
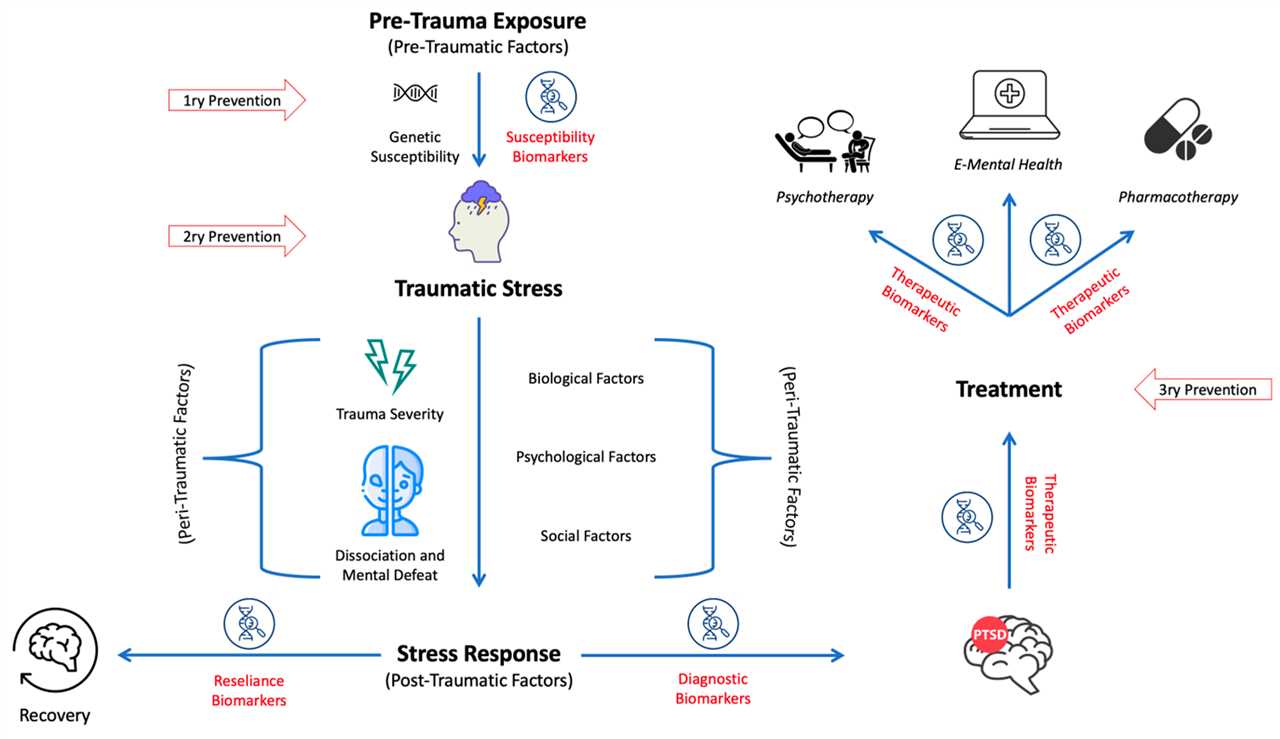
Mental health therapists play a crucial role in supporting individuals who are struggling with various psychological challenges. They dedicate their careers to helping others navigate through the complexities of mental health and find a path towards healing and well-being. However, the nature of their work can expose them to significant stress and potentially lead to the development of secondary traumatic stress.
Secondary traumatic stress, also known as vicarious trauma, refers to the emotional and psychological impact that mental health therapists may experience as a result of hearing about their clients’ traumatic experiences. While therapists are trained to provide empathetic and compassionate care, the constant exposure to stories of trauma can take a toll on their own mental health.
Resilience plays a crucial role in helping mental health therapists cope with the stress and challenges they face in their profession. Resilience can be defined as the ability to bounce back from adversity and maintain mental well-being despite the difficulties encountered. It is not a static trait but rather a dynamic process that can be cultivated and strengthened over time.
