
In today’s fast-paced and demanding world, stress has become an inevitable part of our lives. It can be triggered by various factors such as work pressure, relationship issues, financial problems, and health concerns. The impact of stress on our mental and physical well-being cannot be underestimated, as it often leads to anxiety and other psychological disorders.
However, humans have shown remarkable resilience in coping with stress and adapting to challenging circumstances. This ability to bounce back and thrive in the face of adversity is known as resilience. Understanding the factors that contribute to resilience can help individuals better manage stress and enhance their overall well-being.
In the field of psychology, researchers have developed a comprehensive model to understand the complex relationship between stress and resilience. This model takes into account various factors that influence an individual’s ability to cope with stress and adapt to challenging situations.
The model of stress and resilience highlights the importance of both internal and external factors in determining an individual’s response to stress. Internal factors, such as personality traits and genetic predispositions, play a significant role in shaping one’s resilience. External factors, such as social support, access to resources, and the presence of positive role models, also contribute to an individual’s ability to bounce back from stressful experiences.
By understanding the model of stress and resilience, individuals can gain insight into their own coping mechanisms and develop strategies to enhance their resilience. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a deeper understanding of this model and its implications for managing stress and promoting well-being.
Section 1: Exploring the Concept of Stress

In the field of psychology, stress is a commonly studied phenomenon that affects individuals in various ways. It is important to understand the concept of stress and its associated factors in order to develop effective coping strategies and promote resilience.
Stress can be defined as a state of mental or emotional strain resulting from demanding circumstances or events. It is a natural response to challenging situations and can be caused by both positive and negative experiences. Factors such as work pressure, relationship issues, financial difficulties, and health problems can contribute to the experience of stress.
When individuals face stress, their bodies and minds go through a series of physiological and psychological changes. These changes are part of the body’s natural adaptation process, known as the stress response. The stress response is designed to help individuals cope with stressful situations by increasing alertness, improving focus, and mobilizing energy.
While stress is a normal part of life, prolonged or chronic stress can have negative effects on physical and mental health. It can lead to various health problems, including anxiety disorders, depression, and cardiovascular diseases. Therefore, it is important for individuals to develop effective coping mechanisms and build resilience to better manage stress.
Resilience refers to an individual’s ability to adapt and bounce back from stressful situations. It involves the capacity to maintain a positive outlook, effectively cope with challenges, and seek support when needed. Building resilience can help individuals better navigate stressful experiences and reduce the negative impact of stress on their overall well-being.
Understanding the concept of stress and its associated factors is crucial in the field of psychology. By exploring the different aspects of stress, such as its causes, effects, and coping strategies, researchers and practitioners can develop interventions to promote well-being and resilience in individuals facing stress.
The Definition and Types of Stress

