Physicians face numerous challenges in their demanding profession, including long hours, heavy workloads, and high levels of responsibility. These factors can take a toll on their mental and physical health, leading to burnout and decreased job satisfaction. It is crucial for physicians to develop effective coping strategies to manage stress and enhance their psychological resilience.
Stress is an inevitable part of the medical profession, and physicians must find healthy ways to cope with the pressures they face. Coping strategies can vary among individuals, but they often involve seeking social support, engaging in physical exercise, practicing mindfulness techniques, and adopting a positive mindset. These strategies can help physicians maintain their mental well-being and prevent burnout.
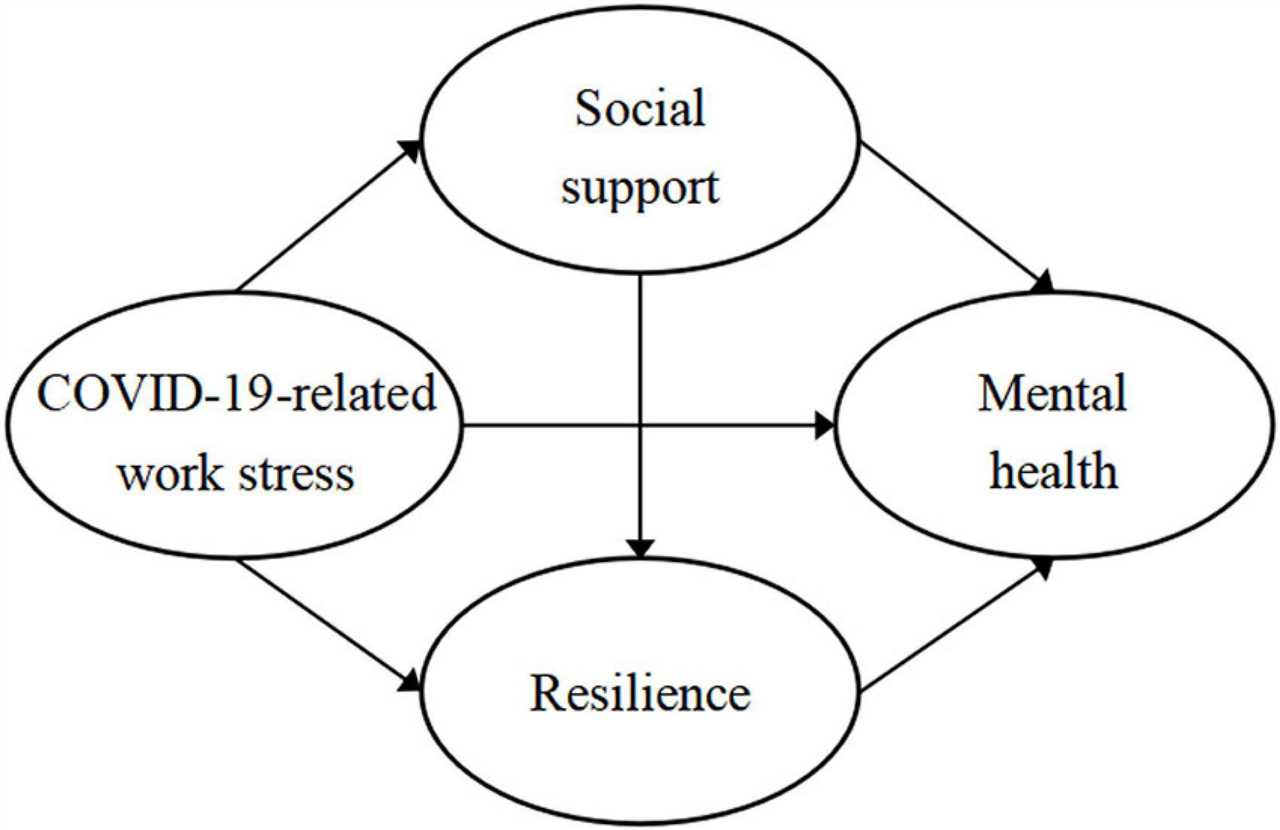
Promoting psychological resilience among physicians is essential for their overall health and job satisfaction. Psychological resilience refers to an individual’s ability to adapt and bounce back from stressful situations. It involves developing a strong support system, cultivating self-care practices, and fostering a sense of purpose and meaning in one’s work. By enhancing their psychological resilience, physicians can better navigate the challenges of their profession and maintain their passion for providing quality patient care.
Understanding the Impact of Stress on Physicians

