
Chronic stresses have become a prevalent issue in today’s fast-paced and demanding world. These ongoing pressures can have a significant impact on our mental and physical health, making it crucial to understand how to effectively manage and adapt to them. Building resilience is key to navigating these chronic stresses and promoting overall well-being.
Support and recovery are essential components of building resilience. It is important to recognize that everyone experiences chronic stresses differently, and what works for one person may not work for another. However, seeking support from trusted individuals, such as friends, family, or professionals, can provide a valuable outlet for expressing emotions and finding solutions. Additionally, taking time for self-care activities, such as exercise, meditation, or engaging in hobbies, can aid in the recovery process and help build resilience.
Understanding the nature of chronic stresses is also crucial in building resilience. Chronic stresses can stem from various sources, such as work, relationships, or financial pressures. These ongoing challenges can lead to mental health issues, such as anxiety or depression, if not properly addressed. By acknowledging and accepting the presence of chronic stresses, individuals can begin the process of adaptation and develop effective coping strategies.
Adaptation is a key factor in building resilience. It involves recognizing the need for change and taking proactive steps to address chronic stresses. This may include setting boundaries, practicing healthy communication, or seeking professional help. It is important to remember that adaptation is an ongoing process, and it may take time to find what works best for you. However, by embracing change and being open to new strategies, individuals can develop the resilience needed to thrive in the face of chronic stresses.
In conclusion, understanding chronic stresses and building resilience are essential for maintaining optimal mental and physical health. Support and recovery, along with a deep understanding of the nature of chronic stresses, are key factors in this process. By embracing adaptation and being open to change, individuals can develop effective strategies to navigate the challenges of everyday life and build resilience for a healthier, happier future.
What are Chronic Stresses?
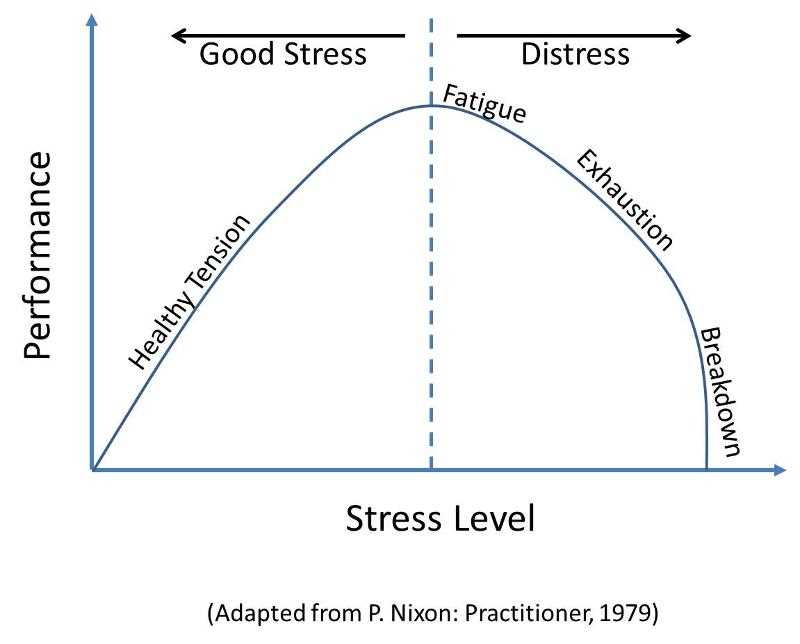
Chronic stresses refer to ongoing, long-term pressures or challenges that individuals face in their daily lives. Unlike acute stresses, which are short-lived and temporary, chronic stresses can persist for extended periods of time, often causing significant mental and physical strain.
Adaptation and resilience are key factors in dealing with chronic stresses. Individuals who are able to adapt to and cope with these ongoing pressures are more likely to maintain their mental and emotional well-being. Resilience, or the ability to bounce back from adversity, plays a crucial role in the recovery and long-term management of chronic stresses.
Chronic stresses can have a profound impact on mental health. They can contribute to the development or exacerbation of conditions such as anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). It is important for individuals experiencing chronic stresses to seek support and professional help to prevent or address these mental health issues.