Stress is a natural response to challenges or demands that individuals experience in their daily lives. It can be defined as the body’s reaction to any change that requires an adjustment or response. Stress can be caused by both positive and negative events, and it affects individuals physically, emotionally, and cognitively.
There are two main types of stress: acute stress and chronic stress. Acute stress is short-term and is often caused by specific events or situations, such as a work deadline or an argument with a loved one. Chronic stress, on the other hand, is long-term and is caused by ongoing or recurring situations, such as financial difficulties or a challenging work environment.
Coping with stress is an important aspect of resilience and adaptation. Individuals have different coping mechanisms, which can be either positive or negative. Positive coping strategies include seeking social support, engaging in physical exercise, practicing mindfulness or relaxation techniques, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Negative coping strategies, such as substance abuse or avoidance, can have detrimental effects on an individual’s well-being.
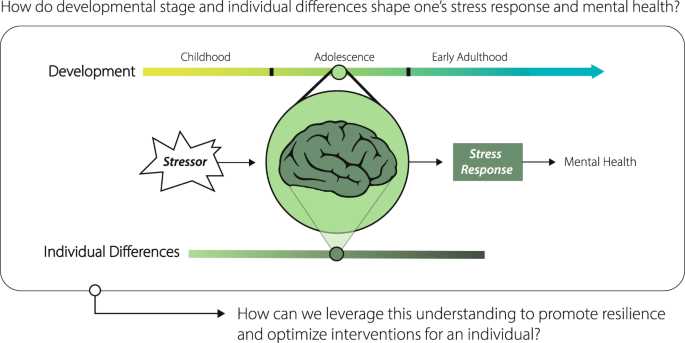
Several factors can influence an individual’s response to stress. These factors include genetics, personality traits, past experiences, social support, and the individual’s perception of the stressful event. Some individuals may be more resilient to stress, while others may be more susceptible to developing anxiety or other mental health issues.
The model of stress and resilience provides a framework for understanding how individuals respond to stress and the factors that contribute to their ability to adapt and cope. By understanding the definition and types of stress, as well as the factors that influence individual responses, we can better support individuals in developing resilience and managing stress in their lives.
The Impact of Stress on Mental and Physical Health
Stress is a natural response to challenging or threatening situations. It can be caused by various factors such as work pressure, personal relationships, financial difficulties, or health problems. While stress is a normal part of life, excessive or prolonged stress can have a negative impact on both mental and physical health.
When exposed to chronic stress, the body’s stress response system becomes overactive, leading to an increased risk of developing mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression. Prolonged stress can also weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to physical illnesses and diseases.
Adaptation and coping strategies play a crucial role in determining how individuals respond to stress. Those with high levels of resilience and positive coping mechanisms are better equipped to handle stress and are more likely to maintain good mental and physical health. On the other hand, individuals with poor coping skills may experience a higher level of stress and may be at a greater risk of developing mental health disorders.
Psychology plays a significant role in understanding the impact of stress on mental and physical health. Researchers have found that chronic stress can lead to changes in brain structure and function, affecting cognitive processes such as memory and decision-making. Additionally, stress can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to fatigue and decreased overall well-being.
It is essential to recognize the signs of stress and take proactive steps to manage it effectively. Engaging in regular exercise, practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation or deep breathing, and seeking support from friends, family, or mental health professionals can all contribute to reducing the impact of stress on mental and physical health.
In conclusion, stress can have a significant impact on both mental and physical health. Understanding the factors that contribute to stress and developing effective coping strategies are essential for maintaining overall well-being and resilience. By prioritizing self-care and seeking support when needed, individuals can minimize the negative effects of stress and promote positive mental and physical health.
Common Causes of Stress in Modern Society
In psychology, stress is defined as a state of mental or emotional strain resulting from demanding circumstances. In modern society, there are several common causes of stress that individuals may encounter on a daily basis.
One of the main factors contributing to stress is the fast-paced nature of modern life. The constant pressure to meet deadlines, juggle multiple responsibilities, and keep up with the ever-increasing demands of work and personal life can lead to feelings of overwhelm and anxiety.
Another common cause of stress is the prevalence of technology and its impact on our lives. While technology has undoubtedly brought many positive advancements, such as improved communication and convenience, it has also created a constant state of connectivity and information overload. The constant notifications, emails, and social media updates can contribute to feelings of being always “on” and unable to truly relax and disconnect.
Social and economic factors also play a significant role in stress levels. Financial pressures, job insecurity, and societal expectations can all contribute to feelings of stress and anxiety. The pressure to succeed, meet societal standards, and maintain a certain lifestyle can create a constant sense of striving and never feeling “good enough.”
Additionally, the lack of work-life balance and the blurring of boundaries between work and personal life can lead to chronic stress. The 24/7 availability and the expectation to be constantly accessible can make it challenging to find time for self-care and relaxation.
However, it is important to note that stress is not solely determined by external factors. Individual coping mechanisms and resilience also play a significant role in how people adapt to and manage stress. Developing positive coping strategies, building social support networks, and prioritizing self-care can all contribute to enhancing resilience and reducing stress levels in modern society.
In conclusion, the common causes of stress in modern society are multifaceted and can vary from person to person. Understanding the factors that contribute to stress is essential for developing effective coping strategies and promoting resilience in the face of challenging circumstances.
Section 2: Building Resilience to Combat Stress

