
Early adversity can have a profound impact on a person’s life, shaping their development and future well-being. Whether it’s experiencing neglect, abuse, or other forms of trauma, the effects of early adversity can be long-lasting and pervasive. One of the key factors that contribute to these negative outcomes is toxic stress.
Toxic stress occurs when a child is exposed to prolonged or extreme adversity, such as chronic neglect or abuse, without the presence of a supportive caregiver. This type of stress can disrupt the developing brain and body, leading to a wide range of physical and mental health issues later in life. It can impair cognitive development, affect emotional regulation, and even increase the risk of chronic diseases.
However, not all children who experience early adversity are destined for a lifetime of negative outcomes. Resilience, the ability to adapt and thrive despite adversity, plays a crucial role in determining the long-term impact of early stress. Some children are able to develop resilience through supportive relationships, positive experiences, and the presence of caring adults in their lives.
Understanding the complex interplay between early adversity, toxic stress, and resilience is essential for creating effective interventions and support systems for children who have experienced trauma. By recognizing the lasting impact of early adversity and promoting resilience, we can help mitigate the negative effects of toxic stress and give children the opportunity to thrive.
The Effects of Early Adversity on Child Development
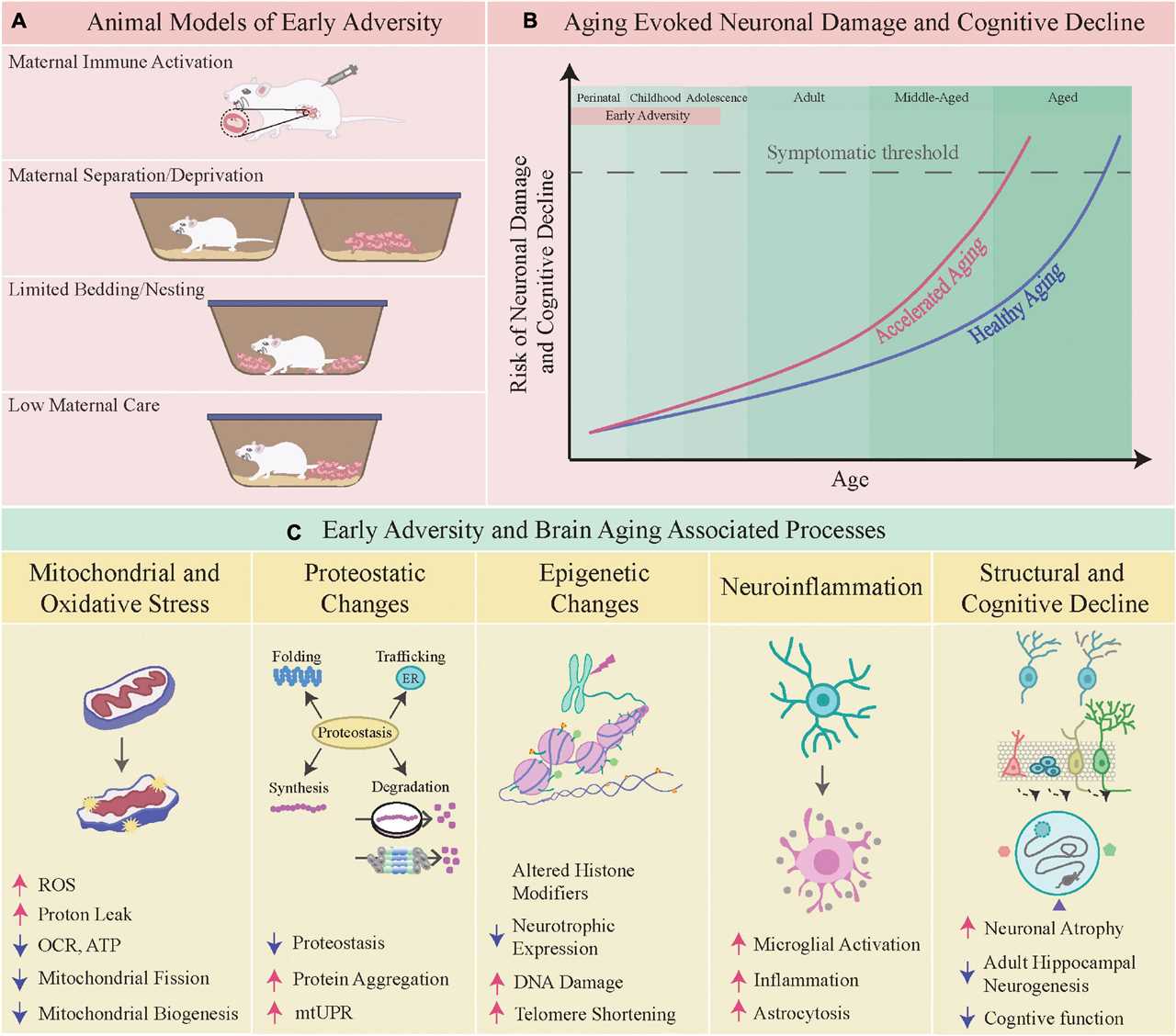
Early adversity and stress can have a profound impact on child development. When children are exposed to adverse experiences such as abuse, neglect, or household dysfunction, their developing brains and bodies can be negatively affected. This toxic stress can disrupt the normal development of important brain circuits and systems, leading to long-term consequences for physical, mental, and emotional health.