Building resilience and managing chronic stresses often requires a multifaceted approach. This may include developing healthy coping mechanisms, seeking social support, engaging in self-care activities, and making lifestyle changes to promote overall well-being. It is important to recognize that recovery from chronic stresses is a process that takes time and effort, and individuals may need ongoing support and resources to maintain their mental and physical health.
In conclusion, chronic stresses are ongoing pressures and challenges that can have a significant impact on mental health. Building resilience and seeking support are key strategies for managing these stresses and promoting recovery. By understanding the factors that contribute to chronic stresses and implementing effective coping strategies, individuals can enhance their overall well-being and improve their quality of life.
Definition and Impact
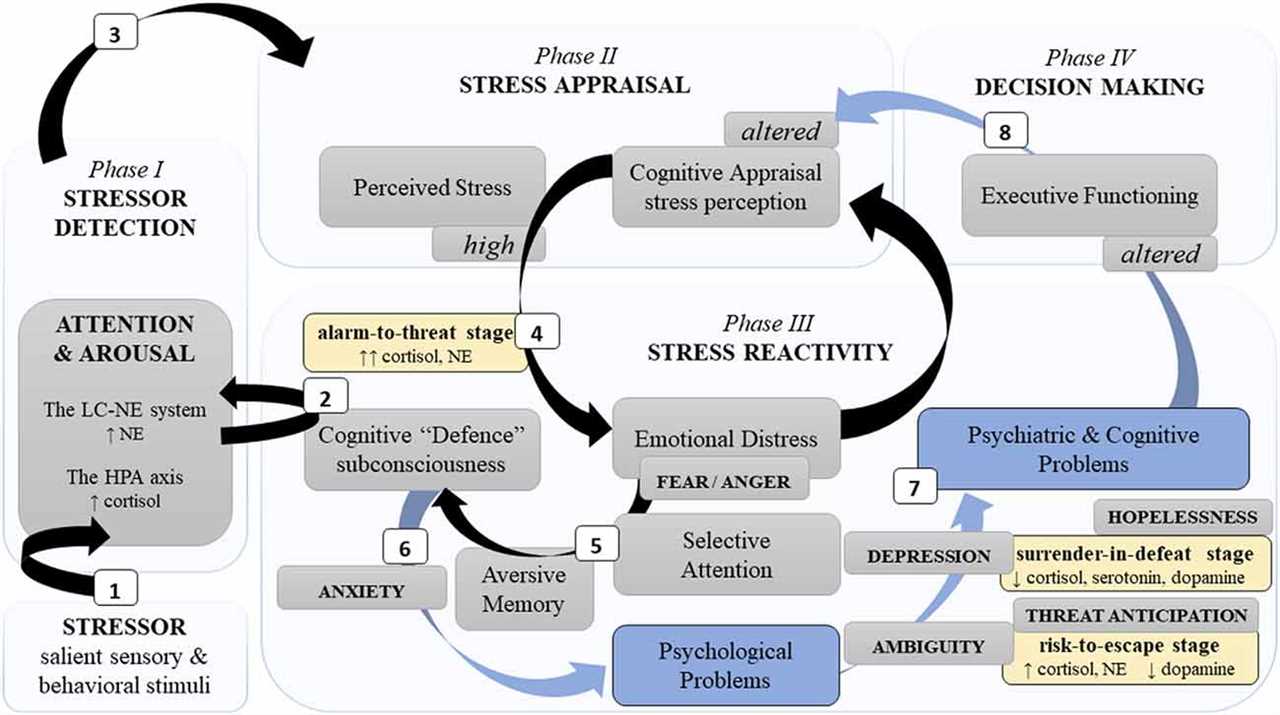
Chronic stresses refer to ongoing and persistent pressures that individuals experience in their daily lives. These stresses can come from various sources, such as work, relationships, financial difficulties, or health problems. Unlike acute stresses, which are short-lived and often resolved quickly, chronic stresses can last for extended periods, causing long-term effects on physical and mental well-being.
