, and self-care practices, to help individuals develop the necessary skills and resources to overcome the challenges posed by toxic stress. By investing in resilience-building strategies, we can empower individuals to not only survive but thrive in the face of adversity.
Understanding Toxic Stress
Toxic stress is a term used to describe the negative and damaging effects of prolonged exposure to stress on the body and mind. It refers to the stress that is chronic, severe, and often uncontrollable, leading to a range of physical and mental health problems.
Time plays a crucial role in understanding toxic stress. When stressors are experienced over a long period of time, the body’s stress response system can become dysregulated, leading to a state of chronic stress. This can have a significant impact on an individual’s resilience and ability to cope with future stressors.
Resilience, on the other hand, refers to the ability to bounce back from adversity and overcome challenges. It is the capacity to adapt and thrive in the face of stress. However, the impact of toxic stress can weaken an individual’s resilience, making it more difficult for them to recover from stressful situations and build their ability to cope.
The toxic stress chart provides a visual representation of the relationship between time and resilience. It shows how prolonged exposure to stress can gradually erode resilience over time, making individuals more vulnerable to the negative effects of stress.
Understanding toxic stress is crucial for identifying and addressing the factors that contribute to its development. By recognizing the impact of chronic stress on resilience, interventions can be implemented to support individuals in building their resilience and reducing the negative effects of toxic stress.
Definition and Causes
Stress is a natural response to challenging or threatening situations. It is a physiological and psychological reaction that helps individuals adapt and cope with various demands. However, when stress becomes excessive and prolonged, it can have detrimental effects on an individual’s well-being.
Toxic stress is a specific type of stress that occurs when an individual is exposed to prolonged and intense adversity, such as physical or emotional abuse, neglect, or chronic poverty. This type of stress can overwhelm the body’s ability to cope and can have long-term negative impacts on physical and mental health.
Time plays a crucial role in the development of toxic stress. When individuals are exposed to prolonged adversity during critical periods of development, such as early childhood, the impact of toxic stress can be particularly severe. The developing brain and body are more vulnerable to the effects of stress during these periods, which can lead to long-lasting changes in brain architecture and functioning.
Resilience is the ability to adapt and bounce back from adversity. It is an essential protective factor against the negative effects of stress. However, the impact of toxic stress can undermine resilience, making it more challenging for individuals to recover and thrive in the face of adversity.
| Causes of Toxic Stress |
|---|
| Physical or emotional abuse |
| Neglect |
| Chronic poverty |
| Parental substance abuse |
| Family dysfunction |
Effects on Physical and Mental Health
Examining the impact of time on resilience is crucial in understanding how toxic stress can affect both physical and mental health. This chart provides a visual representation of the relationship between toxic stress and resilience over time.
| Time | Toxic Stress | Resilience |
|---|---|---|
| Early Childhood | High | Low |
| Adolescence | Moderate | Medium |
| Adulthood | Low | High |
During early childhood, when toxic stress is high, resilience tends to be low. This can have significant impacts on physical and mental health, as children may experience developmental delays, emotional difficulties, and increased risk for chronic diseases.
In adolescence, as toxic stress levels decrease to a moderate level, resilience also increases to a medium level. This is a critical period for intervention and support, as it can mitigate the negative effects of toxic stress and promote better physical and mental health outcomes.
By adulthood, when toxic stress is low, resilience tends to be high. This suggests that individuals who have overcome toxic stress in their earlier years may have developed strong coping mechanisms and protective factors that contribute to better overall health and well-being.
Understanding the effects of toxic stress on physical and mental health over time is essential for implementing effective interventions and strategies to promote resilience and mitigate the negative impacts of toxic stress.
Resilience and its Importance
Resilience is the ability to bounce back and adapt in the face of adversity, including toxic stress. It is the capacity to withstand and recover from difficult experiences, and to maintain mental and emotional well-being despite challenging circumstances.
Stress is a natural response to demanding situations, but when it becomes chronic and overwhelming, it can have detrimental effects on our physical and mental health. Toxic stress refers to prolonged exposure to stressors without adequate support or coping mechanisms, leading to negative outcomes.
Resilience acts as a protective factor against the harmful effects of toxic stress. Individuals with higher levels of resilience are better equipped to handle and overcome adversity, as they possess the skills and resources necessary to navigate challenging situations. They are able to adapt and bounce back from setbacks, maintaining a sense of hope and optimism.
Time plays a crucial role in the development of resilience and its impact on toxic stress. The longer an individual is exposed to stressors, the greater the potential for negative outcomes. However, with time, individuals can also develop and strengthen their resilience, building their capacity to cope with and overcome adversity.
It is important to recognize the significance of resilience in mitigating the effects of toxic stress and promoting well-being. By fostering resilience, individuals can better navigate the challenges they encounter, leading to improved mental and emotional health.
