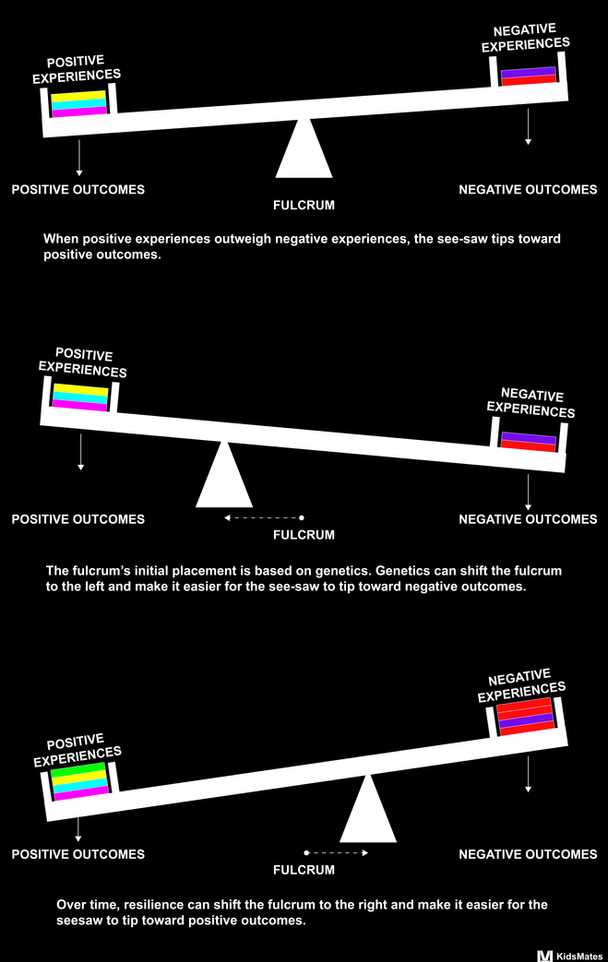
In today’s fast-paced and demanding world, stress has become an inevitable part of our lives. From work pressures to personal challenges, stress can often seem overwhelming and toxic. However, recent research has shown that our ability to cope with stress, known as resilience, has the power to transform potentially toxic stress into tolerable stress.
Resilience is the capacity to bounce back from adversity and maintain mental well-being. It is a trait that can be developed and strengthened through various strategies. When faced with potentially toxic stress, individuals with high levels of resilience are able to adapt and overcome the challenges, turning them into opportunities for growth.
Studies have cited that resilience plays a crucial role in mitigating the negative effects of stress on both physical and mental health. It helps individuals develop effective coping mechanisms, such as seeking support from loved ones or engaging in stress-reducing activities like exercise or meditation. By building resilience, individuals can transform potentially toxic stress into tolerable stress, which can be managed and overcome.
Furthermore, resilience enables individuals to view stressful situations from a different perspective. Rather than seeing stress as a threat, resilient individuals are able to reframe it as a challenge or an opportunity for personal growth. This shift in mindset allows them to approach stressful situations with a sense of control and optimism, reducing the negative impact of stress on their overall well-being.
In conclusion, resilience is a powerful tool that can transform potentially toxic stress into tolerable stress. By building resilience, individuals can develop effective coping mechanisms and view stress as an opportunity for growth. So, next time you find yourself facing stress, remember that resilience has the power to transform it into a manageable and tolerable experience.
What is Resilience?
Resilience is the ability to adapt and cope with stress, particularly in the face of potentially toxic stressors. It is a quality that allows individuals to bounce back from difficult experiences and transform them into tolerable stress. Resilience is often cited as a protective factor against the negative effects of stress on physical and mental health.
When faced with stress, resilience transforms potentially toxic stress into a more manageable and tolerable form. It allows individuals to effectively navigate through challenging situations and maintain their well-being. Resilience is not about avoiding stress or eliminating it entirely, but rather about building the capacity to handle stress in a healthy and adaptive way.
Resilience can be developed and strengthened by various factors, including supportive relationships, positive coping strategies, and a sense of purpose or meaning in life. These protective factors help individuals build resilience and enhance their ability to bounce back from adversity.
By cultivating resilience, individuals can better manage the stressors they encounter and minimize the negative impact on their overall well-being. Resilience empowers individuals to face challenges head-on, adapt to change, and maintain a sense of balance and stability in their lives.
| Key Points: |
| – Resilience is the ability to adapt and cope with stress. |
| – It transforms potentially toxic stress into tolerable stress. |
| – Resilience is a protective factor against the negative effects of stress. |
| – It can be developed and strengthened through supportive relationships and positive coping strategies. |
| – Cultivating resilience empowers individuals to face challenges and maintain well-being. |
The Definition of Resilience

Resilience is the ability to transform potentially toxic stress into tolerable stress. It is a concept that has been widely cited in the field of psychology and has gained significant attention in recent years. Resilience refers to the capacity of an individual to adapt and bounce back from adversity, including stressful situations.