The impact of chronic stresses on individuals can be significant. They can lead to a state of constant tension and exhaustion, making it challenging to relax and recover. Prolonged exposure to chronic stresses can weaken the body’s immune system, increase the risk of developing chronic diseases, and impair cognitive functions. Furthermore, chronic stresses can negatively affect relationships, work performance, and overall quality of life.
Recovery from chronic stresses requires time and support. It is essential for individuals to have access to resources and social networks that provide emotional and practical assistance. Support from family, friends, and professionals can help individuals develop resilience and cope with the challenges they face. Building resilience involves adapting to stressors, developing healthy coping mechanisms, and maintaining good physical and mental health.
Resilience is the ability to bounce back from adversity and adapt to difficult circumstances. It is a crucial factor in mitigating the negative impact of chronic stresses. Resilient individuals can effectively navigate through challenges, maintain a positive outlook, and find ways to protect their well-being. Developing resilience involves strengthening personal skills, fostering social connections, and seeking professional help when needed.
Understanding the definition and impact of chronic stresses is essential for promoting health and well-being. By recognizing the signs and effects of chronic stresses, individuals can take proactive steps to build resilience, seek support, and implement strategies to cope effectively with ongoing pressures.
Common Sources

Chronic stresses can arise from various aspects of life, impacting both physical and mental health. Understanding these common sources is essential for developing effective coping strategies and building resilience.
One common source of chronic stress is work-related pressures. The demands of a job, such as long hours, tight deadlines, and high expectations, can take a toll on an individual’s well-being. This can lead to mental health issues and hinder the ability to cope with stress effectively.
Another common source is financial stress. Money-related concerns, such as debt, job insecurity, or the inability to meet basic needs, can create ongoing worries and anxieties. The constant strain of financial difficulties can significantly impact mental health and overall resilience.
Relationships can also be a significant source of chronic stress. Difficulties in personal relationships, whether it be with a partner, family member, or friend, can lead to ongoing emotional strain. This can affect mental health and make it challenging to adapt and recover from stressful situations.
Health-related issues, both physical and mental, can be chronic stressors. Dealing with chronic illnesses, managing pain, or navigating mental health conditions can be incredibly challenging and impact an individual’s ability to cope with stress effectively. The continuous adaptation and recovery process can be exhausting and put a strain on resilience.
It is important to recognize these common sources of chronic stress and develop strategies to address them. Building resilience involves finding healthy coping mechanisms, seeking support, and fostering a mindset of adaptation and growth. By understanding and actively addressing these sources, individuals can better navigate the challenges of chronic stresses and build their resilience.
Long-Term Effects
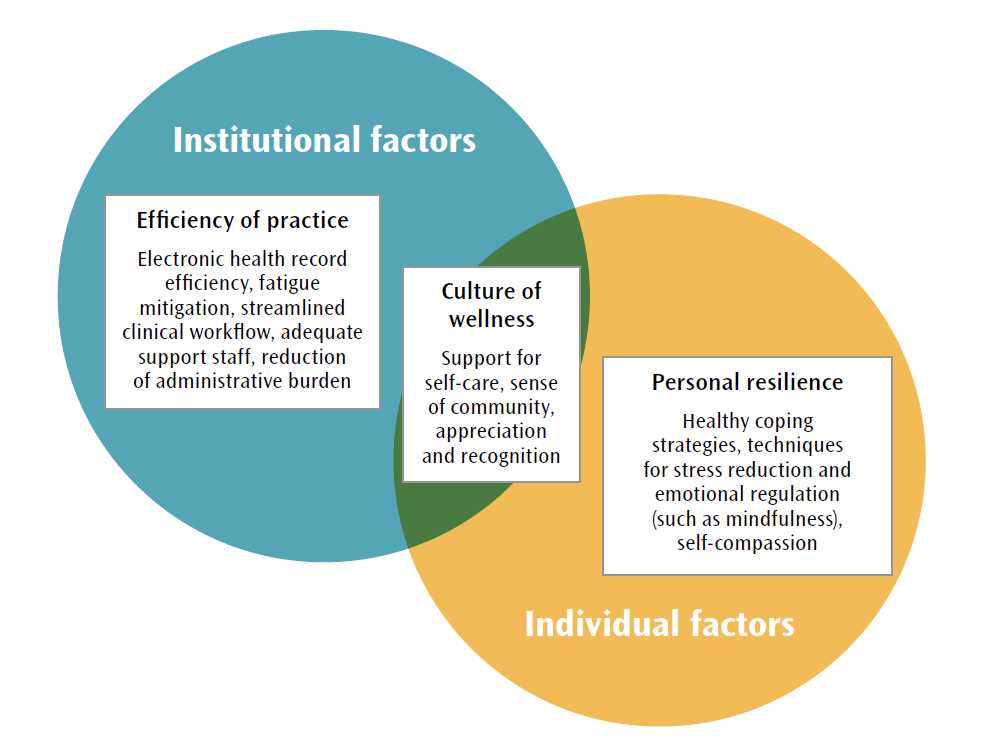
Chronic stresses can have significant long-term effects on an individual’s mental and physical well-being. Coping with prolonged stress can be challenging, leading to various negative outcomes. However, it is important to note that individuals have the capacity for recovery and adaptation, and building resilience is key to mitigating the long-term effects of chronic stress.