Definition and Factors Influencing Resilience
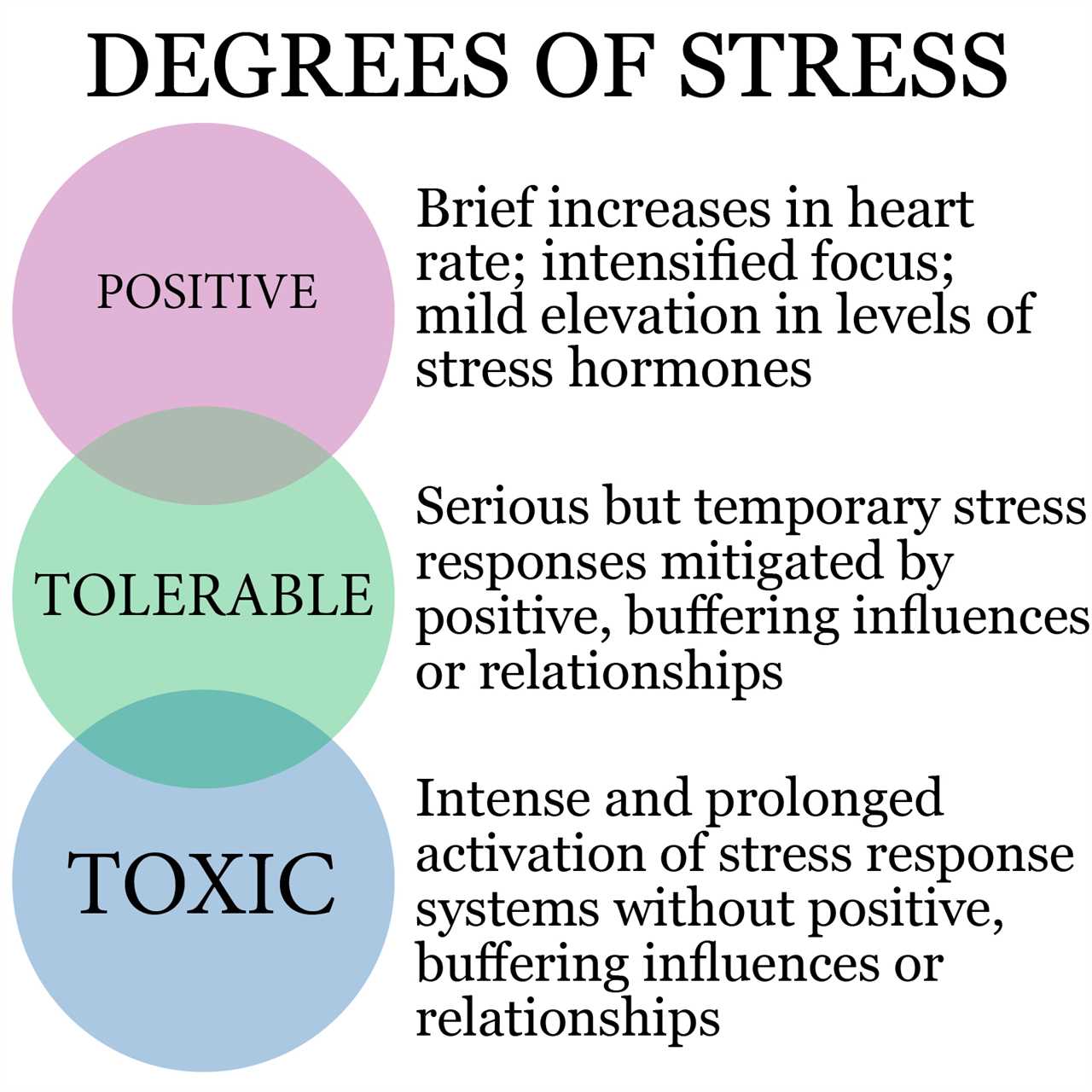
Resilience is the ability to bounce back from adversity and adapt to new challenges. It is a crucial factor in determining how individuals respond to toxic stress over time. Resilience can be thought of as a protective buffer that helps individuals cope with and overcome difficult circumstances.
There are several factors that influence an individual’s resilience. These factors can be categorized into internal and external factors. Internal factors include a person’s temperament, genetics, and cognitive abilities. Some individuals may be naturally more resilient due to their personality traits or genetic makeup.
External factors that influence resilience include social support, access to resources, and the quality of relationships. Having a strong support system and positive relationships can help individuals build resilience and navigate through challenging situations. Additionally, access to resources such as education, healthcare, and employment opportunities can also contribute to an individual’s resilience.
It is important to note that resilience is not a fixed trait, but rather a dynamic process that can be developed and strengthened over time. Building resilience involves developing coping skills, problem-solving abilities, and a positive mindset. It is a lifelong journey that requires continuous effort and self-reflection.
The toxic stress chart highlights the impact of time on resilience. It shows that prolonged exposure to toxic stress can significantly affect an individual’s resilience levels. However, it also demonstrates that with the right support and interventions, individuals can overcome the negative effects of toxic stress and build resilience.
Role of Resilience in Overcoming Toxic Stress
Resilience plays a critical role in overcoming toxic stress and mitigating its long-term effects. The chart examining the impact of time on resilience vs stress clearly demonstrates the importance of resilience in buffering the negative consequences of toxic stress.
