
Water is an essential resource for all living creatures on our planet. It plays a crucial role in sustaining life and maintaining the delicate balance of ecosystems. However, with the increasing global population and climate change, water stress has become a pressing issue in many parts of the world.
Water stress occurs when the demand for water exceeds the available supply. It can lead to a wide range of problems, such as water scarcity, decreased water quality, and the depletion of natural water sources. These issues not only affect human populations but also have a significant impact on agriculture, industry, and the environment.
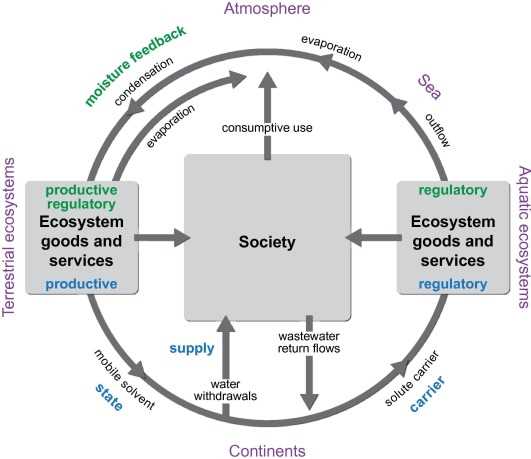
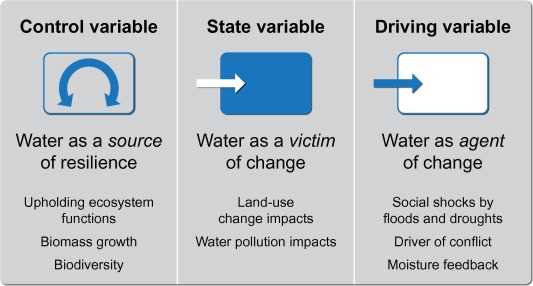
In order to address the challenges posed by water stress, it is important to understand the concept of resilience. Resilience refers to the ability of a system or community to withstand and recover from disturbances or shocks. In the context of water stress, building resilience involves implementing strategies and practices that can help mitigate the effects of water scarcity and ensure the sustainable use of water resources.
Building resilience to stress water levels requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes promoting water conservation and efficiency measures, investing in water infrastructure and technology, and implementing policies that protect and manage water resources effectively. Additionally, raising awareness and educating communities about the importance of water conservation can also play a crucial role in building resilience.
What is Stress Water Level?

Stress water level refers to the amount of stress an individual experiences at any given time. It is a measure of the emotional and psychological pressure that can be caused by various factors, such as work, relationships, or financial difficulties.
Understanding and managing stress water levels is essential for maintaining overall well-being and building resilience. When stress water levels are high, it can have a negative impact on both physical and mental health. Chronic stress can lead to a range of health problems, including heart disease, depression, and anxiety.
Resilience plays a crucial role in managing stress water levels. Resilience is the ability to bounce back from adversity and adapt to change. By developing resilience, individuals can better cope with stress and maintain a healthy stress water level.
There are various strategies that can help build resilience and manage stress water levels. These include practicing self-care, engaging in regular exercise, seeking social support, and practicing mindfulness techniques. Additionally, it is important to identify and address the underlying causes of stress to prevent it from becoming overwhelming.
Overall, understanding and building resilience to stress water levels is essential for maintaining a healthy lifestyle and promoting overall well-being. By managing stress effectively, individuals can improve their quality of life and reduce the negative impacts of stress on their physical and mental health.
Definition of Stress Water Level

Stress water level refers to the amount of pressure and tension that an individual experiences in relation to their water resources. It is a measure of the impact that various stressors have on the availability and quality of water.
Water stress occurs when the demand for water exceeds the available supply. This can be caused by various factors such as population growth, industrialization, climate change, and inefficient water management practices.
The stress water level is determined by assessing the balance between water availability and water demand. When the demand for water surpasses the available supply, it can lead to negative consequences for both human and ecological systems.
Understanding and monitoring the stress water level is crucial for effective water resource management and building resilience to water-related stressors. It helps identify areas that are most vulnerable to water scarcity and allows for the development of strategies to mitigate the impacts of water stress.
Factors Affecting Stress Water Level
Resilience is a key factor that affects the stress water level. Individuals with high levels of resilience are better able to cope with and adapt to stressful situations, resulting in lower stress water levels. On the other hand, individuals with low resilience may struggle to manage stress, leading to higher stress water levels.
The level of stress experienced can also impact the stress water level. High levels of chronic stress can lead to an increased stress water level, as the body’s stress response system becomes overworked and less effective at managing stress. In contrast, low levels of stress can help to maintain a lower stress water level.
Additionally, external factors can influence the stress water level. Supportive relationships and social connections can help to reduce stress and lower the stress water level. On the other hand, a lack of social support or negative relationships can contribute to higher stress water levels.
Individual coping strategies and resilience-building techniques can also play a role in affecting the stress water level. Effective coping strategies, such as exercise, mindfulness, and seeking support, can help to reduce stress and lower the stress water level. Conversely, ineffective coping mechanisms or a lack of resilience-building techniques can contribute to higher stress water levels.
Overall, a combination of resilience, stress levels, external factors, and individual coping strategies all contribute to the stress water level. By understanding and addressing these factors, individuals can work towards building resilience and effectively managing stress to maintain a lower stress water level.
Impacts of High Stress Water Level
When water levels reach high stress levels, it can have significant impacts on both the environment and human populations. The level of stress in the water can directly affect the quality and availability of drinking water sources, as well as the health and well-being of aquatic ecosystems.
High stress water levels can lead to increased erosion and sedimentation, which can negatively impact water quality. Excessive sedimentation can smother aquatic plants and animals, disrupt their habitats, and reduce the overall biodiversity of the ecosystem. This can have far-reaching consequences for both wildlife and humans who depend on these ecosystems for their livelihoods.
Additionally, high stress water levels can contribute to increased flooding and damage to infrastructure. When water levels rise beyond their normal range, it can overwhelm drainage systems and cause water to enter homes, businesses, and public spaces. This can result in significant property damage, economic losses, and even loss of life.
In terms of human health, high stress water levels can increase the risk of waterborne diseases and contamination. When water sources become stressed, there is a higher likelihood of harmful bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens entering the water supply. This can lead to outbreaks of diseases such as cholera, dysentery, and typhoid, which can be particularly devastating in vulnerable populations.
Overall, understanding and mitigating the impacts of high stress water levels is crucial for building resilience to climate change and ensuring the sustainability of water resources. By implementing measures to manage water levels, improve water quality, and protect ecosystems, we can minimize the negative impacts of stress on water and create a more sustainable future for all.
Understanding Resilience to Stress Water Levels

