Stress has become an inevitable part of modern life, affecting individuals from all walks of life. Whether it’s due to work pressures, personal relationships, or financial difficulties, stress can have a profound impact on our overall well-being. However, recent studies have shown that there is a strong connection between heart rate variability (HRV) and stress resilience.
Heart rate variability refers to the variation in time intervals between consecutive heartbeats. A higher HRV indicates a healthier and more adaptable cardiovascular system. It is believed that individuals with higher HRV are better equipped to handle stressful situations and have higher levels of resilience.
Research has shown that chronic stress can have a negative impact on HRV, leading to decreased resilience and increased risk of various health problems. On the other hand, individuals with higher HRV tend to exhibit better emotional regulation, improved cognitive function, and a greater ability to bounce back from stressful events.
Understanding the connection between HRV and stress resilience opens up new possibilities for improving our ability to cope with stress. By monitoring and improving our HRV, we can potentially enhance our resilience and minimize the negative effects of stress on our health and well-being. This can be achieved through various methods such as mindfulness practices, exercise, and stress management techniques.
In conclusion, the relationship between heart rate variability and stress resilience is an area of growing interest in the field of psychology and medicine. By exploring this connection and implementing strategies to improve HRV, we can potentially enhance our ability to cope with stress and lead healthier, more resilient lives.
Understanding Heart Rate Variability
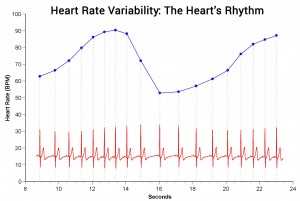
Heart rate variability (HRV) is a measure of the variation in time intervals between consecutive heartbeats. It is an important indicator of stress resilience and overall cardiovascular health. HRV reflects the ability of the heart to adapt to different situations and maintain a balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, which control the body’s stress response.
Stress can have a significant impact on heart rate variability. When we experience stress, our heart rate tends to increase, and the variation in time intervals between heartbeats decreases. This reduced variability is associated with a decreased ability to adapt to stress and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
On the other hand, individuals with high heart rate variability are generally more resilient to stress and have better overall cardiovascular health. They are able to quickly recover from stressful situations and maintain a balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
Measuring heart rate variability can provide valuable insights into an individual’s stress resilience and overall well-being. It can help identify potential risk factors for cardiovascular disease and guide interventions to improve stress management and resilience.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Heart rate variability (HRV) is a measure of the variation in time intervals between consecutive heartbeats. |
| HRV reflects the ability of the heart to adapt to different situations and maintain a balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. |
| Reduced HRV is associated with decreased stress resilience and increased risk of cardiovascular disease. |
| Individuals with high HRV are generally more resilient to stress and have better overall cardiovascular health. |
| Measuring HRV can provide valuable insights into an individual’s stress resilience and guide interventions to improve stress management and resilience. |
What is Heart Rate Variability?
Heart rate variability (HRV) refers to the variation in the time interval between consecutive heartbeats. It is a measure of the resilience of the heart and the autonomic nervous system to stress. HRV is influenced by various factors, including physical activity, emotions, and overall health.
Stress can have a significant impact on HRV. When the body experiences stress, the heart rate tends to become more regular and less variable. This decrease in HRV is often associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular disease and other health issues.
Monitoring heart rate variability can provide valuable insights into an individual’s stress levels and overall well-being. By tracking changes in HRV over time, individuals can identify patterns and triggers that may be contributing to their stress levels.
Improving heart rate variability can help individuals build resilience to stress. Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and physical exercise have been shown to increase HRV and promote relaxation. By incorporating these practices into their daily routine, individuals can enhance their ability to cope with stress and maintain optimal health.
Definition and Explanation
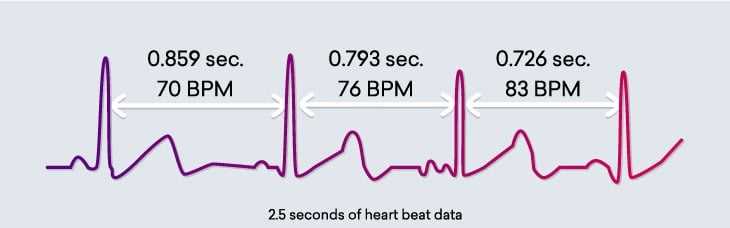
In the context of stress resilience, heart rate variability (HRV) refers to the variation in the time interval between consecutive heartbeats. It is a measure of the flexibility and adaptability of the heart’s response to different situations and stressors.