Understanding the factors that contribute to resilience in mental health therapists is essential for promoting their well-being and preventing burnout. Research has shown that self-care practices, such as engaging in regular exercise, practicing mindfulness and self-reflection, and seeking support from colleagues and supervisors, can enhance therapists’ resilience and protect them from the negative effects of secondary traumatic stress.
Exploring the Impact of Trauma Exposure

Mental health therapists play a crucial role in supporting individuals who have experienced traumatic events. However, this work exposes therapists to secondary traumatic stress, a condition that can significantly impact their well-being and professional practice.
Secondary traumatic stress, also known as vicarious trauma or compassion fatigue, refers to the emotional and psychological distress that can arise from hearing about and witnessing the traumatic experiences of others. Therapists who work with trauma survivors are particularly vulnerable to developing secondary traumatic stress due to the nature of their work.
The impact of trauma exposure on mental health therapists can be profound. It can lead to symptoms such as intrusive thoughts, nightmares, hypervigilance, emotional numbing, and avoidance behaviors. These symptoms can interfere with therapists’ ability to provide effective care and can also have a negative impact on their personal lives.
However, it is important to note that not all therapists who are exposed to trauma develop secondary traumatic stress. Research has shown that therapists with higher levels of resilience are more likely to be able to cope with the emotional demands of their work and maintain their well-being.
Resilience refers to the ability to bounce back from adversity and maintain a sense of well-being. Therapists who are resilient are better able to regulate their emotions, set boundaries, and engage in self-care practices that help them manage the impact of trauma exposure. Building resilience can be achieved through various strategies, such as seeking supervision and support, practicing self-care, and engaging in activities that promote personal growth and well-being.
By exploring the impact of trauma exposure on mental health therapists, we can better understand the challenges they face and develop strategies to support their well-being and professional development. It is crucial to prioritize the mental health and resilience of therapists so that they can continue to provide high-quality care to those who have experienced trauma.
The Role of Trauma Exposure in Mental Health Therapists

Mental health therapists play a crucial role in supporting individuals who have experienced trauma. However, in their efforts to help others, therapists themselves may be exposed to secondary traumatic stress. This stress can have a significant impact on their own mental health and well-being.
Resilience is a key factor in how therapists are able to cope with the trauma they are exposed to. Resilient therapists are able to bounce back from the challenges they face and continue to provide effective care to their clients. They are able to maintain a sense of self-efficacy and a positive attitude, even in the face of difficult situations.
However, not all therapists are equally resilient, and the level of trauma exposure they experience can greatly impact their ability to cope. Therapists who are exposed to high levels of trauma may be more susceptible to developing symptoms of secondary traumatic stress. This can include feelings of helplessness, anxiety, and even symptoms similar to post-traumatic stress disorder.
It is important for mental health organizations to provide support and resources to help therapists build their resilience and cope with the trauma they may encounter. This can include regular supervision and debriefing sessions, access to counseling services, and training in self-care techniques. By prioritizing the well-being of mental health therapists, organizations can ensure that they are able to continue providing high-quality care to their clients.
| Key Points |
|---|
| – Trauma exposure can have a significant impact on the mental health of mental health therapists. |
| – Resilience is an important factor in how therapists cope with trauma. |
| – Therapists who are exposed to high levels of trauma may be more susceptible to developing secondary traumatic stress. |
| – Mental health organizations should provide support and resources to help therapists build resilience and cope with trauma. |
Understanding Secondary Traumatic Stress

Mental health therapists play a crucial role in helping individuals navigate their mental health challenges. However, their work can also put them at risk for experiencing secondary traumatic stress.
Secondary traumatic stress refers to the emotional and psychological impact that therapists may experience as a result of hearing about or witnessing the traumatic experiences of their clients. It is often characterized by symptoms similar to those of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), including intrusive thoughts, avoidance behaviors, and emotional numbing.