Resilience is a crucial aspect of a physician’s psychological well-being and ability to cope with the challenges of their profession. However, the demanding nature of their work can often lead to high levels of stress, which can have a significant impact on their mental and physical health.
Physicians face numerous stressors in their daily lives, including long working hours, heavy workload, high patient expectations, and the need to make critical decisions under pressure. These stressors can contribute to burnout and may lead to negative consequences for both physicians and their patients.
The psychological impact of stress on physicians is well-documented. It can result in emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and a decreased sense of personal accomplishment. This not only affects their mental well-being but also their ability to provide quality patient care.
Coping with stress is essential for physicians to maintain their mental resilience and continue to deliver effective healthcare. Various coping mechanisms, such as seeking social support, engaging in physical activity, practicing mindfulness, and cultivating hobbies, can help physicians manage stress and promote their overall well-being.
Understanding the impact of stress on physicians is crucial for developing interventions and support systems that can help them cope effectively. By addressing the underlying causes of stress and promoting psychological resilience, healthcare organizations can create a healthier work environment for physicians and improve patient outcomes.
The Prevalence of Stress Among Physicians
Healthcare professionals, especially physicians, often face high levels of stress due to the demanding nature of their work. Coping with the pressures and responsibilities of their profession can lead to burnout and negatively impact their well-being. The mental and psychological toll of stress on physicians is a significant concern that needs to be addressed.
Studies have shown that a substantial number of physicians experience symptoms of stress, including anxiety, depression, and emotional exhaustion. The prevalence of stress among physicians is alarming, as it can not only affect their own mental health but also impact the quality of care they provide to their patients.
Psychological resilience plays a crucial role in helping physicians cope with stress. It refers to the ability to bounce back from adversity and maintain mental well-being in the face of challenges. Developing resilience can help physicians better manage their stress levels and enhance their overall job satisfaction.
Efforts should be made to raise awareness about the prevalence of stress among physicians and the importance of developing coping strategies. Providing support systems, such as counseling services and stress management programs, can significantly contribute to the well-being and resilience of physicians.
In conclusion, stress among physicians is a prevalent issue that needs to be addressed to ensure their well-being and the quality of healthcare. By promoting psychological resilience and providing resources for coping with stress, healthcare organizations can create a healthier work environment for physicians and enhance patient care.
The Consequences of Chronic Stress on Physicians’ Mental Health

Chronic stress can have significant consequences on the mental health and well-being of physicians. The demanding nature of their profession, coupled with long hours and high levels of responsibility, can lead to a range of negative outcomes.
One of the primary consequences of chronic stress is a decrease in psychological resilience. Resilience refers to an individual’s ability to bounce back from adversity and maintain mental well-being. When physicians are constantly exposed to high levels of stress, their resilience can become compromised, making it more difficult for them to cope with the challenges they face.
The impact of chronic stress on physicians’ mental health can manifest in various ways. One common outcome is burnout, which is characterized by emotional exhaustion, depersonalization, and a decreased sense of personal accomplishment. Burnout can significantly impact a physician’s ability to provide quality care and can lead to decreased job satisfaction and increased turnover rates.
In addition to burnout, chronic stress can also contribute to the development of mental health disorders, such as anxiety and depression. The constant pressure and demands placed on physicians can take a toll on their mental well-being, leading to the onset of these conditions. Left untreated, these disorders can further exacerbate the negative consequences of chronic stress.
Coping strategies play a crucial role in mitigating the consequences of chronic stress on physicians’ mental health. Effective coping mechanisms, such as seeking social support, engaging in self-care activities, and practicing mindfulness, can help physicians build resilience and protect their mental well-being.
It is essential for healthcare organizations to recognize the impact of chronic stress on physicians and take steps to support their mental health. Implementing workplace interventions, providing access to mental health resources, and promoting a culture of self-care can help mitigate the negative consequences of chronic stress and promote the well-being of physicians.
| Key Words |
|---|
| resilience |
| stress |
| health |
| mental |
| physicians |
| well-being |
| burnout |
| coping |
Exploring Coping Strategies and Psychological Resilience