Mental health is one area that can be greatly impacted by chronic stress. Prolonged exposure to stressors can lead to the development of mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression. These conditions can further exacerbate the effects of chronic stress, creating a cycle of negative emotions and thoughts. Building resilience through strategies such as seeking support, practicing self-care, and engaging in stress-reducing activities can help mitigate these long-term effects.
Physical health is another aspect that can be affected by chronic stress. The body’s stress response system is designed to handle short-term stressors, but chronic stress can overload this system, leading to a variety of health issues. These can include cardiovascular problems, weakened immune function, and gastrointestinal disorders. Developing resilience through healthy lifestyle choices, such as regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and adequate sleep, can help support overall physical health and minimize the long-term effects of chronic stress.
In conclusion, chronic stresses can have lasting impacts on an individual’s mental and physical health. However, by focusing on building resilience and implementing strategies to cope with and recover from chronic stress, individuals can mitigate these effects and improve their overall well-being.
Factors Influencing Resilience

Resilience is the ability to recover and adapt to chronic stresses and challenges. It is influenced by a variety of factors that can support an individual’s mental and emotional well-being.
One important factor influencing resilience is social support. Having a strong network of friends, family, and community can provide individuals with the necessary support and resources to cope with and overcome challenges. Social support can come in the form of emotional support, practical assistance, or simply having someone to talk to. It can help individuals feel less alone and more capable of facing their stresses.
Another factor is the ability to cope effectively with stress. Individuals who have developed healthy coping mechanisms and strategies are better equipped to handle chronic stresses. These coping mechanisms can include activities such as exercise, meditation, journaling, or engaging in hobbies. They can help individuals manage their emotions, reduce stress levels, and promote a sense of well-being.
Adaptation is also a key factor in resilience. Being able to adapt to new and challenging situations can help individuals navigate through chronic stresses. This can involve being open to change, learning new skills, and being flexible in one’s thinking. Adaptation allows individuals to find new ways of approaching problems and finding solutions.
Mental health is another important factor influencing resilience. Taking care of one’s mental well-being through practices such as therapy, self-care, and mindfulness can help individuals build resilience. It is important to prioritize mental health and seek help when needed, as it can significantly impact an individual’s ability to cope with chronic stresses.
In conclusion, factors such as social support, effective coping mechanisms, adaptation, and mental health all play a significant role in influencing resilience. By developing and nurturing these factors, individuals can better navigate and overcome the challenges that come with chronic stresses.
Genetic Factors

Understanding the role of genetic factors in health and adaptation to chronic stresses is essential for developing effective strategies to build resilience and promote recovery. Genetics plays a significant role in mental health and the ability to cope with chronic stressors.
Research has shown that certain genetic variations can impact an individual’s susceptibility to chronic stress and their resilience in the face of adversity. These genetic factors can influence the functioning of various biological systems involved in stress response and regulation, such as the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and the immune system.
Genetic factors can affect an individual’s ability to regulate stress hormones and inflammatory responses, which are key processes in the body’s response to chronic stress. Variations in genes involved in the production and regulation of stress hormones, such as cortisol, can influence an individual’s vulnerability to developing mental health disorders and their ability to recover from chronic stress.