While therapists are trained to provide support and care to their clients, it is important to recognize that they are not immune to the effects of the stories they hear. The empathetic nature of their work can lead to a deep emotional connection with their clients, making them vulnerable to absorbing their clients’ trauma.
Resilience plays a crucial role in mitigating the impact of secondary traumatic stress. Therapists who are resilient are better able to cope with the emotional demands of their work and maintain their own mental well-being. Building resilience involves developing self-care strategies, seeking support from colleagues and supervisors, and engaging in activities that promote personal well-being.
It is also important for mental health organizations to implement policies and practices that support the well-being of their therapists. This can include providing regular supervision and debriefing sessions, offering training on self-care and resilience-building techniques, and promoting a culture of support and self-care within the workplace.
| Key Points |
|---|
| – Mental health therapists are at risk for experiencing secondary traumatic stress. |
| – Secondary traumatic stress is characterized by symptoms similar to PTSD. |
| – Resilience plays a crucial role in mitigating the impact of secondary traumatic stress. |
| – Building resilience involves self-care strategies and seeking support. |
| – Mental health organizations should implement policies that support therapist well-being. |
By understanding the potential risks of secondary traumatic stress and taking steps to promote resilience and self-care, mental health therapists can continue to provide effective and compassionate care to their clients while maintaining their own well-being.
Building Resilience in Mental Health Therapists
Mental health therapists are often exposed to traumatic stories and experiences, which can lead to secondary traumatic stress. This stress can have a significant impact on their mental and physical health, as well as their ability to provide effective care for their clients. However, building resilience can help therapists better cope with the challenges they face in their profession.
Resilience is the ability to bounce back from adversity and maintain a sense of well-being in the face of stress. For mental health therapists, resilience is crucial in order to continue providing high-quality care to their clients. Here are some strategies that therapists can use to build resilience:
1. Self-care: Taking care of oneself is essential for mental health therapists. This includes getting enough sleep, eating well, and engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation. By prioritizing self-care, therapists can replenish their energy and build physical and emotional resilience.
2. Seeking support: It is important for therapists to have a strong support system. This can include colleagues, supervisors, or mentors who can provide guidance and understanding. Additionally, therapists can benefit from participating in professional organizations or support groups where they can connect with others who share similar experiences.
3. Setting boundaries: Establishing clear boundaries is crucial for mental health therapists. This includes setting limits on the number of clients they see in a day, as well as creating boundaries around personal time and space. By setting boundaries, therapists can prevent burnout and maintain a healthy work-life balance.
4. Practicing mindfulness: Mindfulness is a powerful tool for building resilience. By being present in the moment and cultivating an attitude of non-judgment and acceptance, therapists can reduce stress and enhance their ability to cope with difficult situations.
5. Continuing education: Staying up to date with the latest research and techniques in the field of mental health can help therapists feel more confident and competent in their work. By investing in their own professional development, therapists can build resilience and enhance their ability to provide effective care.
Building resilience is an ongoing process that requires commitment and self-reflection. By implementing these strategies, mental health therapists can better navigate the challenges of their profession and continue to provide compassionate and effective care to their clients.
Identifying Protective Factors

In order to promote the health and well-being of mental health therapists and reduce the risk of developing secondary traumatic stress, it is important to identify and understand the protective factors that can help build resilience. These protective factors can serve as buffers against the negative impacts of traumatic experiences and can contribute to the therapist’s ability to cope effectively.
One of the key protective factors is having a strong support system. This can include supportive colleagues, supervisors, friends, and family members who can provide emotional support and understanding. Having someone to talk to and share experiences with can help therapists process their own emotions and prevent the accumulation of stress.
Another protective factor is self-care. Engaging in activities that promote physical and mental health, such as exercise, hobbies, and relaxation techniques, can help therapists recharge and reduce stress levels. Taking breaks and setting boundaries to ensure a healthy work-life balance is also important.