Psychological resilience is a crucial factor in maintaining the mental well-being and health of physicians. The demanding nature of their profession often leads to burnout and other stress-related issues. Therefore, understanding coping strategies and developing psychological resilience is essential for physicians to thrive in their careers.
Coping strategies are the mechanisms individuals use to manage and deal with stressors. Physicians employ various coping strategies to navigate the challenges they face in their daily work. These strategies can be categorized into two main types: problem-focused coping and emotion-focused coping.
Problem-focused coping involves taking practical steps to address the stressors and solve the underlying problems. This may include seeking support from colleagues, engaging in problem-solving discussions, or implementing changes in their work environment to reduce stress. By actively addressing the root causes of stress, physicians can gain a sense of control and improve their overall well-being.
Emotion-focused coping, on the other hand, focuses on regulating the emotional response to stress. Physicians may engage in activities such as meditation, exercise, or seeking emotional support from friends and family to manage their stress levels. These strategies help physicians process their emotions and alleviate the negative impact of stress on their mental health.
Psychological resilience plays a vital role in enabling physicians to cope with the challenges of their profession. Resilience refers to the ability to bounce back from adversity and maintain a positive outlook in the face of difficulties. It involves developing a set of skills, beliefs, and attitudes that enhance one’s ability to adapt and thrive in stressful situations.
Building psychological resilience requires physicians to cultivate self-awareness, develop coping strategies, and foster a supportive network of colleagues and mentors. By strengthening their resilience, physicians can better manage stress, maintain their mental well-being, and provide optimal care to their patients.
In conclusion, exploring coping strategies and developing psychological resilience are essential for physicians to navigate the challenges of their profession. By employing effective coping mechanisms and building resilience, physicians can enhance their well-being, reduce burnout, and ultimately provide better care to their patients.
Effective Coping Strategies for Physicians

Physicians face unique challenges when it comes to their health and well-being. The demands of their profession, coupled with the high levels of stress and burnout, can have a significant impact on their overall mental and physical health. Therefore, it is crucial for physicians to develop effective coping strategies to enhance their resilience and maintain their well-being.
One of the most important coping strategies for physicians is self-care. Taking care of oneself physically, emotionally, and mentally is essential to prevent burnout and maintain a healthy work-life balance. This can include regular exercise, getting enough sleep, eating a balanced diet, and engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation.
Another effective coping strategy for physicians is seeking support from colleagues and peers. Connecting with others who understand the unique challenges of the medical profession can provide a sense of camaraderie and support. This can be done through formal support groups or informal networks where physicians can share experiences, exchange advice, and provide emotional support.
Additionally, cultivating a positive mindset and practicing mindfulness can be powerful coping strategies for physicians. Mindfulness involves being fully present in the moment and non-judgmentally accepting one’s thoughts and emotions. This practice can help physicians manage stress, improve focus and concentration, and enhance overall well-being.
Furthermore, setting boundaries and managing workload effectively are crucial coping strategies for physicians. Learning to say no to excessive work demands and prioritizing self-care can prevent burnout and promote a healthier work-life balance. Delegating tasks, seeking assistance when needed, and practicing time management techniques can also help physicians manage their workload more efficiently.
Lastly, continuing education and professional development can be effective coping strategies for physicians. Staying updated with the latest research and advancements in their field can enhance physicians’ confidence and competence, reducing stress and improving job satisfaction.
| Effective Coping Strategies for Physicians |
|---|
| Self-care |
| Seeking support from colleagues and peers |
| Practicing mindfulness |
| Setting boundaries and managing workload effectively |
| Continuing education and professional development |
In conclusion, physicians face significant stress and burnout in their profession, which can impact their health and well-being. However, by adopting effective coping strategies such as self-care, seeking support, practicing mindfulness, setting boundaries, and continuing education, physicians can enhance their resilience and maintain their psychological well-being.

I am Patrina de Silva, a psychologist and mental health blogger in Sri Lanka. After obtaining psychology degrees from the University of Colombo and Monash University, I returned home to work as a counselor while also starting the popular blog “Pressy but Happy” to provide advice on psychological issues. Over the past decade, my empathetic articles have made my blog a leading mental health resource in the country. In addition to writing, I maintain a private therapy practice, frequently volunteer counseling time, and conduct seminars, driven by my passion for destigmatizing mental illness and educating the public on the mind-body connection. I strive to be an influential voice in my field through my compassionate approach.