The term “potentially toxic stress” refers to the negative impact that stress can have on an individual’s physical and mental well-being. This type of stress can be caused by various factors, such as traumatic events, chronic illness, or ongoing difficult circumstances. Resilience is the process by which an individual transforms this potentially toxic stress into tolerable stress.
Tolerable stress, on the other hand, refers to the stress that can be managed and overcome with the right support and coping mechanisms. Resilience allows individuals to develop the skills and strategies necessary to navigate through challenging situations and come out stronger on the other side.
Resilience is not a fixed trait that some people possess and others do not. It is a dynamic process that can be developed and strengthened over time. Through resilience, individuals can build their capacity to cope with and adapt to stress, ultimately leading to improved well-being and overall mental health.
The Importance of Resilience in Mental Health
Resilience is a crucial factor in maintaining good mental health. It transforms potentially toxic stress into tolerable stress, allowing individuals to cope with and overcome difficult situations. Resilience is the ability to bounce back from adversity, to adapt and thrive in the face of challenges.
Stress is a natural part of life, but when it becomes toxic, it can have detrimental effects on mental health. Toxic stress is chronic and overwhelming, and it can lead to anxiety, depression, and other mental health disorders. Resilience acts as a protective factor, buffering the impact of toxic stress and preventing it from taking a toll on mental well-being.
Research has shown that resilience is a skill that can be cultivated and strengthened. By developing resilience, individuals can learn to manage stress more effectively and build their capacity to cope with adversity. Resilience is not about avoiding stress or eliminating it entirely, but rather about developing healthy coping mechanisms and strategies to navigate through challenging times.
Resilience has been cited as a key factor in promoting mental health and preventing mental illness. It helps individuals develop a positive mindset, maintain a sense of optimism, and find meaning and purpose in life. Resilience also fosters social connections and support networks, which are essential for mental well-being.
In conclusion, resilience plays a crucial role in mental health. It transforms potentially toxic stress into tolerable stress, allowing individuals to navigate through challenging situations without compromising their well-being. By cultivating resilience, individuals can build their capacity to cope with adversity and maintain good mental health.
Factors Affecting Resilience
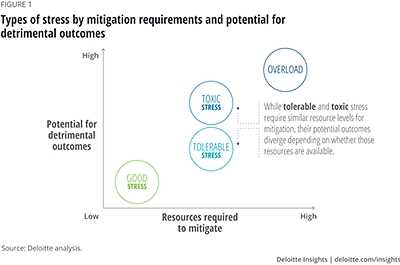
Resilience is the ability to adapt and bounce back from stress, whether it is toxic or tolerable. It is a complex process that involves various factors that can either hinder or enhance an individual’s ability to cope with adversity.
One of the most significant factors affecting resilience is stress itself. Different levels of stress can have different effects on an individual’s ability to bounce back. While toxic stress can overwhelm and damage the developing brain, tolerable stress can be managed and transformed by resilience.
Another factor that influences resilience is the presence of supportive relationships. Having a strong support network, such as family, friends, or mentors, can provide individuals with the emotional and practical support they need during challenging times. These relationships can help individuals build resilience by offering guidance, encouragement, and a sense of belonging.
Additionally, individual characteristics and traits play a role in resilience. Some people may naturally possess certain qualities, such as optimism, perseverance, or a positive self-view, that contribute to their ability to bounce back from adversity. However, resilience is not solely determined by innate characteristics, as it can also be developed and strengthened through various strategies and interventions.
Furthermore, access to resources and opportunities can impact resilience. Individuals who have access to education, healthcare, and economic stability may be better equipped to navigate through challenging circumstances and build resilience. On the other hand, those who face systemic barriers and lack necessary resources may find it more difficult to develop resilience.
In conclusion, resilience is influenced by various factors, including stress levels, supportive relationships, individual characteristics, and access to resources. Understanding and addressing these factors can help individuals and communities build resilience and effectively transform potentially toxic stress into tolerable stress.
Recognizing Potentially Toxic Stress
Potentially toxic stress refers to a level of stress that can have detrimental effects on an individual’s physical and mental well-being. It is important to recognize and address potentially toxic stress in order to promote resilience and prevent long-term negative consequences.
Resilience, by definition, is the ability to adapt and bounce back from adversity. However, when stress becomes toxic, it overwhelms an individual’s ability to cope, resulting in negative outcomes.
Recognizing potentially toxic stress involves identifying the factors that contribute to its development. These factors can include traumatic events, ongoing exposure to stressors, and a lack of supportive relationships or resources.
Research has cited various sources of potentially toxic stress, such as childhood abuse or neglect, chronic illness, poverty, and discrimination. These experiences can have long-lasting effects on an individual’s physical and mental health.
Transforming potentially toxic stress into tolerable stress is crucial for promoting resilience. Tolerable stress refers to stress that is more manageable and can be buffered by supportive relationships and resources.