Adversity in early childhood can lead to a range of developmental challenges. Children who experience high levels of stress early in life may have difficulty regulating their emotions, forming healthy attachments, and managing stress later on. They may also experience delays in cognitive development, language skills, and social-emotional development.
However, not all children who experience early adversity are negatively impacted. Resilience, or the ability to bounce back from adversity, plays a crucial role in mitigating the effects of toxic stress. Some children are able to develop protective factors, such as strong relationships with supportive adults or access to high-quality early childhood programs, that can help buffer the negative effects of early adversity.
Understanding the effects of early adversity on child development is essential for developing effective interventions and support systems. By promoting resilience and providing children with the tools they need to navigate and overcome adversity, we can help mitigate the long-term effects of toxic stress and promote healthy development for all children.
Cognitive and Emotional Development
Resilience plays a crucial role in the cognitive and emotional development of individuals who have experienced early adversity and toxic stress. Early adversity, such as neglect, abuse, or household dysfunction, can have a profound impact on the developing brain and can lead to long-term cognitive and emotional difficulties.
However, research has shown that individuals who possess resilience are better able to overcome the negative effects of early adversity and stress. Resilience can be defined as the ability to adapt and bounce back from difficult experiences, and it is a key factor in promoting healthy cognitive and emotional development.
Children who have experienced early adversity and toxic stress often face challenges in various areas of cognitive development, such as attention, memory, and problem-solving skills. These difficulties can impact their academic performance and overall cognitive abilities.
Furthermore, early adversity and stress can also have a significant impact on emotional development. Children who have experienced trauma may struggle with regulating their emotions, forming healthy attachments, and managing stress. This can lead to difficulties in social relationships and emotional well-being.
However, individuals who possess resilience are more likely to develop positive coping strategies and emotional regulation skills. They are better able to adapt to challenging situations, form healthy relationships, and manage stress effectively.
It is crucial to recognize the importance of resilience in promoting healthy cognitive and emotional development in children who have experienced early adversity and toxic stress. By providing support, nurturing environments, and opportunities for positive experiences, we can help foster resilience and promote optimal development in these individuals.
Social and Behavioral Development
Resilience plays a crucial role in social and behavioral development, especially in the face of toxic stress experienced during early childhood. Toxic stress refers to prolonged exposure to adverse experiences, such as abuse, neglect, or household dysfunction, which can have detrimental effects on a child’s development.
However, research has shown that some children are able to develop resilience and overcome the negative impacts of early adversity. Resilience can be defined as the ability to adapt and thrive despite challenging circumstances. It is a dynamic process that involves the interaction between individual characteristics and external factors, such as supportive relationships and community resources.
In terms of social development, resilient children are more likely to form positive relationships with peers and adults. They have the ability to regulate their emotions and behaviors, which enables them to engage in prosocial behaviors and navigate social situations effectively. These skills contribute to the development of healthy relationships and social competence.
Similarly, resilient children also demonstrate positive behavioral development. They are less likely to engage in risky behaviors, such as substance abuse or delinquency, and more likely to exhibit self-control and problem-solving skills. This resilience in the face of early adversity can have long-term positive effects on their overall well-being and success later in life.
Overall, understanding the impact of early adversity, toxic stress, and resilience on social and behavioral development is crucial for developing effective interventions and support systems for children who have experienced trauma. By promoting resilience and providing a supportive environment, we can help mitigate the negative effects of early adversity and foster healthy social and behavioral development in children.
