In today’s fast-paced world, stress has become an inevitable part of our lives. Whether it’s the pressure to meet deadlines at work, financial difficulties, or personal relationships, stress can take a toll on our mental well-being. The field of psychology explores the intricacies of how stress affects our mental health and the mechanisms of adaptation and resilience that help us cope with traumatic experiences.
Stress is a natural response to challenging situations, triggering a cascade of physiological and emotional reactions in our bodies. However, when stress becomes chronic or overwhelming, it can lead to mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Understanding the psychology behind stress and trauma is crucial for developing effective strategies for recovery and promoting mental resilience.
Traumatic experiences, such as physical or emotional abuse, accidents, or natural disasters, can have a profound impact on our mental well-being. The field of psychology delves into the complex interplay between our cognitive, emotional, and behavioral responses to trauma, exploring how these experiences shape our perception of the world and our ability to cope. By unraveling the psychological mechanisms behind trauma, psychologists can develop evidence-based therapies that facilitate healing and promote resilience.
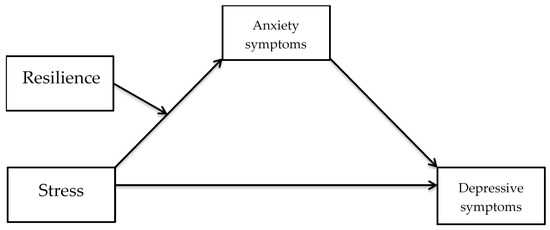
Resilience, the capacity to bounce back from adversity, is a key concept in the psychology of stress and trauma. While some individuals may be more naturally resilient, it is a skill that can be cultivated through various therapeutic approaches. By enhancing emotional regulation, promoting adaptive coping strategies, and fostering social support networks, psychologists empower individuals to develop resilience and recover from traumatic experiences. Understanding the psychological underpinnings of resilience is essential for promoting mental well-being and facilitating long-term recovery.
Understanding Stress

Stress is a natural response to challenging or threatening situations. It is a psychological and emotional reaction that occurs when individuals perceive a situation as overwhelming or beyond their ability to cope. Stress can be caused by various factors, including trauma, work pressure, relationship issues, financial difficulties, or health problems.
Resilience is the ability to adapt and recover from stress and trauma. It involves the capacity to bounce back and maintain mental well-being despite adversities. Resilient individuals are better equipped to cope with stress, as they have developed effective coping strategies and emotional intelligence.
Trauma refers to an emotional response to a distressing or disturbing event. It can result from a single event, such as a car accident or a natural disaster, or from prolonged exposure to stressful situations, such as abuse or war. Trauma can have long-lasting effects on mental health and may require professional intervention for recovery.
Coping mechanisms are strategies individuals use to manage stress and emotional challenges. These can include seeking social support, engaging in physical activity, practicing mindfulness or relaxation techniques, or seeking professional help. Effective coping mechanisms can contribute to mental well-being and help individuals navigate through difficult times.
The field of psychology plays a crucial role in understanding stress and its impact on mental health. Psychologists study the cognitive, emotional, and behavioral aspects of stress and trauma, as well as the factors that contribute to resilience and adaptation. Understanding the psychological mechanisms involved in stress can help individuals develop effective strategies for recovery and enhance their overall well-being.
The Definition of Stress

Stress, in the field of psychology, is a natural response to a demanding or threatening situation that requires adaptation or coping. It is an emotional and mental state that occurs when individuals perceive that they do not have the resources to meet the demands of a particular situation. Stress can result from various sources, such as work pressures, relationship problems, financial difficulties, or traumatic events.
When individuals experience stress, their bodies and minds go through a series of physiological and psychological changes. These changes can include increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, heightened alertness, and the release of stress hormones. The body’s stress response is an adaptive mechanism that prepares individuals to deal with potential threats or challenges.
However, prolonged or excessive stress can have detrimental effects on mental health and well-being. Chronic stress can lead to the development of various mental health disorders, including anxiety disorders, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). It can also weaken the immune system and increase the risk of physical health problems.
Resilience plays a crucial role in how individuals respond to stress. Resilience refers to the ability to bounce back and adapt in the face of adversity or trauma. Individuals with high levels of resilience are better equipped to cope with stress and recover from traumatic experiences. Resilience can be cultivated and strengthened through various strategies, such as social support, self-care practices, and positive coping mechanisms.
Understanding the definition of stress and its impact on mental health is essential for developing effective interventions and support systems. By promoting resilience and providing individuals with the necessary tools to cope with stress, we can help mitigate the negative effects of stress and promote overall well-being.
The Causes of Stress
Stress is a common phenomenon in today’s fast-paced world, affecting individuals of all ages and backgrounds. It is a mental and emotional strain caused by various factors, which can have a significant impact on an individual’s overall well-being.
The causes of stress can vary from person to person, as each individual has their own unique set of circumstances and experiences. However, there are several common factors that can contribute to stress:
1. Trauma: Experiencing a traumatic event, such as a natural disaster, accident, or violence, can lead to significant stress. The emotional and psychological impact of trauma can disrupt an individual’s sense of safety and security, leading to ongoing stress and anxiety.
2. Mental Health Issues: Conditions such as anxiety disorders, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) can cause chronic stress. These conditions often involve ongoing emotional and psychological challenges that can be overwhelming and difficult to manage.
3. Life Transitions: Major life changes, such as starting a new job, getting married, or moving to a new city, can be stressful. These transitions require adaptation and coping skills, and the uncertainty and pressure associated with change can contribute to stress.
4. Work-related Stress: High workloads, demanding deadlines, and workplace conflicts can all contribute to stress. The pressure to perform well and meet expectations can take a toll on an individual’s mental and emotional well-being.
5. Financial Issues: Money problems, such as debt, unemployment, or financial instability, can cause significant stress. The fear and uncertainty associated with financial difficulties can have a profound impact on an individual’s mental health.
It is important to recognize the causes of stress in order to effectively address and manage it. By understanding the factors that contribute to stress, individuals can develop strategies and seek support to promote recovery and resilience.
The Effects of Stress on Mental Health

