
As our planet continues to experience the effects of climate change, it is becoming increasingly important for communities and governments to develop strategies that can withstand the stressors associated with a changing world. In order to ensure the resilience of these strategies, it is essential to conduct thorough test case studies that evaluate their effectiveness under various stress scenarios.
These studies provide valuable insights into the vulnerabilities and strengths of different resilience strategies, allowing policymakers and planners to make informed decisions about which approaches are most suitable for their specific circumstances. By subjecting these strategies to stress tests, we can simulate the challenges they may face in the future and identify areas that require improvement or adjustment.
One such stress test case study could involve examining the resilience of coastal communities in the face of rising sea levels and increased storm activity. By analyzing the effectiveness of different adaptation measures, such as the construction of sea walls or the implementation of managed retreat strategies, we can determine which approaches are most successful in protecting these vulnerable areas.
Another case study might focus on the resilience of agricultural systems to extreme weather events, such as droughts or floods. By testing different strategies, such as crop diversification or the use of innovative irrigation techniques, we can identify the most effective ways to ensure food security in the face of climate-related challenges.
In conclusion, stress test case studies play a crucial role in the development of climate resilience strategies. By subjecting these strategies to various stress scenarios, we can identify their strengths and weaknesses and make informed decisions about their implementation. These studies are essential in ensuring that our communities and ecosystems can adapt and thrive in a changing world.
Understanding the importance of stress testing

Stress testing plays a crucial role in assessing the resilience of climate strategies in a changing world. These tests are designed to simulate extreme scenarios and measure the ability of a system or strategy to withstand and recover from them. By subjecting strategies to high-stress situations, researchers can identify weaknesses, vulnerabilities, and areas for improvement.
Case studies have shown that stress testing can reveal insights that may not be apparent under normal conditions. For example, a resilience strategy that appears robust and effective in theory may prove inadequate when faced with the intensified impacts of climate change. Stress tests can help expose these limitations and prompt adjustments to enhance the strategy’s resilience.
Stress testing also helps in identifying the interdependencies and cascading effects that can occur during extreme events. By understanding how different components of a system or strategy interact under stress, policymakers can develop more comprehensive and effective resilience strategies. These insights can inform decision-making processes and enable proactive measures to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Moreover, stress testing provides an opportunity to assess the effectiveness of adaptation measures and identify potential trade-offs. It allows researchers to evaluate the resilience of different strategies and determine which ones are most suitable for a given context. This information can guide policymakers in making informed decisions about allocating resources and implementing climate resilience strategies.