Developing and maintaining a positive mindset is another important protective factor. This can involve cultivating a sense of optimism and gratitude, practicing mindfulness and self-compassion, and reframing negative thoughts. A positive mindset can help therapists maintain perspective and resilience in the face of challenging situations.
Continuing education and professional development can also be protective factors. Staying up to date with the latest research and techniques in the field can enhance therapists’ skills and confidence, and provide a sense of competence and mastery. This can contribute to feelings of effectiveness and reduce the risk of burnout.
Lastly, having a sense of purpose and meaning in one’s work can be a powerful protective factor. Understanding the impact that their work has on the lives of others and connecting with their values and passions can provide therapists with a sense of fulfillment and motivation. This can help sustain their resilience and prevent the negative effects of secondary traumatic stress.
By identifying and fostering these protective factors, mental health therapists can enhance their resilience and minimize the risk of developing secondary traumatic stress. It is important for therapists, organizations, and society as a whole to recognize the importance of supporting and promoting the well-being of those who provide vital mental health services.
Developing Coping Strategies
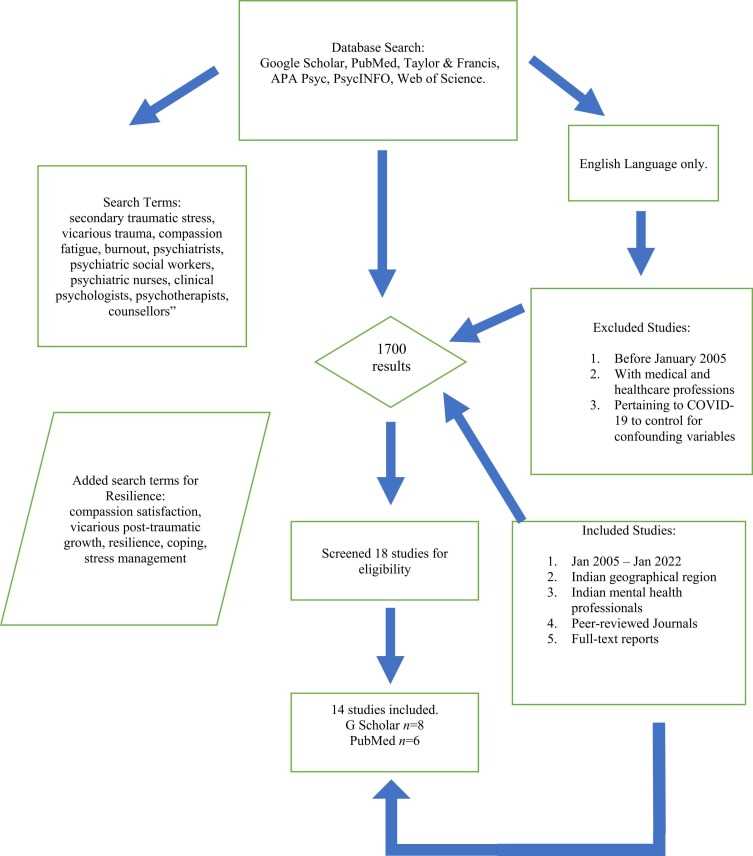
Therapists who work with individuals who have experienced trauma are at risk of developing secondary traumatic stress. This stress can have a significant impact on the mental well-being of these therapists. It is important for therapists to develop coping strategies to help them navigate the challenges associated with their work.
One coping strategy that therapists can employ is self-care. Taking care of oneself physically, emotionally, and mentally is crucial in maintaining resilience and preventing burnout. Engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation, such as exercise, hobbies, or spending time with loved ones, can help therapists recharge and manage stress.
Another coping strategy is seeking support. Connecting with colleagues who understand the challenges of working with trauma can provide a valuable source of support and validation. Supervision and consultation with experienced professionals can also offer guidance and help therapists process their experiences.
