
Resilience is a key factor in our ability to overcome challenges and thrive in the face of adversity. It is the capacity to bounce back, adapt, and grow stronger from difficult experiences. One area where resilience plays a crucial role is in our ability to deal with shame. Shame, a complex and powerful emotion, can have a profound impact on our well-being and relationships. Understanding the importance of resilience in the face of shame is essential for personal growth and emotional well-being.
Shame Resilience Theory is a framework that helps us understand and navigate the impact of shame in our lives. Developed by renowned researcher and author Brené Brown, this theory explores how shame affects us and offers strategies for building resilience. According to the theory, shame is the intensely painful feeling that we are flawed, unworthy, and fundamentally inadequate. It can arise from a variety of sources, including societal expectations, personal experiences, and internalized beliefs.
The importance of shame resilience lies in its ability to help us break free from the grip of shame and develop a healthier relationship with ourselves and others. Building resilience allows us to recognize and challenge the shame triggers that hold us back, and to cultivate self-compassion and empathy. By developing shame resilience, we can learn to embrace vulnerability, practice authenticity, and foster stronger connections with others.
Overall, understanding the importance of resilience in the face of shame is crucial for personal growth and emotional well-being. Shame Resilience Theory provides a valuable framework for navigating the impact of shame and building resilience. By cultivating shame resilience, we can break free from the grip of shame, develop healthier relationships, and live more authentically. It is a powerful tool for transforming shame into growth and connection.
What is Shame Resilience Theory?
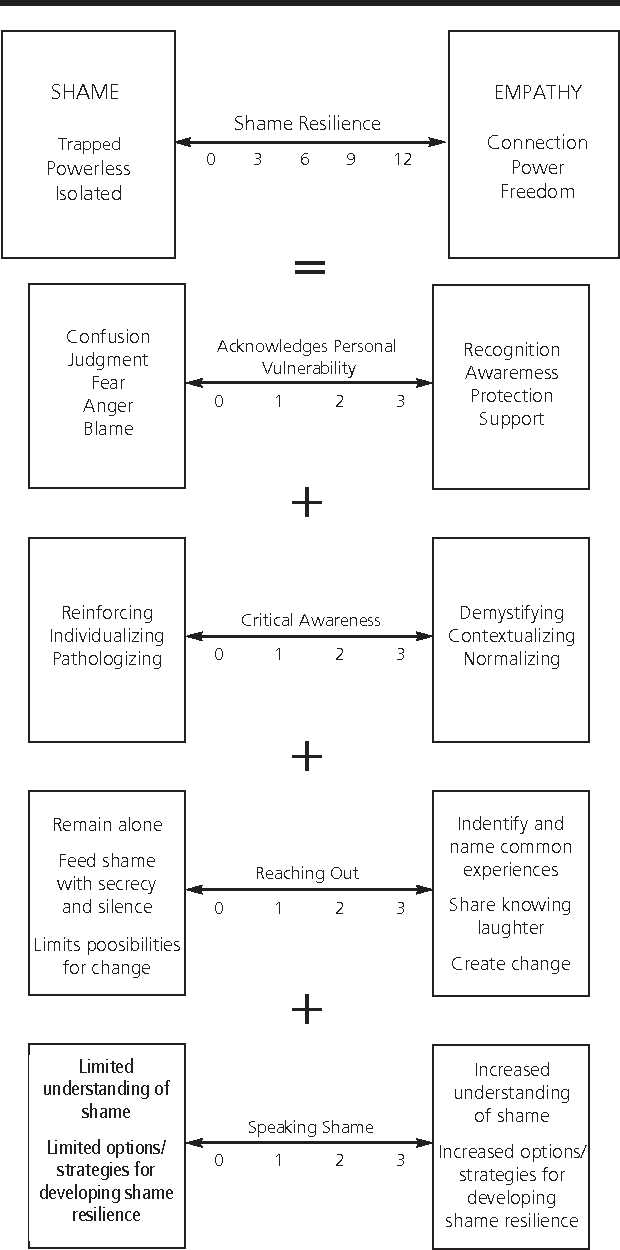
The Shame Resilience Theory is a psychological theory that focuses on the understanding and importance of shame and resilience. Shame is a powerful emotion that can have a profound impact on individuals and their well-being. It is often associated with feelings of worthlessness, inadequacy, and self-judgment.
The theory of shame resilience emphasizes the importance of developing the ability to effectively cope with and overcome shame. Resilience refers to the capacity to bounce back from difficult experiences and maintain a sense of well-being. In the context of shame, resilience involves developing strategies and skills to effectively manage and navigate shame experiences.
Shame resilience theory suggests that individuals who are able to build resilience in the face of shame are more likely to experience improved mental health, increased self-esteem, and better overall well-being. This theory emphasizes the importance of recognizing and understanding shame, as well as developing strategies to address and overcome it.
Key components of shame resilience theory include:
- Recognizing shame: Developing an awareness of shame and its impact on emotions, thoughts, and behaviors.
- Understanding triggers: Identifying the situations, experiences, or thoughts that tend to trigger shame.
- Practicing empathy and self-compassion: Cultivating a sense of empathy and understanding towards oneself, and learning to treat oneself with kindness and compassion.
- Reaching out for support: Building a network of supportive relationships and seeking help when needed.
- Developing resilience skills: Learning and practicing skills such as mindfulness, self-care, and positive self-talk to effectively cope with and overcome shame.
Overall, the shame resilience theory provides a framework for understanding the importance of resilience in the face of shame and offers strategies for building resilience. By developing these skills, individuals can enhance their well-being and navigate shame experiences in a healthier and more adaptive way.