In conclusion, stress testing is a vital tool for understanding the resilience of climate strategies in a changing world. Through case studies and tests, researchers can identify weaknesses, uncover hidden vulnerabilities, and make necessary adjustments to enhance the effectiveness of resilience strategies. By subjecting strategies to extreme scenarios, policymakers can develop comprehensive and proactive measures to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Challenges in developing climate resilience strategies
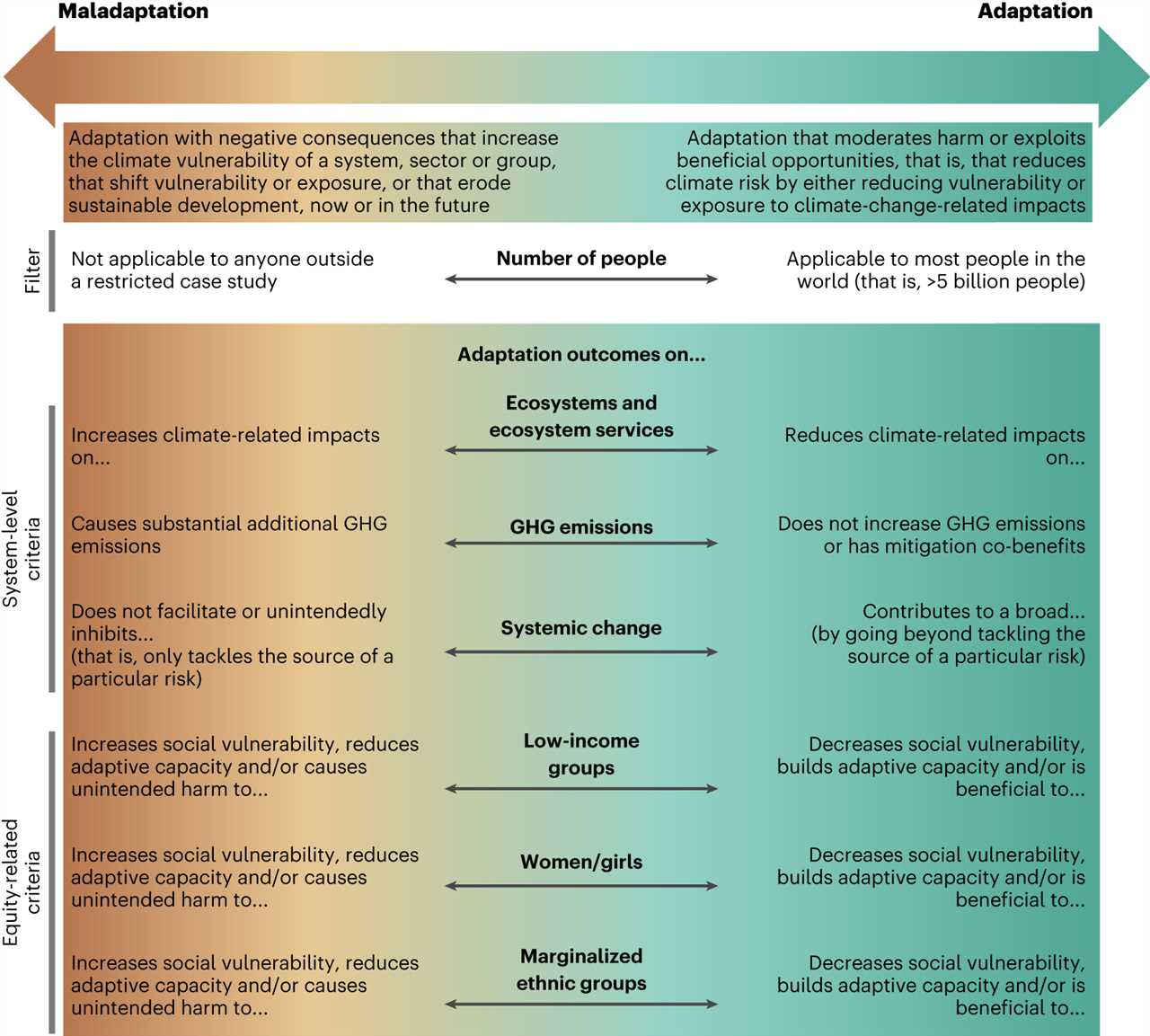
Developing climate resilience strategies can be a complex and challenging endeavor. It requires careful consideration of various factors and the ability to anticipate and plan for future changes. Stress test case studies play a crucial role in understanding the vulnerabilities and strengths of different strategies.
One of the main challenges in developing climate resilience strategies is the uncertainty surrounding future climate conditions. Climate change is a dynamic process, and the impacts can vary greatly depending on the region and the time scale considered. This uncertainty makes it difficult to accurately predict the specific challenges that communities and ecosystems will face in the future.
Another challenge is the limited availability of data and resources for conducting comprehensive stress tests. Climate resilience strategies require a thorough understanding of the current vulnerabilities and potential risks. However, collecting and analyzing the necessary data can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Furthermore, developing effective climate resilience strategies requires interdisciplinary collaboration. Climate change affects various sectors, including agriculture, infrastructure, and public health. Developing strategies that address these diverse challenges requires input from experts in different fields and coordination among various stakeholders.
Case studies are essential in addressing these challenges. By examining real-world examples, researchers and policymakers can gain insights into the effectiveness of different strategies and identify areas for improvement. These studies provide valuable data and evidence that can inform future resilience planning efforts.
| Key Challenges | Solutions |
|---|---|
| Uncertainty about future climate conditions | Use scenario planning and adaptive management approaches |
| Limited availability of data and resources | Invest in data collection and analysis efforts |
| Interdisciplinary collaboration | Promote cross-sectoral partnerships and knowledge sharing |
Overall, developing climate resilience strategies is a complex task that requires addressing various challenges. Stress test case studies provide valuable insights into the vulnerabilities and strengths of different strategies, helping to inform future planning efforts and enhance resilience in a changing world.
