
Resilience is the ability to bounce back and adapt in the face of adversity, but for individuals with insecure attachment, this trait is often lacking. Attachment refers to the emotional bond formed between a child and their primary caregiver, and it plays a crucial role in shaping how individuals navigate relationships and handle stress throughout their lives.
When attachment is insecure, individuals may struggle to develop healthy coping mechanisms and may experience difficulties in managing stress. Poor resilience to stress is a common consequence of insecure attachment, as these individuals often have trouble regulating their emotions and seeking support from others.
Research has shown that individuals with insecure attachment are more likely to experience chronic stress and have higher rates of mental health issues such as anxiety and depression. The impact of insecure attachment can be long-lasting, affecting not only the individual’s emotional well-being but also their physical health and overall quality of life.
Understanding the impact of insecure attachment on resilience to stress is crucial for developing effective interventions and support systems. By recognizing the unique challenges faced by individuals with insecure attachment, we can work towards creating a more compassionate and understanding society that promotes healthy attachment and resilience in all individuals.
The Importance of Secure Attachment
Secure attachment plays a crucial role in an individual’s overall resilience to stress. When individuals have a secure attachment style, they have a strong foundation of trust and emotional support, which helps them navigate through challenging situations with greater ease.
Resilience is the ability to bounce back from adversity and cope with stress effectively. Research has shown that individuals with secure attachment styles are more likely to develop resilience, as they have a secure base from which to explore the world and seek support when needed.
On the other hand, insecure attachment can have a detrimental impact on an individual’s resilience. When individuals have insecure attachment styles, such as anxious or avoidant attachment, they may struggle to form trusting relationships and experience difficulties in regulating their emotions.
Stress can be particularly challenging for individuals with insecure attachment, as they may have limited access to reliable support systems. This can lead to feelings of isolation, increased vulnerability to stressors, and difficulties in effectively coping with stress.
In contrast, individuals with secure attachment styles are more likely to have a strong support network, which provides them with emotional and practical support during times of stress. This support helps to buffer the negative impact of stress and promotes resilience.
Overall, secure attachment is crucial for building resilience and effectively coping with stress. By fostering secure attachment in individuals, we can help them develop the necessary skills and support systems to navigate through life’s challenges with greater ease.
Building Trust and Emotional Security
When individuals have an insecure attachment style and poor resilience to stress, it is crucial to focus on building trust and emotional security in their lives. Trust is the foundation of any healthy relationship, and it is especially important for those who have experienced insecure attachments in the past.
Building trust starts with creating a safe and supportive environment. This can be achieved by being consistent and reliable in our actions and words. When individuals with insecure attachment styles see that others are dependable and trustworthy, it helps to alleviate their anxieties and fears.
Emotional security is closely tied to trust and is essential for individuals with poor resilience to stress. It involves creating an environment where individuals feel safe expressing their emotions without fear of judgment or rejection. Emotional security can be fostered by actively listening and validating the feelings of others, offering support and empathy.
Additionally, it is important to establish clear boundaries and expectations in relationships. By setting boundaries, individuals with insecure attachment styles can learn to develop a sense of self and understand their own needs and desires. This can help them feel more secure and confident in their relationships.
Building trust and emotional security takes time and effort. It requires patience, understanding, and a willingness to be vulnerable. However, by creating a safe and supportive environment, individuals with insecure attachment styles can begin to develop healthier, more resilient ways of relating to others and managing stress.
Developing Healthy Coping Mechanisms
Resilience is crucial for individuals with insecure attachment and poor resilience to stress. Developing healthy coping mechanisms can greatly improve their ability to handle stress and overcome challenges.
One important step in developing healthy coping mechanisms is understanding the impact of stress on one’s mental and physical well-being. Stress can have a detrimental effect on both the mind and body, leading to increased anxiety, depression, and physical health issues. Recognizing the signs of stress and its impact is the first step towards developing healthier coping strategies.
It is essential to identify the specific triggers that cause stress and insecurity. This could include certain situations, relationships, or past traumas. By pinpointing these triggers, individuals can work towards finding healthier ways to cope with them.
One effective coping mechanism is seeking support from trusted individuals. This could be friends, family, or mental health professionals. Talking about one’s feelings and experiences with supportive individuals can provide a sense of relief and help in finding healthier perspectives and solutions to problems.
Engaging in regular physical activity can also significantly improve resilience and reduce stress levels. Exercise releases endorphins, which are natural mood boosters. It can also help individuals feel more in control of their bodies and minds.
Practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and mindfulness can also be beneficial. These techniques help individuals calm their minds and bodies, reducing stress and promoting emotional well-being.
Finally, developing healthy coping mechanisms involves cultivating self-care habits. This includes prioritizing sleep, eating well-balanced meals, and engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation. Taking care of oneself physically and emotionally is essential for building resilience and managing stress effectively.
Overall, developing healthy coping mechanisms is crucial for individuals with insecure attachment and poor resilience to stress. By understanding the impact of stress, identifying triggers, seeking support, engaging in physical activity, practicing relaxation techniques, and prioritizing self-care, individuals can build resilience and improve their ability to handle stress in a healthier way.
Forming Positive Relationships
Building positive relationships is crucial for individuals with poor attachment and insecure attachment styles, as it can help improve resilience to stress. Forming positive relationships involves establishing trust, open communication, and emotional connection with others.
Individuals with poor attachment may struggle with forming positive relationships due to their fear of rejection or abandonment. They may have difficulty trusting others and may be hesitant to open up emotionally. However, it is important for these individuals to work on building healthy connections with others to improve their resilience to stress.
One way to form positive relationships is by seeking support from trusted individuals, such as friends, family members, or therapists. These individuals can provide a safe space for individuals with poor attachment to express their emotions and receive validation and understanding.
Another important aspect of forming positive relationships is developing effective communication skills. This involves actively listening to others, expressing oneself clearly and assertively, and being open to constructive feedback. Effective communication can help individuals with poor attachment build trust and establish deeper connections with others.
Additionally, individuals with poor attachment can benefit from participating in activities or groups that align with their interests and values. This can provide opportunities to meet like-minded individuals and form connections based on shared experiences and passions.
In conclusion, forming positive relationships is essential for individuals with poor attachment and insecure attachment styles to improve their resilience to stress. By seeking support, developing effective communication skills, and engaging in activities that align with their interests, these individuals can build trust, establish emotional connections, and ultimately enhance their ability to cope with stress.
The Effects of Insecure Attachment
Insecure attachment can have significant negative effects on an individual’s overall well-being and resilience to stress. When a person has a poor attachment style, they may struggle to form and maintain healthy relationships with others. This can lead to feelings of isolation, loneliness, and a lack of support when faced with challenging situations.
Individuals with insecure attachment may also have difficulty regulating their emotions, which can make it harder for them to cope with stress. They may be more prone to experiencing anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues. Additionally, insecure attachment can impact an individual’s ability to trust others, which can further hinder their resilience to stress.
Furthermore, insecure attachment can affect an individual’s ability to effectively communicate and express their needs and emotions. This can lead to misunderstandings and conflicts in relationships, adding to the individual’s stress levels. The lack of secure attachment can also make it harder for individuals to seek support and ask for help when needed, further exacerbating their stress and reducing their resilience.
| Effects of Insecure Attachment: |
|---|
| – Difficulty forming and maintaining healthy relationships |
| – Feelings of isolation and loneliness |
| – Lack of support in challenging situations |
| – Difficulty regulating emotions |
| – Increased risk of anxiety and depression |
| – Impaired ability to trust others |
| – Challenges in communication and expressing needs |
| – Difficulty seeking support and asking for help |
Overall, insecure attachment can have a profound impact on an individual’s ability to cope with stress and adapt to challenging situations. It is crucial to recognize the effects of insecure attachment and provide support and interventions to promote healthy attachment styles and enhance resilience.
Increased Vulnerability to Stress
Insecure attachment and poor resilience to stress can lead to an increased vulnerability to stress. When individuals have insecure attachment styles, they may struggle to form and maintain healthy relationships, which can contribute to feelings of loneliness and isolation. This lack of social support can make it difficult for individuals to cope with stress and may exacerbate its impact on their mental and physical health.
Poor resilience to stress can also make individuals more susceptible to the negative effects of stress. Resilience refers to an individual’s ability to adapt and bounce back from difficult situations. When individuals have low resilience, they may be less able to effectively cope with stressors, leading to a prolonged stress response and increased vulnerability to stress-related disorders.
Furthermore, insecure attachment and poor resilience to stress can create a cycle of stress and negative coping mechanisms. Individuals with insecure attachment styles may be more likely to engage in maladaptive coping strategies, such as substance abuse or self-destructive behaviors, in an attempt to alleviate stress. These coping mechanisms can further exacerbate the negative impact of stress and contribute to a downward spiral of poor mental and physical health.