Practicing mindfulness and self-reflection is another effective coping strategy. Mindfulness techniques, such as deep breathing exercises or meditation, can help therapists stay present and grounded. Self-reflection allows therapists to examine their own reactions and emotions, fostering self-awareness and personal growth.
Finally, setting boundaries is essential in preventing secondary traumatic stress. Therapists need to establish limits on their workload and prioritize self-care. This may involve saying no to additional clients or taking time off when needed. By setting boundaries, therapists can protect their own well-being and maintain their resilience.
In conclusion, developing coping strategies is crucial for therapists working with trauma to maintain their mental well-being and resilience. Self-care, seeking support, practicing mindfulness and self-reflection, and setting boundaries are effective strategies that can help therapists navigate the challenges of their work and prevent secondary traumatic stress.
Promoting Self-Care

Self-care is a crucial aspect of maintaining resilience and managing stress for mental health therapists. As they work in a field that deals with traumatic experiences and emotional challenges on a daily basis, it is important for therapists to prioritize their own well-being in order to provide effective care to their clients.
Here are some strategies that therapists can employ to promote self-care:
| 1. Prioritize Physical Health | Engaging in regular exercise, eating nutritious meals, and getting enough sleep are essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. Physical activity can help reduce stress levels and improve mood, while a balanced diet and adequate rest can provide the energy needed to cope with the demands of the job. |
| 2. Establish Boundaries | Setting clear boundaries between work and personal life is crucial for preventing burnout and maintaining a healthy work-life balance. This may involve scheduling dedicated time for relaxation, hobbies, and spending time with loved ones. |
| 3. Seek Support | Therapists should not hesitate to seek support from their colleagues, supervisors, or professional networks. Connecting with others who understand the unique challenges of the profession can provide a sense of validation, reassurance, and guidance. |
| 4. Engage in Self-Reflection | Taking time to reflect on one’s own experiences, emotions, and reactions can help therapists gain insight into their own well-being and identify areas for personal growth. This can be done through journaling, therapy, or participating in supervision or consultation groups. |
| 5. Practice Self-Care Activities | Engaging in activities that bring joy, relaxation, and rejuvenation is vital for therapists to recharge and replenish their emotional reserves. This may include hobbies, creative outlets, mindfulness practices, or simply taking time for oneself. |
By prioritizing self-care, mental health therapists can enhance their resilience and reduce the risk of experiencing secondary traumatic stress. Taking care of their own well-being allows therapists to continue providing high-quality care to their clients and maintain their own mental health in the process.