Case Studies
Resilience is a key factor in adapting to the challenges posed by climate change. To understand how different strategies can enhance resilience, it is important to study real-world examples. The following case studies highlight the importance of stress testing climate resilience strategies in a changing world.
| Case | Stress Test | Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Case Study 1 | In this case, the resilience strategy was tested by simulating extreme weather events such as hurricanes and heatwaves. | The stress tests revealed that the strategy was effective in mitigating the impacts of these events, resulting in minimal damage and loss. |
| Case Study 2 | For this case, the stress test focused on the resilience of a coastal community to sea level rise and storm surges. | The study found that the community’s strategy of building protective barriers and implementing early warning systems significantly reduced the vulnerability to flooding. |
| Case Study 3 | In this case, the stress test examined the resilience of an agricultural region to drought and changing precipitation patterns. | The study showed that implementing water conservation measures and diversifying crops helped the region maintain productivity despite the changing climate conditions. |
These case studies demonstrate the importance of stress testing climate resilience strategies to identify potential weaknesses and improve preparedness. By learning from real-world examples, communities and policymakers can develop effective strategies to adapt to a changing climate and ensure a more resilient future.
Case Study 1: Coastal cities and rising sea levels

In this case study, we will examine the test of resilience that coastal cities face in the wake of rising sea levels caused by climate change. Coastal cities around the world are experiencing the stress of increasing flood risks and erosion due to the rising sea levels.
Climate change has led to a rise in global sea levels, primarily due to the melting of glaciers and ice caps. This phenomenon poses a significant threat to coastal cities, as they are vulnerable to flooding and storm surges. The resilience of these cities is being put to the test as they implement strategies to adapt to the changing climate.
One example of a coastal city facing this challenge is Miami, Florida. With its low-lying geography, Miami is particularly susceptible to the impacts of rising sea levels. The city has already experienced increased flooding and saltwater intrusion into its freshwater sources.
To enhance its resilience, Miami has implemented several climate resilience strategies. These include the construction of sea walls and flood barriers, the elevation of roads and buildings, and the implementation of stormwater management systems. Additionally, the city has invested in green infrastructure, such as mangrove restoration projects, to provide natural defenses against sea-level rise.
Despite these efforts, Miami and other coastal cities continue to face significant challenges in adapting to rising sea levels. The costs of implementing resilience strategies are high, and there are ongoing debates about the most effective approaches. Furthermore, the long-term sustainability of these strategies is uncertain, as sea levels are projected to continue rising in the coming decades.
In conclusion, the case of coastal cities and rising sea levels demonstrates the need for robust climate resilience strategies. The test of adapting to the impacts of climate change requires innovative solutions and collaboration between governments, communities, and stakeholders. By investing in resilience measures and continuously evaluating and adapting strategies, coastal cities can better prepare for the challenges posed by a changing climate.
Case Study 2: Agriculture and extreme weather events

One of the key sectors affected by climate change is agriculture, which heavily relies on favorable weather conditions for successful crop growth and productivity. Extreme weather events, such as droughts, floods, heatwaves, and storms, pose significant stress and challenges to agricultural systems around the world.
In order to test the resilience of agriculture to these extreme weather events, several case studies have been conducted. These studies aim to understand the impacts of climate change on agricultural productivity and identify strategies to enhance resilience.
One such study focused on the effects of prolonged drought on crop yields in a region heavily dependent on rain-fed agriculture. The study analyzed historical climate data and compared it with crop yields over a specific time period. The findings revealed a clear correlation between drought severity and reduced crop productivity. This stress test highlighted the vulnerability of rain-fed agriculture to changing climate patterns and emphasized the need for adaptation measures.