When individuals face stressful situations, their ability to bounce back and adapt to adversity becomes crucial. Resilience acts as a protective factor, allowing individuals to cope with and overcome the challenges associated with toxic stress.
The chart reveals that as time progresses, the negative effects of stress can accumulate and intensify. However, individuals with higher levels of resilience are better equipped to withstand and recover from the impact of toxic stress.
Resilience can be fostered and developed through various strategies, such as building strong support systems, practicing self-care, and cultivating positive coping mechanisms. These factors enhance individuals’ ability to manage stress and promote their overall well-being.
Furthermore, resilience is not a fixed trait but can be strengthened over time. By actively engaging in activities that promote resilience, individuals can enhance their ability to navigate and overcome the challenges posed by toxic stress.
In conclusion, the role of resilience in overcoming toxic stress is crucial. The chart highlighting the relationship between resilience and stress over time emphasizes the significance of resilience in mitigating the negative impact of stress. By fostering resilience, individuals can build the necessary skills and resources to overcome adversity and lead healthier, more fulfilling lives.
Examining the Impact of Time on Resilience
Resilience is the ability to bounce back and adapt in the face of adversity, and it plays a crucial role in our overall well-being. However, when exposed to toxic stress, our resilience can be put to the test.
Time is a key factor in understanding how resilience is impacted by toxic stress. The longer the exposure to stress, the more it can wear down our resilience. This can lead to a variety of negative outcomes, such as increased risk of mental health issues, decreased ability to cope with future stressors, and impaired overall functioning.
One way to visualize the impact of time on resilience is through a chart. This chart can show how resilience levels change over time, with the y-axis representing resilience and the x-axis representing time. As time goes on, resilience may start high but gradually decline as the effects of toxic stress accumulate.
It is important to note that resilience is not fixed and can be strengthened through various strategies, such as building a support network, practicing self-care, and seeking professional help when needed. By understanding the impact of time on resilience, we can better support individuals in their journey towards healing and growth.
In conclusion, time plays a significant role in determining the impact of toxic stress on resilience. By recognizing this relationship and implementing strategies to strengthen resilience, we can help individuals navigate and overcome the challenges they face.
Short-term Effects of Toxic Stress
Toxic stress can have immediate and detrimental effects on individuals, particularly children. When exposed to high levels of stress over a short period of time, the body’s stress response system can become overwhelmed and dysregulated.
- Increased heart rate and blood pressure
- Elevated levels of stress hormones, such as cortisol
- Impaired cognitive function and memory
- Difficulty concentrating and paying attention
- Emotional and behavioral changes, including irritability and aggression
- Sleep disturbances and insomnia
- Physical symptoms, such as headaches and stomachaches
These short-term effects of toxic stress can have a significant impact on an individual’s overall well-being and functioning. They can interfere with daily activities, relationships, and academic performance.
It is important to recognize and address toxic stress in a timely manner to prevent further negative consequences and promote resilience. Providing support, creating safe and nurturing environments, and teaching coping strategies can help individuals mitigate the short-term effects of toxic stress and build resilience over time.
Long-term Effects of Toxic Stress
Toxic stress refers to prolonged exposure to high levels of stress, often in the absence of supportive and nurturing relationships. This type of stress can have detrimental effects on a person’s physical, emotional, and cognitive well-being.
Research has shown that the impact of toxic stress can be long-lasting, with effects that extend well into adulthood. A chart examining the impact of time on resilience shows that individuals who experienced toxic stress in childhood are more likely to face a range of challenges later in life.
One of the key findings from this chart is that the effects of toxic stress are cumulative. The longer a person is exposed to high levels of stress, the greater the impact on their overall well-being. This suggests that early intervention is crucial in mitigating the long-term effects of toxic stress.
Furthermore, the chart highlights the differences in resilience between individuals who have experienced toxic stress and those who have not. While some individuals may be able to bounce back from adversity and develop strong coping mechanisms, others may struggle to recover from the effects of toxic stress.
It is important to note that the long-term effects of toxic stress can manifest in various ways. Some individuals may experience physical health problems, such as chronic illnesses or weakened immune systems. Others may face mental health challenges, including anxiety, depression, and difficulties with self-regulation.
In conclusion, the time spent exposed to toxic stress can have a significant impact on an individual’s resilience and overall well-being. Early intervention and support are crucial in mitigating the long-term effects of toxic stress and promoting healthy development.

I am Patrina de Silva, a psychologist and mental health blogger in Sri Lanka. After obtaining psychology degrees from the University of Colombo and Monash University, I returned home to work as a counselor while also starting the popular blog “Pressy but Happy” to provide advice on psychological issues. Over the past decade, my empathetic articles have made my blog a leading mental health resource in the country. In addition to writing, I maintain a private therapy practice, frequently volunteer counseling time, and conduct seminars, driven by my passion for destigmatizing mental illness and educating the public on the mind-body connection. I strive to be an influential voice in my field through my compassionate approach.