In conclusion, insecure attachment and poor resilience to stress can significantly increase an individual’s vulnerability to stress. The lack of healthy relationships and social support, combined with a reduced ability to effectively cope with stressors, can have detrimental effects on mental and physical well-being. It is important to recognize the impact of attachment styles and resilience on stress management and to provide support and resources to help individuals develop healthier coping strategies.
Difficulties in Regulating Emotions
Resilience is an important factor in an individual’s ability to cope with stress and adversity. However, individuals with insecure attachment styles often exhibit poor resilience, which can lead to difficulties in regulating emotions.
Attachment theory suggests that the quality of early relationships with caregivers plays a significant role in the development of an individual’s ability to regulate emotions. Those with insecure attachment styles may have experienced inconsistent or neglectful caregiving, leading to difficulties in developing effective emotion regulation strategies.
Individuals with insecure attachment styles may struggle to identify and understand their own emotions, making it challenging for them to effectively manage and regulate their emotional responses. This can result in difficulties in coping with stress, as well as increased vulnerability to mental health issues such as anxiety and depression.
Poor resilience can also contribute to difficulties in regulating emotions. Individuals with low resilience may be more likely to become overwhelmed by stressors, leading to heightened emotional responses and difficulties in effectively managing their emotions.
Furthermore, the lack of a secure attachment figure to provide support and comfort can exacerbate these difficulties. Without a reliable source of emotional support, individuals may struggle to regulate their emotions and may be more prone to experiencing intense emotional reactions.
In summary, individuals with insecure attachment styles and poor resilience are likely to experience difficulties in regulating their emotions. This can have a significant impact on their overall well-being and ability to cope with stress and adversity. Understanding the relationship between attachment, resilience, and emotional regulation is crucial in developing effective interventions and support systems for individuals who struggle in these areas.
Impaired Problem-Solving Skills
Resilience, attachment, and stress have a significant impact on an individual’s problem-solving skills. Poor attachment and low resilience can impair an individual’s ability to effectively solve problems, leading to difficulties in various areas of life.
Individuals with insecure attachment styles often struggle with problem-solving due to their difficulties in forming and maintaining secure relationships. Their fear of rejection and abandonment can hinder their ability to seek help or collaborate with others in finding solutions. This lack of social support and cooperation can further exacerbate their stress levels, making it even harder for them to think clearly and find effective solutions.
Poor resilience to stress can also contribute to impaired problem-solving skills. When faced with challenging situations, individuals with low resilience may become overwhelmed and struggle to think rationally. Their negative coping mechanisms, such as avoidance or aggression, can hinder their ability to approach problems in a logical and systematic manner. This can lead to a cycle of escalating stress and ineffective problem-solving, further perpetuating their poor resilience.
Improving problem-solving skills in individuals with poor attachment and low resilience requires a multifaceted approach. Building secure attachments and fostering supportive relationships can provide individuals with the emotional safety and confidence needed to tackle problems effectively. Additionally, developing resilience through stress management techniques, such as mindfulness and self-care, can help individuals regulate their emotions and think more clearly when faced with challenges.
In conclusion, impaired problem-solving skills are closely linked to poor attachment and low resilience to stress. Recognizing and addressing these factors can help individuals develop the necessary skills and strategies to overcome obstacles and improve their problem-solving abilities.
Understanding Resilience to Stress
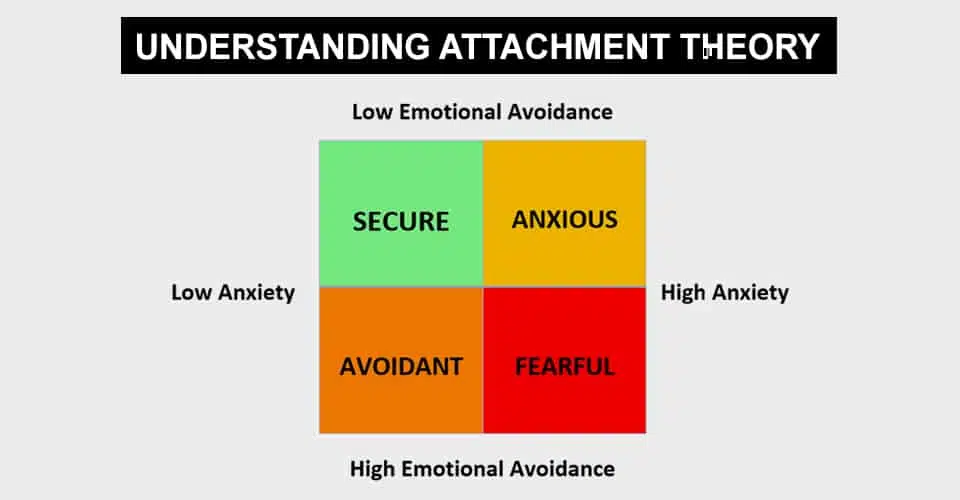
Resilience refers to an individual’s ability to adapt and cope with stress and adversity. It is an essential quality that allows individuals to maintain their well-being and mental health. Understanding resilience to stress is crucial, especially in the context of insecure attachment and poor resilience.