Resilience is the ability to withstand and recover from stress. When it comes to water levels, resilience refers to the ability of an ecosystem or a community to adapt and bounce back from changes in water levels caused by various stressors.
Water levels can be influenced by natural factors such as rainfall patterns, tides, and climate change. They can also be affected by human activities such as damming, irrigation, and pollution. These changes in water levels can have significant impacts on the environment and the communities that rely on them.
Understanding resilience to stress water levels involves studying the interactions between the physical, biological, and social components of an ecosystem. It requires assessing the capacity of the ecosystem to absorb and recover from disturbances caused by changes in water levels.
Resilience to stress water levels can be enhanced through various strategies. These include implementing sustainable water management practices, restoring natural habitats, and promoting community engagement and participation in decision-making processes. It is important to consider both short-term and long-term impacts when developing resilience strategies.
Building resilience to stress water levels is crucial for the sustainability of ecosystems and the well-being of communities. By understanding the factors that contribute to resilience and implementing appropriate strategies, we can ensure the continued availability of clean water, the protection of biodiversity, and the resilience of communities in the face of changing water levels.
Definition of Resilience

Resilience is the ability to adapt and bounce back from difficult situations or stressors. It is the capacity to maintain a stable level of functioning despite the challenges faced. Resilience is not about avoiding stress or eliminating it completely, but rather about developing the skills and mindset to effectively navigate through it.
Resilience can be thought of as a dynamic process that involves the interaction between an individual and their environment. It is influenced by various factors such as genetics, upbringing, and life experiences. Resilience can be developed and strengthened through intentional efforts and practice.
At the individual level, resilience is characterized by qualities such as optimism, perseverance, and the ability to regulate emotions. It involves having a positive outlook on life, being able to bounce back from setbacks, and having the flexibility to adapt to new circumstances.
Resilience is also important at the community and societal levels. Building resilient communities involves creating supportive environments and social networks that promote well-being and provide resources for individuals to cope with stressors. This can include access to healthcare, education, and social support systems.
| Key Elements of Resilience |
|---|
| Positive outlook |
| Adaptability |
| Emotional regulation |
| Perseverance |
| Supportive environment |
| Strong social networks |
Resilience is a valuable skill that can help individuals and communities navigate through stressful situations and maintain well-being. By understanding and building resilience, we can better cope with the challenges that come our way and thrive in the face of adversity.
Importance of Building Resilience
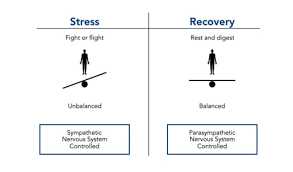
Resilience is crucial when it comes to dealing with stress and adapting to changes in water levels. It refers to the ability to bounce back and recover from difficult situations, maintaining a sense of well-being and mental strength.
Building resilience is especially important in the context of water levels, as these can fluctuate and have a significant impact on various aspects of life. For example, droughts can lead to water scarcity and affect agriculture, while floods can cause property damage and displace communities.
By building resilience, individuals and communities can better cope with the stress and challenges that arise from changing water levels. This can involve developing strategies to adapt to water scarcity, such as implementing efficient irrigation techniques or finding alternative water sources. It can also involve preparing for and responding to floods, such as creating emergency plans and improving infrastructure.
Moreover, building resilience can help reduce the negative impacts of stress on mental and physical health. Stress is often associated with increased vulnerability to illness and decreased overall well-being. By developing resilience, individuals can better manage stress and maintain their health and well-being even in the face of challenging circumstances.
In conclusion, building resilience is of utmost importance when it comes to dealing with stress and adapting to changes in water levels. It not only helps individuals and communities cope with the challenges and impacts of fluctuating water levels but also promotes overall well-being and mental strength.

I am Patrina de Silva, a psychologist and mental health blogger in Sri Lanka. After obtaining psychology degrees from the University of Colombo and Monash University, I returned home to work as a counselor while also starting the popular blog “Pressy but Happy” to provide advice on psychological issues. Over the past decade, my empathetic articles have made my blog a leading mental health resource in the country. In addition to writing, I maintain a private therapy practice, frequently volunteer counseling time, and conduct seminars, driven by my passion for destigmatizing mental illness and educating the public on the mind-body connection. I strive to be an influential voice in my field through my compassionate approach.