Another case study examined the impact of heatwaves on livestock production. High temperatures and heat stress can significantly reduce animal productivity, leading to economic losses for farmers. The study analyzed data from multiple regions and found that heatwaves resulted in decreased milk production and weight gain in cattle. This stress test underscored the need for improved cooling and ventilation systems in livestock facilities to mitigate the negative effects of extreme heat.
Furthermore, a study explored the impacts of flooding on crop resilience and soil health. Excessive rainfall and flooding can damage crops, erode soil, and cause nutrient loss. The study examined flood-prone areas and assessed the effectiveness of different soil management practices in minimizing flood damage. The findings highlighted the importance of implementing measures such as improved drainage systems, soil conservation techniques, and flood-resistant crop varieties to enhance agricultural resilience in flood-prone regions.
| Case Study | Climate Stress | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Drought and crop yields | Prolonged drought | Clear correlation between drought severity and reduced crop productivity |
| Heatwaves and livestock | High temperatures and heat stress | Decreased milk production and weight gain in cattle during heatwaves |
| Flooding and crop resilience | Excessive rainfall and flooding | Importance of improved drainage systems, soil conservation techniques, and flood-resistant crop varieties |
These case studies contribute valuable insights into the vulnerabilities of agriculture to extreme weather events and provide evidence-based strategies to enhance climate resilience. By understanding the stressors and testing the resilience of agricultural systems, policymakers and stakeholders can develop effective adaptation measures to ensure food security and sustainable agricultural practices in a changing world.
Case Study 3: Infrastructure and urban planning
In this case study, we will examine the resilience of infrastructure and urban planning strategies in the face of climate change stressors. The goal of this test case study is to evaluate the effectiveness of these strategies in adapting to a changing world.
Infrastructure and urban planning are critical components of a community’s ability to withstand and recover from climate-related stress. As extreme weather events become more frequent and intense, it is crucial to ensure that our built environment can withstand these challenges.
Through a series of stress tests, we will assess the vulnerabilities and strengths of existing infrastructure and urban planning strategies. By simulating various climate change scenarios, we can identify potential weaknesses and design effective adaptation strategies.
These stress tests will examine the ability of infrastructure systems, such as transportation networks and utility systems, to withstand extreme weather events. We will evaluate the capacity of these systems to maintain functionality and provide essential services during and after a climate-related disaster.
Additionally, we will analyze the effectiveness of urban planning strategies in mitigating the impacts of climate change. This includes evaluating the resilience of building codes, zoning regulations, and land use policies. By identifying areas of improvement, we can develop strategies to enhance the resilience of our cities and communities.
Overall, this case study aims to provide valuable insights into the resilience of infrastructure and urban planning strategies. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of these strategies, we can develop effective adaptation plans to ensure the long-term sustainability of our communities in a changing world.
Best Practices for Climate Resilience

Climate resilience is a critical aspect of adapting to the changing climate and ensuring the sustainability of our communities and ecosystems. To develop effective strategies for climate resilience, it is essential to conduct stress test cases that assess the vulnerabilities and strengths of different systems.
One of the best practices for climate resilience is to analyze past case studies and learn from successful examples. By studying how other communities and regions have responded to climate stressors, we can identify strategies that have proven effective in enhancing resilience.
Another important practice is to develop stress test cases that simulate various climate scenarios. These tests can help us understand the potential impacts of different climate events and identify areas that are most vulnerable. By conducting these tests, we can develop targeted strategies to strengthen resilience in these specific areas.
Building resilience requires a comprehensive approach that considers both physical infrastructure and social systems. It is important to invest in resilient infrastructure that can withstand climate stressors, such as extreme weather events. Additionally, fostering social resilience through community engagement and education can enhance the ability of communities to adapt and recover from climate shocks.
Climate resilience strategies should also prioritize the protection and restoration of natural ecosystems. Healthy ecosystems provide numerous benefits, such as flood control, water filtration, and carbon sequestration. By preserving and restoring these ecosystems, we can enhance their ability to mitigate climate impacts and support the resilience of surrounding communities.
Lastly, it is crucial to continuously monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of climate resilience strategies. Regular assessments can help identify areas for improvement and allow for adjustments to be made in response to new climate challenges. Ongoing monitoring also provides an opportunity to share best practices and lessons learned with other communities and regions.