The Concept of Toxic Stress
Adversity is a common part of life, and individuals are often able to develop resilience and cope with stressful situations. However, when adversity becomes chronic or overwhelming, it can lead to toxic stress. Toxic stress refers to the prolonged activation of the body’s stress response system, without the presence of a supportive and nurturing environment to help mitigate the effects. This type of stress can have a significant impact on a person’s physical and mental health.
Adversity can take many forms, such as poverty, neglect, abuse, or exposure to violence. When individuals are exposed to these adverse experiences for an extended period of time, their stress response system can become dysregulated. This dysregulation can lead to a variety of negative outcomes, including increased risk for chronic diseases, impaired cognitive development, and mental health problems.
Resilience plays a crucial role in mitigating the effects of toxic stress. Resilience refers to the ability to adapt and bounce back from adversity. Individuals with high levels of resilience are better able to cope with stress and maintain positive mental and physical health outcomes. Building resilience can involve developing strong social support networks, engaging in self-care practices, and seeking professional help when needed.
Understanding the concept of toxic stress is essential for addressing the impact of early adversity on individuals’ lives. By recognizing the effects of toxic stress and promoting resilience-building strategies, we can work towards creating a society that supports the well-being of all individuals, especially those who have experienced early adversity.
Definition and Causes
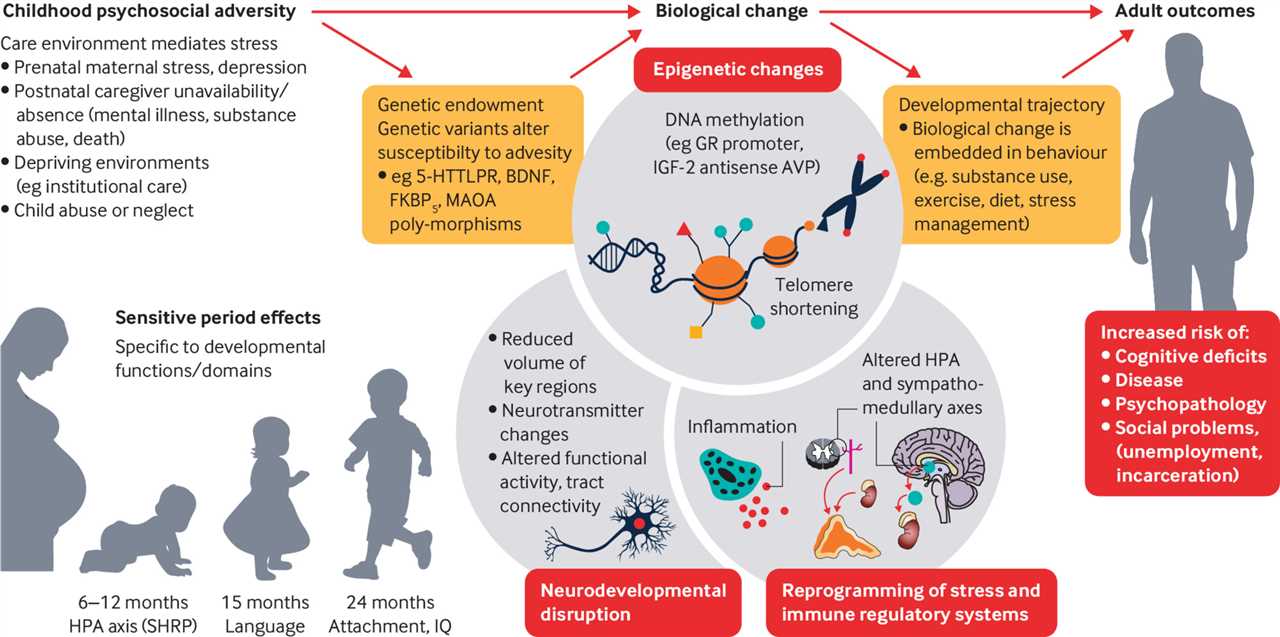
Early adversity refers to stressful experiences that occur during childhood, particularly in the early years of life. These experiences can include neglect, abuse, poverty, and exposure to violence. Such stressors can have a profound impact on a child’s development, leading to long-lasting effects on their physical, cognitive, and emotional well-being.
Toxic stress is a term used to describe the prolonged activation of the body’s stress response system in the face of overwhelming adversity. This type of stress can be particularly damaging to a child’s developing brain, as it can disrupt the normal process of brain development and lead to a range of negative outcomes.