By recognizing potentially toxic stress, individuals and communities can take steps to address and mitigate its effects. This can involve seeking support from mental health professionals, building strong social connections, and advocating for policies that promote well-being.
Overall, recognizing and addressing potentially toxic stress is essential for fostering resilience and promoting overall health and well-being.
Identifying Sources of Potentially Toxic Stress
Tolerable stress can be transformed into resilience, but it is important to identify the sources of potentially toxic stress. These sources can vary from individual to individual, but there are some common factors that have been cited by experts.
One potential source of toxic stress is exposure to violence or abuse. Children who witness or experience violence in their homes or communities may be at risk for toxic stress. This can include physical, emotional, or sexual abuse, as well as witnessing domestic violence.
Another source of potentially toxic stress is neglect or lack of consistent care. Children who do not receive the love, attention, and support they need from their caregivers may experience toxic stress. This can include physical neglect, emotional neglect, or a lack of stable and nurturing relationships.
Chronic illness or disability can also be a source of potentially toxic stress. Children who have chronic health conditions or disabilities may face ongoing challenges that can contribute to toxic stress. This can include physical limitations, frequent medical interventions, or the need for ongoing medical care.
Other sources of potentially toxic stress can include poverty, discrimination, or community violence. These external factors can have a significant impact on a child’s well-being and contribute to toxic stress. It is important to recognize and address these sources of stress in order to promote resilience and protect children from the negative effects of toxic stress.
The Impact of Potentially Toxic Stress on Mental Well-being
Potentially toxic stress, as cited by numerous studies, has a profound impact on mental well-being. This type of stress, which is characterized by intense and prolonged adversity, can have detrimental effects on the brain and overall mental health.
When individuals are exposed to toxic stress, their ability to cope and adapt is often compromised. This can lead to a variety of mental health issues, including anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). The constant activation of the body’s stress response system can also contribute to physical health problems, such as cardiovascular disease and immune system dysfunction.
Resilience, however, plays a crucial role in transforming potentially toxic stress into tolerable stress. Resilience refers to the ability to bounce back and recover from adversity, and it can be cultivated and strengthened over time. Individuals with high levels of resilience are better equipped to cope with and overcome the challenges posed by toxic stress.
Resilience transforms toxic stress by providing individuals with the tools and strategies necessary to navigate difficult situations. It enables individuals to develop healthy coping mechanisms, such as seeking support from others, engaging in self-care activities, and practicing mindfulness. By building resilience, individuals can mitigate the negative impact of toxic stress on their mental well-being.
It is important to recognize the potential impact of toxic stress on mental well-being and to prioritize resilience-building strategies. This includes promoting access to supportive resources, such as therapy and counseling, and implementing preventive measures to reduce the occurrence of toxic stress in individuals’ lives. By addressing toxic stress and fostering resilience, we can work towards improving mental well-being and creating a more resilient society.
Strategies for Coping with Potentially Toxic Stress
When stress transforms into toxic stress, it can have detrimental effects on both physical and mental health. However, there are strategies that can be employed to help cope with and transform potentially toxic stress into tolerable stress.
One strategy that is often cited is the practice of mindfulness. By being present in the moment and focusing on the sensations of the body and the breath, individuals can learn to observe and accept their stress without judgment. This can help to reduce the negative impact of potentially toxic stress and promote a sense of calm and resilience.
Another strategy is the use of social support. Building strong relationships and connecting with others who can provide emotional support and understanding can help to buffer the effects of stress. Talking to a trusted friend or family member about one’s stressors can provide a sense of relief and perspective, making the stress more tolerable.
Engaging in regular physical activity is also a helpful strategy for coping with potentially toxic stress. Exercise has been shown to release endorphins, which are natural mood-boosting chemicals in the brain. This can help to alleviate the negative effects of stress and promote a sense of well-being and resilience.
Additionally, practicing self-care is essential for coping with potentially toxic stress. This includes getting enough sleep, eating a balanced diet, and engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation. Taking time for oneself can help to recharge and build resilience, making the stress more tolerable.
| Strategies for Coping with Potentially Toxic Stress |
|---|
| Mindfulness |
| Social support |
| Regular physical activity |
| Self-care |
By employing these strategies, individuals can transform potentially toxic stress into tolerable stress. It is important to remember that everyone copes with stress differently, so finding the strategies that work best for oneself is key. With the right tools and support, it is possible to overcome the negative effects of stress and build resilience.

I am Patrina de Silva, a psychologist and mental health blogger in Sri Lanka. After obtaining psychology degrees from the University of Colombo and Monash University, I returned home to work as a counselor while also starting the popular blog “Pressy but Happy” to provide advice on psychological issues. Over the past decade, my empathetic articles have made my blog a leading mental health resource in the country. In addition to writing, I maintain a private therapy practice, frequently volunteer counseling time, and conduct seminars, driven by my passion for destigmatizing mental illness and educating the public on the mind-body connection. I strive to be an influential voice in my field through my compassionate approach.