In conclusion, developing climate resilience requires a proactive and comprehensive approach. By analyzing case studies, conducting stress test cases, investing in resilient infrastructure, fostering social resilience, protecting natural ecosystems, and monitoring progress, we can enhance our ability to adapt and thrive in a changing climate.
Integration of climate data and modeling

Climate data plays a crucial role in the test case studies for stress testing climate resilience strategies. By analyzing historical climate data, researchers can gain insights into past climate patterns and trends, which can help inform future climate projections.
In the case studies, climate data is used to assess the potential impacts of climate change on various sectors, such as agriculture, water resources, and infrastructure. This data includes information on temperature, precipitation, sea level rise, and extreme weather events.
Modeling is another important component of the integration process. Climate models are used to simulate future climate conditions based on different scenarios and assumptions. These models take into account various factors, including greenhouse gas emissions, land use changes, and natural climate variability.
By combining climate data with modeling techniques, researchers can generate projections of future climate conditions at both global and regional scales. These projections are then used to assess the vulnerability of different sectors and develop climate resilience strategies.
The integration of climate data and modeling allows decision-makers to make informed choices and develop robust strategies to adapt to a changing climate. It helps identify potential risks and opportunities, enabling proactive planning and implementation of measures to enhance climate resilience.
Collaboration and stakeholder engagement
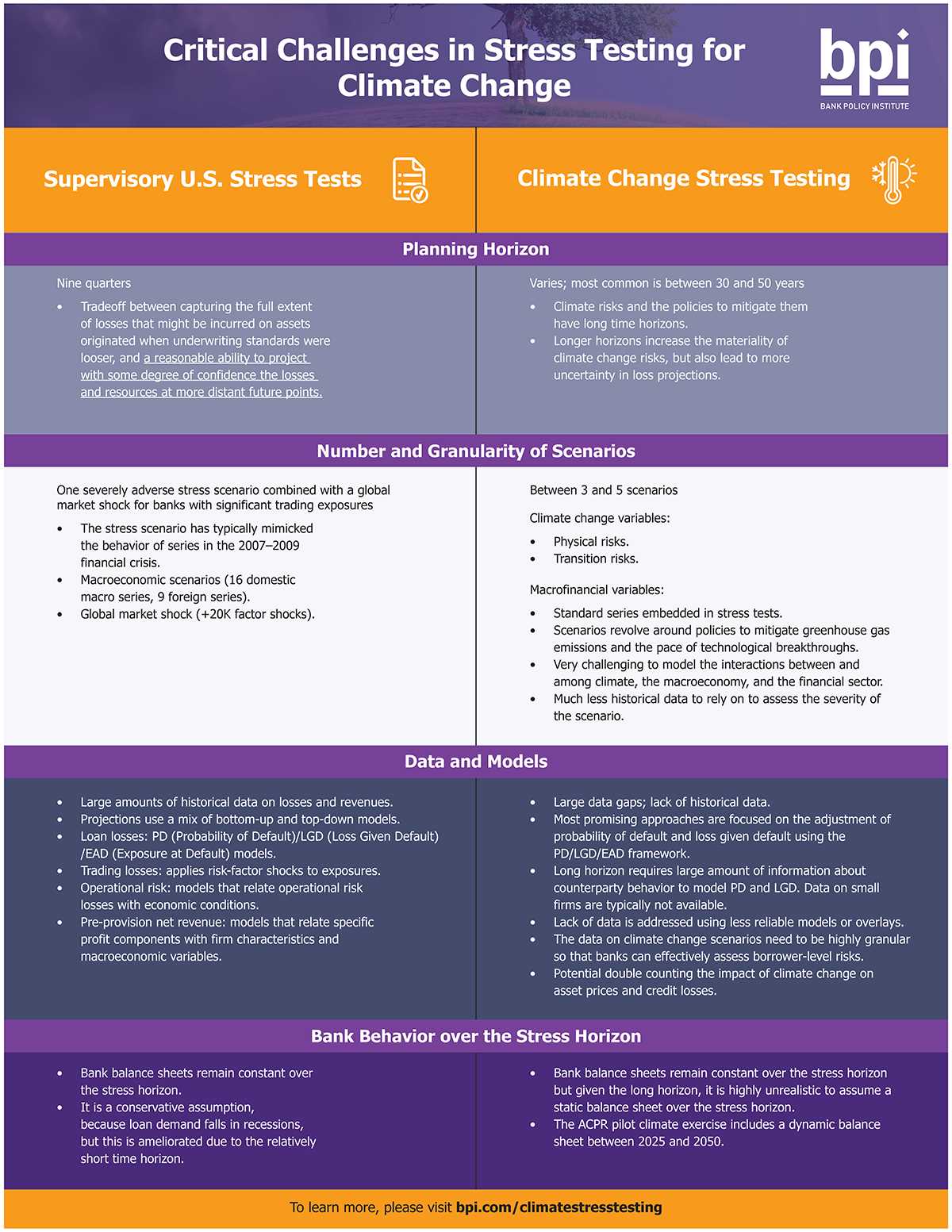
Collaboration and stakeholder engagement are crucial elements in conducting stress test case studies for climate resilience strategies. These studies involve analyzing the impact of climate change on various sectors and identifying strategies to mitigate risks and enhance resilience.
Engaging with stakeholders, such as government agencies, local communities, businesses, and non-profit organizations, is essential to ensure that the stress test case studies are comprehensive and representative of the diverse perspectives and needs of the community.
Collaboration allows for the sharing of knowledge, expertise, and resources among different stakeholders. It helps in identifying potential risks and vulnerabilities, as well as developing effective strategies to address them. By involving stakeholders in the process, the stress test case studies can incorporate local knowledge and experiences, making them more relevant and impactful.
Stakeholder engagement also promotes transparency and accountability in the decision-making process. It allows for open dialogue and the inclusion of different viewpoints, fostering trust and understanding among stakeholders. By involving stakeholders in the development and implementation of climate resilience strategies, the chances of successful outcomes are significantly increased.