Attachment plays a significant role in the development of resilience. Insecure attachment, characterized by a lack of trust, emotional availability, and inconsistent caregiving, can hinder an individual’s ability to effectively cope with stress. Those with insecure attachment styles may struggle to form healthy relationships and rely on maladaptive coping mechanisms.
Poor resilience to stress is often observed in individuals with insecure attachment. They may have difficulty regulating their emotions, experience heightened anxiety, and struggle with self-esteem. These individuals may exhibit a tendency to avoid challenging situations or become overwhelmed by stressors, leading to a cycle of poor resilience and increased vulnerability to stress.
Understanding the impact of insecure attachment on resilience to stress can help inform interventions and support systems. By addressing the underlying attachment issues and providing individuals with tools and strategies to build resilience, it is possible to mitigate the negative effects of stress and promote healthier coping mechanisms.
Building resilience involves cultivating self-awareness, developing healthy coping strategies, and fostering supportive relationships. It requires individuals to recognize and challenge negative thought patterns, practice self-care, and seek help when needed. Developing resilience is a lifelong process that can be nurtured through therapy, mindfulness practices, and engaging in activities that promote well-being.
In conclusion, understanding resilience to stress is crucial in the context of insecure attachment and poor resilience. By recognizing the impact of insecure attachment on an individual’s ability to cope with stress, interventions can be tailored to address these underlying issues and promote healthier coping mechanisms. Building resilience is a lifelong journey that requires self-awareness, support, and the cultivation of healthy strategies for managing stress.
Definition and Components of Resilience
Resilience can be defined as the ability to adapt and bounce back from adversity, stress, or trauma. It is a psychological strength that allows individuals to maintain a sense of well-being and function effectively in the face of challenges. In the context of insecure attachment and poor resilience, it refers to the lack of ability to cope with stress and overcome difficult situations.
Resilience is composed of several components that contribute to an individual’s ability to navigate through life’s challenges. These components include:
1. Emotional regulation: This component involves the ability to manage and regulate one’s emotions in a healthy and adaptive way. It includes recognizing and understanding one’s emotions, as well as being able to express them appropriately.
2. Problem-solving skills: Resilience also involves having effective problem-solving skills to address and overcome obstacles. This includes the ability to think critically, analyze situations, and develop creative solutions.
3. Social support: Having a strong support system, such as family, friends, or mentors, is crucial for resilience. Social support provides individuals with emotional validation, guidance, and resources that can help them cope with stress and adversity.
4. Self-efficacy: Resilience is also influenced by an individual’s belief in their own abilities and capacity to overcome challenges. Having a sense of self-efficacy, or confidence in one’s own competence, can enhance resilience and motivate individuals to persevere in the face of setbacks.
In summary, resilience is a multifaceted concept that encompasses various components, including emotional regulation, problem-solving skills, social support, and self-efficacy. In the context of insecure attachment and poor resilience, individuals may struggle with these components, making it more difficult for them to cope with stress and bounce back from adversity. Understanding these components is essential for developing interventions and strategies to enhance resilience in individuals with insecure attachment.

I am Patrina de Silva, a psychologist and mental health blogger in Sri Lanka. After obtaining psychology degrees from the University of Colombo and Monash University, I returned home to work as a counselor while also starting the popular blog “Pressy but Happy” to provide advice on psychological issues. Over the past decade, my empathetic articles have made my blog a leading mental health resource in the country. In addition to writing, I maintain a private therapy practice, frequently volunteer counseling time, and conduct seminars, driven by my passion for destigmatizing mental illness and educating the public on the mind-body connection. I strive to be an influential voice in my field through my compassionate approach.