Definition of Shame Resilience Theory

The Shame Resilience Theory is a psychological framework that focuses on understanding the importance of building resilience in the face of shame. Shame, a complex emotion that arises from feelings of inadequacy or unworthiness, can have significant negative impacts on an individual’s mental health and well-being. The Shame Resilience Theory aims to provide individuals with the tools and strategies necessary to effectively cope with and overcome shame.
Resilience, in the context of this theory, refers to the ability to bounce back from shame and navigate through difficult experiences without being overwhelmed by feelings of shame. It involves developing a strong sense of self-worth and self-compassion, as well as cultivating supportive relationships and engaging in healthy coping mechanisms.
The theory emphasizes the importance of understanding shame triggers and recognizing the impact of shame on one’s thoughts, emotions, and behaviors. By increasing self-awareness and developing a non-judgmental attitude towards oneself, individuals can begin to build resilience and effectively manage shame.
Building shame resilience involves cultivating empathy, both towards oneself and others, as well as practicing vulnerability and authenticity. It also includes challenging societal and cultural norms that contribute to shame and fostering a sense of belonging and connection.
Overall, the Shame Resilience Theory highlights the importance of acknowledging and addressing shame in order to build resilience and promote mental well-being. By understanding the underlying mechanisms of shame and developing effective coping strategies, individuals can navigate through shame-related experiences with increased self-compassion and self-confidence.
Key Concepts of Shame Resilience Theory
The Shame Resilience Theory stresses the importance of understanding the role and impact of shame in our lives. It recognizes that shame is a universal emotion that can be experienced by anyone, regardless of age, gender, or background. The theory emphasizes that shame is not inherently bad, but rather a natural response to certain situations or experiences.
One of the key concepts of the theory is the idea that shame can be both adaptive and maladaptive. Adaptive shame serves as a signal that alerts us to our own values and helps us align our behavior with those values. It motivates us to make amends and repair relationships. On the other hand, maladaptive shame is excessive, self-destructive, and can lead to feelings of worthlessness and isolation.
The theory also highlights the importance of empathy and connection as protective factors against shame. Building strong connections with others and cultivating empathy towards ourselves and others can help us develop shame resilience. This involves recognizing and challenging the shame triggers, practicing self-compassion, and seeking support from trusted individuals.
Another key concept is the idea of shame resilience as a skill that can be learned and developed. It involves the ability to recognize shame, understand its impact, and respond to it in a healthy and adaptive way. Developing shame resilience requires self-awareness, self-acceptance, and the willingness to engage in vulnerability and self-reflection.
In summary, the Shame Resilience Theory emphasizes the importance of understanding and addressing shame in order to build resilience. It highlights the adaptive and maladaptive aspects of shame, the role of empathy and connection, and the development of shame resilience as a skill. By cultivating these key concepts, individuals can better navigate shame and lead more authentic and fulfilling lives.
Importance of Shame Resilience
Shame is a powerful emotion that can have detrimental effects on an individual’s mental and emotional well-being. It is often associated with feelings of inadequacy, guilt, and embarrassment. The stresses of shame can be overwhelming and can lead to a variety of negative outcomes, including anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem.
However, building resilience to shame is of utmost importance in order to effectively cope with and overcome these challenges. Shame resilience refers to an individual’s ability to recognize and respond to shame in a healthy and constructive manner. It involves developing skills and strategies to navigate through shame-inducing situations and to maintain a positive sense of self-worth.
Resilience to shame is important because it allows individuals to break free from the cycle of shame and its negative impacts. It empowers individuals to challenge their negative self-perceptions and to cultivate self-compassion and self-acceptance. By building resilience to shame, individuals can develop a stronger sense of identity and improve their overall well-being.
Furthermore, shame resilience is crucial in fostering healthy relationships and social connections. Shame often leads individuals to isolate themselves and withdraw from others due to fear of judgment and rejection. By developing resilience to shame, individuals can build and maintain meaningful relationships, as they are able to communicate their emotions and vulnerabilities without the fear of shame.
In conclusion, the importance of shame resilience cannot be overstated. It is essential for individuals to develop the skills and strategies necessary to effectively cope with shame and its negative impacts. By doing so, individuals can break free from the stresses of shame and cultivate a healthier and more resilient mindset.
Impact of Shame on Mental Health
The Shame Resilience Theory emphasizes the importance of understanding the impact of shame on mental health. Shame, as defined by this theory, is the intense feeling of being flawed or unworthy. When individuals experience shame, it can have detrimental effects on their mental well-being.
Research has shown that shame can contribute to the development and exacerbation of various mental health conditions, including depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem. Shame can also lead to feelings of isolation and social withdrawal, as individuals may fear judgment and rejection from others.
Furthermore, the theory suggests that shame can create a vicious cycle in which individuals are more susceptible to experiencing shame in response to future stressful situations. This cycle can perpetuate negative thoughts and emotions, further impacting mental health.
Understanding the impact of shame on mental health is crucial for developing strategies to build resilience. By recognizing and addressing shame, individuals can work towards improving their mental well-being and reducing the negative effects of shame on their overall quality of life.

I am Patrina de Silva, a psychologist and mental health blogger in Sri Lanka. After obtaining psychology degrees from the University of Colombo and Monash University, I returned home to work as a counselor while also starting the popular blog “Pressy but Happy” to provide advice on psychological issues. Over the past decade, my empathetic articles have made my blog a leading mental health resource in the country. In addition to writing, I maintain a private therapy practice, frequently volunteer counseling time, and conduct seminars, driven by my passion for destigmatizing mental illness and educating the public on the mind-body connection. I strive to be an influential voice in my field through my compassionate approach.