Moreover, collaboration and stakeholder engagement help in building a sense of ownership and responsibility among stakeholders. When stakeholders are actively involved in the process, they are more likely to support and implement the recommended strategies. This collective effort ensures the long-term sustainability and effectiveness of climate resilience strategies.
In conclusion, collaboration and stakeholder engagement are vital components of stress test case studies for climate resilience strategies. By involving stakeholders, these studies can benefit from diverse perspectives, local knowledge, and shared resources, leading to more robust and effective strategies to address the challenges posed by climate change.
Adaptive management and continuous improvement

Resilience studies require a systematic and adaptive approach to test and evaluate different case scenarios in order to develop effective strategies for climate resilience. This includes stress testing various resilience strategies to identify weaknesses and areas for improvement.
Adaptive management is a key component of this process, as it allows for ongoing assessment and adjustment of resilience strategies based on new information and changing conditions. By continuously monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of different strategies, organizations can identify what works and what doesn’t, and make necessary adjustments to improve their resilience to climate change.
Continuous improvement is another important aspect of adaptive management. As new stress test case studies are conducted and new data becomes available, organizations can learn from past experiences and apply those lessons to develop more effective strategies in the future. This iterative process allows for constant learning and improvement, ensuring that resilience strategies remain up-to-date and effective in a changing world.
Overall, adaptive management and continuous improvement are essential for developing and implementing effective climate resilience strategies. By testing and evaluating different case scenarios, organizations can identify weaknesses and areas for improvement, and make necessary adjustments to enhance their resilience to climate change.

I am Patrina de Silva, a psychologist and mental health blogger in Sri Lanka. After obtaining psychology degrees from the University of Colombo and Monash University, I returned home to work as a counselor while also starting the popular blog “Pressy but Happy” to provide advice on psychological issues. Over the past decade, my empathetic articles have made my blog a leading mental health resource in the country. In addition to writing, I maintain a private therapy practice, frequently volunteer counseling time, and conduct seminars, driven by my passion for destigmatizing mental illness and educating the public on the mind-body connection. I strive to be an influential voice in my field through my compassionate approach.