Supporting Mental Health Therapists
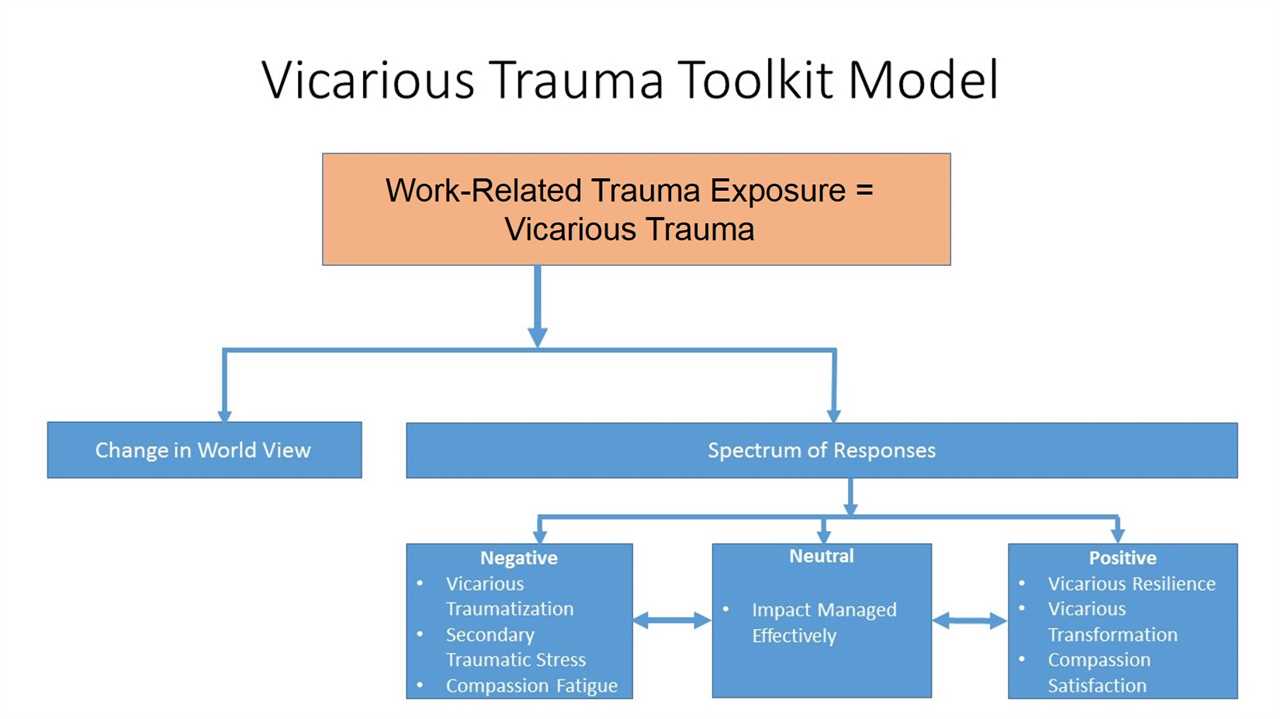
Mental health therapists play a crucial role in supporting individuals who are experiencing various mental health challenges. However, the nature of their work can expose them to secondary traumatic stress, which can impact their own mental well-being. It is essential to provide support and resources to help therapists maintain their resilience and navigate the challenges they face.
One way to support mental health therapists is by offering regular supervision and debriefing sessions. These sessions provide a space for therapists to process their experiences, discuss any secondary traumatic stress they may be experiencing, and receive guidance and support from their peers or supervisors. This can help therapists feel validated and reduce the risk of burnout.
Another important aspect of supporting mental health therapists is providing access to self-care resources. This can include offering workshops or training on stress management techniques, mindfulness practices, and other coping strategies. By equipping therapists with these tools, they can better manage the emotional toll of their work and maintain their mental well-being.
Creating a supportive work environment is also crucial for supporting mental health therapists. This can involve fostering a culture of open communication and collaboration, where therapists feel comfortable sharing their challenges and seeking support from their colleagues. Additionally, providing opportunities for professional development and growth can help therapists feel valued and motivated in their roles.
Finally, it is important to recognize and address any systemic issues that may contribute to secondary traumatic stress in mental health therapists. This can involve advocating for better work-life balance, addressing high caseloads, and promoting policies that prioritize therapist well-being. By addressing these factors, we can create a more supportive and sustainable environment for mental health therapists.
- Offer regular supervision and debriefing sessions
- Provide access to self-care resources
- Create a supportive work environment
- Recognize and address systemic issues
By implementing these strategies, we can better support mental health therapists in their important work and help them maintain their resilience in the face of secondary traumatic stress. Ultimately, this will contribute to better outcomes for both therapists and the individuals they serve.

I am Patrina de Silva, a psychologist and mental health blogger in Sri Lanka. After obtaining psychology degrees from the University of Colombo and Monash University, I returned home to work as a counselor while also starting the popular blog “Pressy but Happy” to provide advice on psychological issues. Over the past decade, my empathetic articles have made my blog a leading mental health resource in the country. In addition to writing, I maintain a private therapy practice, frequently volunteer counseling time, and conduct seminars, driven by my passion for destigmatizing mental illness and educating the public on the mind-body connection. I strive to be an influential voice in my field through my compassionate approach.