Resilience, on the other hand, refers to the ability to adapt and thrive in the face of adversity. Some children are able to overcome early adversity and develop into healthy, successful adults, while others may struggle to overcome the effects of toxic stress. The factors that contribute to resilience include supportive relationships, positive experiences, and the presence of protective factors such as access to healthcare and education.
There are multiple causes of early adversity, including poverty, parental substance abuse, mental illness, and family dysfunction. These factors can increase the likelihood of exposure to stressors such as neglect, abuse, and violence. Additionally, systemic factors such as racism and discrimination can also contribute to early adversity and toxic stress.
Long-Term Consequences
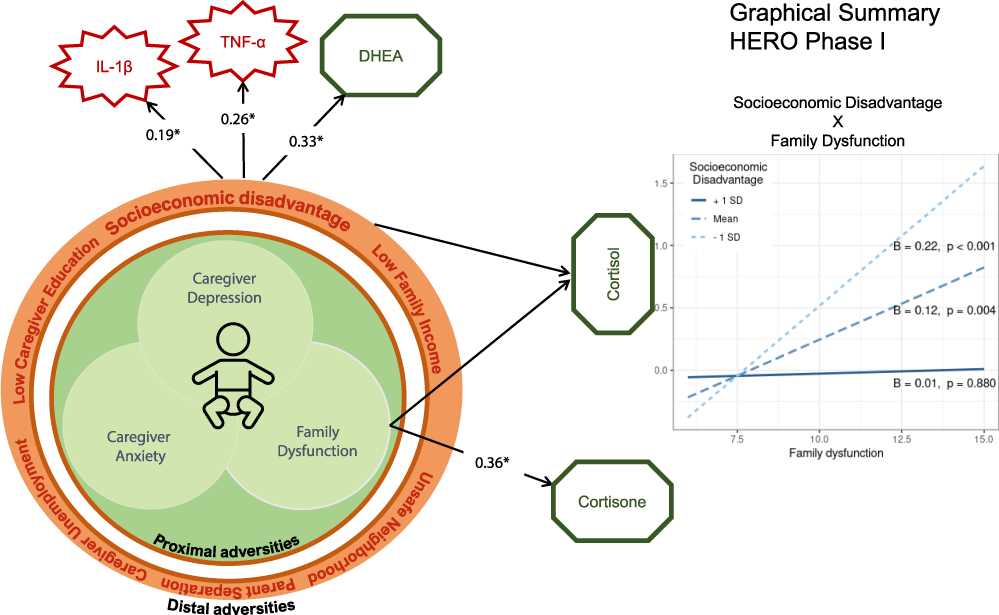
Early adversity and toxic stress can have profound and lasting effects on individuals throughout their lives. The impact of early adversity on brain development, behavior, and overall health is well-documented. Children who experience high levels of stress and adversity in their early years are more likely to develop mental health disorders, such as anxiety and depression, and have difficulty regulating their emotions.
Furthermore, the long-term consequences of early adversity can extend into adulthood. Research has shown that individuals who experienced significant adversity in childhood are at higher risk for chronic health conditions, such as heart disease, diabetes, and obesity. This is thought to be due, in part, to the effects of toxic stress on the body’s stress response system.
However, it is important to note that not all individuals who experience early adversity will develop negative outcomes. Resilience plays a critical role in determining how individuals respond to stress and adversity. Some individuals are able to overcome the effects of early adversity and go on to lead healthy and successful lives.
| Long-Term Consequences | Resilience |
|---|---|
| Increased risk of mental health disorders | Ability to overcome adversity |
| Higher risk for chronic health conditions | Positive adaptation to stress |
| Impaired brain development | Ability to regulate emotions |
In conclusion, early adversity and toxic stress can have a lasting impact on individuals, affecting their mental and physical health. However, resilience plays a crucial role in determining the long-term consequences of early adversity. By fostering resilience in individuals who have experienced adversity, we can help mitigate the negative effects and promote positive outcomes.

I am Patrina de Silva, a psychologist and mental health blogger in Sri Lanka. After obtaining psychology degrees from the University of Colombo and Monash University, I returned home to work as a counselor while also starting the popular blog “Pressy but Happy” to provide advice on psychological issues. Over the past decade, my empathetic articles have made my blog a leading mental health resource in the country. In addition to writing, I maintain a private therapy practice, frequently volunteer counseling time, and conduct seminars, driven by my passion for destigmatizing mental illness and educating the public on the mind-body connection. I strive to be an influential voice in my field through my compassionate approach.