Stress is a common experience that can have a significant impact on mental health. When individuals are faced with stressful situations, their ability to cope and adapt can be tested. The field of psychology has studied the effects of stress on mental health and has identified various ways in which it can impact individuals.
One of the key effects of stress on mental health is the development of trauma. Trauma occurs when individuals experience an event or series of events that are emotionally or physically harmful. This can lead to a range of psychological symptoms such as anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
However, not all individuals who experience stress develop trauma. Some individuals are able to demonstrate resilience and recover from stressful experiences without experiencing long-term negative effects on their mental health. Resilience refers to an individual’s ability to adapt and bounce back from adversity. It involves the use of coping strategies and support systems to maintain mental well-being.
| Effects of Stress on Mental Health |
|---|
| 1. Trauma |
| 2. Resilience |
| 3. Coping |
| 4. Adaptation |
| 5. Recovery |
Stress can also impact mental health through its effect on coping mechanisms. Coping refers to the strategies individuals use to manage and reduce stress. When individuals are faced with high levels of stress, they may turn to unhealthy coping mechanisms such as substance abuse or avoidance. These coping strategies can further exacerbate mental health issues and contribute to the development of disorders such as addiction or anxiety.
Adaptation is another key factor in the effects of stress on mental health. Individuals who are unable to adapt to stressful situations may experience increased levels of stress and have difficulty in maintaining their mental well-being. Adaptation involves the ability to adjust and respond effectively to changing circumstances, which can help individuals manage stress and prevent the development of mental health issues.
Finally, recovery is an important aspect of the effects of stress on mental health. Recovery refers to the process of returning to a state of well-being after experiencing stress or trauma. It involves the use of support systems, therapy, and self-care practices to heal and restore mental health.
In conclusion, stress can have a significant impact on mental health. It can lead to the development of trauma, affect coping mechanisms, hinder adaptation, and impede recovery. Understanding the effects of stress on mental health is crucial for individuals, healthcare professionals, and researchers in order to develop effective strategies for prevention and intervention.
The Impact of Trauma

Trauma can have a profound impact on an individual’s mental health and overall well-being. It is a psychological response to a distressing event or series of events that exceed a person’s ability to cope with the stress they are experiencing. This can include events such as physical or sexual abuse, natural disasters, or witnessing violence.
When individuals experience trauma, their mental and emotional adaptation can be greatly affected. Trauma can lead to a variety of psychological symptoms, including anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). These symptoms can significantly impact a person’s ability to function in daily life and can have long-lasting effects on their overall mental health.
Coping with trauma can be a complex and challenging process. Individuals may develop various coping mechanisms to deal with the emotional and psychological distress caused by the trauma. These coping mechanisms can range from healthy strategies such as seeking support from loved ones or engaging in therapy, to unhealthy strategies such as substance abuse or self-harm.
However, it is important to note that not all individuals who experience trauma will develop mental health issues. Some individuals may possess a natural resilience, which allows them to bounce back from traumatic events and adapt to the stress they have experienced. Resilience is the ability to recover and thrive in the face of adversity, and it plays a significant role in an individual’s ability to cope with trauma.
Understanding the impact of trauma on mental health is crucial for mental health professionals, as it allows them to provide appropriate support and interventions for individuals who have experienced trauma. By recognizing the psychological effects of trauma and promoting resilience, mental health professionals can help individuals navigate the healing process and regain control of their lives.

I am Patrina de Silva, a psychologist and mental health blogger in Sri Lanka. After obtaining psychology degrees from the University of Colombo and Monash University, I returned home to work as a counselor while also starting the popular blog “Pressy but Happy” to provide advice on psychological issues. Over the past decade, my empathetic articles have made my blog a leading mental health resource in the country. In addition to writing, I maintain a private therapy practice, frequently volunteer counseling time, and conduct seminars, driven by my passion for destigmatizing mental illness and educating the public on the mind-body connection. I strive to be an influential voice in my field through my compassionate approach.