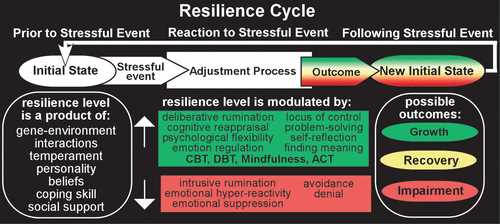
Resilience is a psychological model that focuses on the positive adaptation and coping mechanisms individuals can develop to combat stress and anxiety. It is a valuable concept in psychology that helps individuals overcome challenges and bounce back from difficult situations.
Building resilience involves developing a set of skills and strategies that can help individuals manage stress and maintain their mental well-being. One key aspect of building resilience is recognizing and understanding the sources of stress in one’s life. By identifying these sources, individuals can take proactive steps to address and manage them.
Another important aspect of building resilience is cultivating a positive mindset. This involves reframing negative thoughts and focusing on the positive aspects of a situation. By shifting one’s perspective, individuals can reduce anxiety and build a more resilient mindset.
Additionally, building resilience involves developing effective coping mechanisms. This can include practicing relaxation techniques, engaging in regular exercise, seeking support from loved ones, and engaging in activities that bring joy and fulfillment.
It is important to note that building resilience is a process that takes time and effort. It requires self-reflection, self-care, and a commitment to personal growth. However, by actively working on building resilience, individuals can develop the skills and strategies necessary to combat stress and thrive in the face of adversity.
Understanding the Concept of Resilience

Resilience is a psychological concept that refers to an individual’s ability to adapt and bounce back from difficult situations or experiences. It is the capacity to cope with stress, adversity, and life’s challenges in a positive and healthy way. Resilience is not about avoiding or eliminating stress, but rather about developing effective strategies for managing and navigating through it.
In the field of psychology, resilience is often seen as a dynamic process that involves the interaction of various factors. These factors can include personal characteristics, such as self-esteem and optimism, as well as external factors, such as social support and access to resources. Resilience is also influenced by environmental factors, including family dynamics, cultural norms, and socioeconomic status.
One of the key components of resilience is the ability to regulate emotions and manage anxiety. Resilient individuals are able to recognize and understand their emotions, and they have effective coping mechanisms to deal with stress. This can include engaging in activities that promote relaxation and self-care, seeking social support, or practicing mindfulness and other stress-reducing techniques.
Another important aspect of resilience is the ability to adapt and problem-solve. Resilient individuals are flexible and open to new ideas and perspectives. They are able to identify and utilize available resources and seek out alternative solutions when faced with challenges. This adaptability allows them to navigate through difficult situations and find ways to overcome obstacles.
The concept of resilience is often studied and applied in the context of trauma and adversity. It is important to note that resilience is not a fixed trait, but rather a skill that can be developed and strengthened over time. Through therapy, education, and practice, individuals can learn and enhance their resilience, enabling them to better cope with stress and bounce back from challenging experiences.
In summary, resilience is an essential concept in psychology that refers to an individual’s ability to adapt and thrive in the face of stress and adversity. It involves developing effective coping strategies, regulating emotions, and being flexible and adaptable. By understanding and cultivating resilience, individuals can enhance their overall well-being and navigate through life’s challenges with greater ease.

I am Patrina de Silva, a psychologist and mental health blogger in Sri Lanka. After obtaining psychology degrees from the University of Colombo and Monash University, I returned home to work as a counselor while also starting the popular blog “Pressy but Happy” to provide advice on psychological issues. Over the past decade, my empathetic articles have made my blog a leading mental health resource in the country. In addition to writing, I maintain a private therapy practice, frequently volunteer counseling time, and conduct seminars, driven by my passion for destigmatizing mental illness and educating the public on the mind-body connection. I strive to be an influential voice in my field through my compassionate approach.