Furthermore, genetic factors can also impact an individual’s resilience by influencing their cognitive and emotional responses to stress. Certain genetic variations have been associated with increased risk of developing negative cognitive biases and maladaptive coping strategies, which can hinder an individual’s ability to adapt and recover from chronic stress.
It is important to note that while genetic factors can contribute to an individual’s vulnerability to chronic stress, they do not determine one’s fate. Resilience is a complex trait that is influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and experiential factors. Supportive environments, positive social relationships, and effective coping strategies can enhance resilience and promote recovery, even for individuals with genetic predispositions to mental health disorders and chronic stress.
In conclusion, understanding the role of genetic factors in health and adaptation to chronic stresses is crucial for developing effective strategies to build resilience and promote recovery. Genetic variations can influence an individual’s susceptibility to chronic stress, their ability to regulate stress hormones and inflammatory responses, and their cognitive and emotional responses to stress. However, resilience is not solely determined by genetics, and supportive environments and effective coping strategies can play a significant role in promoting resilience and recovery.
Environmental Factors

Environmental factors play a crucial role in understanding chronic stresses and building resilience. The environment in which individuals live and work can have a significant impact on their mental and physical health.
Chronic stresses, such as pollution, noise, and overcrowding, can negatively affect an individual’s well-being. These stresses can lead to increased levels of anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues. Additionally, exposure to environmental toxins can have long-term effects on the body, leading to chronic illnesses and decreased overall health.
However, the environment can also play a positive role in recovery and adaptation. Supportive and nurturing environments can help individuals cope with chronic stresses and build resilience. Access to green spaces, for example, has been shown to have a positive impact on mental health, reducing stress levels and promoting overall well-being.
Furthermore, social support from the environment can also contribute to resilience-building. Having a strong support network and access to resources can help individuals better navigate and adapt to chronic stresses. Community programs and initiatives that promote mental health and well-being can provide individuals with the support they need to overcome challenges and build resilience.
In conclusion, environmental factors are key in understanding chronic stresses and building resilience. The impact of the environment on an individual’s mental and physical health cannot be underestimated. By creating supportive environments and providing access to resources and support, individuals can better cope with chronic stresses and adapt to the challenges they face.
Psychological Factors

Psychological factors play a crucial role in understanding chronic stresses and building resilience. Resilience refers to the ability to bounce back from adversity and recover quickly from setbacks.
Chronic stresses can have a significant impact on an individual’s mental health and well-being. These stresses can include ongoing financial difficulties, relationship problems, work-related stress, and health issues. The ability to adapt and cope with these stresses is essential for maintaining good mental and physical health.
Support from family, friends, and other social networks is a vital psychological factor in building resilience. Having a support system in place can provide individuals with the emotional and practical support they need to navigate through difficult times.
Another important psychological factor is effective coping strategies. Coping mechanisms can help individuals manage stress and maintain their mental well-being. These strategies can include engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation, practicing mindfulness and meditation, seeking professional help, and fostering a positive mindset.
Mental health professionals often emphasize the importance of self-care and self-compassion. Taking care of one’s mental health through regular exercise, proper nutrition, and adequate sleep can contribute to building resilience and reducing the impact of chronic stresses.
Overall, understanding and addressing psychological factors are key to building resilience and promoting mental well-being in the face of chronic stresses. By recognizing the importance of support, coping strategies, and self-care, individuals can develop the skills needed to adapt and thrive in challenging circumstances.

I am Patrina de Silva, a psychologist and mental health blogger in Sri Lanka. After obtaining psychology degrees from the University of Colombo and Monash University, I returned home to work as a counselor while also starting the popular blog “Pressy but Happy” to provide advice on psychological issues. Over the past decade, my empathetic articles have made my blog a leading mental health resource in the country. In addition to writing, I maintain a private therapy practice, frequently volunteer counseling time, and conduct seminars, driven by my passion for destigmatizing mental illness and educating the public on the mind-body connection. I strive to be an influential voice in my field through my compassionate approach.