Resilience is the ability to bounce back and recover from stressful situations. It is an important trait that helps individuals cope with and manage stress effectively. HRV has been found to be closely related to resilience, as higher HRV is associated with better stress management and emotional regulation.
Stress is a natural response to challenging situations, and it can have both physical and psychological effects on the body. Chronic stress can lead to a variety of health problems, including cardiovascular disease, depression, and anxiety. Understanding and improving stress resilience is crucial for maintaining overall well-being.
HRV is influenced by various factors, including genetics, lifestyle choices, and environmental factors. It can be measured using specialized devices or through certain smartphone applications. By monitoring and analyzing HRV, individuals can gain insights into their stress levels and make lifestyle changes to improve their resilience.
In summary, HRV is a measure of the variation in the time interval between consecutive heartbeats and is closely related to stress resilience. Understanding and improving HRV can help individuals better cope with and manage stress, leading to improved overall well-being.
Factors Affecting Heart Rate Variability

Heart rate variability (HRV) is a measure of the variation in time intervals between consecutive heartbeats. It is widely regarded as an indicator of the resilience of the heart and the autonomic nervous system. Several factors can influence HRV, including:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Stress | High levels of stress can negatively impact HRV. Chronic stress can lead to a decrease in HRV, indicating reduced resilience and increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. |
| Physical Activity | Regular exercise has been shown to improve HRV. Aerobic exercise, in particular, can increase HRV, indicating better heart health and increased resilience. |
| Sleep Quality | Poor sleep quality or insufficient sleep can affect HRV. Lack of sleep can lead to decreased HRV, indicating reduced resilience and increased risk of cardiovascular problems. |
| Age | HRV tends to decrease with age. Older individuals generally have lower HRV, which may indicate reduced resilience and increased vulnerability to stress-related health issues. |
| Autonomic Nervous System Imbalance | An imbalance in the autonomic nervous system, particularly a dominance of the sympathetic nervous system over the parasympathetic nervous system, can result in decreased HRV and reduced resilience. |
| Smoking | Smoking has been found to decrease HRV. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can negatively affect the autonomic nervous system, leading to reduced HRV and increased risk of cardiovascular diseases. |
Understanding the factors that affect HRV is crucial for improving stress resilience and overall heart health. By managing stress, engaging in regular physical activity, prioritizing sleep, and adopting a healthy lifestyle, individuals can enhance their HRV and promote better heart resilience.
Measuring Heart Rate Variability
Heart rate variability (HRV) is a measure of the variation in time between each heartbeat. It is a useful tool for assessing stress resilience, as it provides insights into the functioning of the autonomic nervous system, which regulates the body’s stress response.
HRV is typically measured using electrocardiography (ECG) or photoplethysmography (PPG). ECG involves placing electrodes on the chest to detect the electrical activity of the heart, while PPG uses a light-based sensor to measure changes in blood volume in the fingertip or earlobe.
Once the heart rate data is collected, it is analyzed to calculate various HRV parameters. These parameters include time domain measures, such as the standard deviation of normal-to-normal intervals (SDNN) and the root mean square of successive differences (RMSSD), as well as frequency domain measures, such as high frequency (HF) and low frequency (LF) power.
SDNN is a measure of overall HRV and reflects the balance between sympathetic and parasympathetic activity. Higher SDNN values indicate better stress resilience, as they suggest a more flexible autonomic nervous system that can adapt to changing demands.
RMSSD, on the other hand, is a measure of short-term HRV and reflects parasympathetic activity. Higher RMSSD values indicate a more relaxed state and better stress resilience.
HF power represents the high frequency component of HRV, which is associated with parasympathetic activity. LF power represents the low frequency component, which is influenced by both sympathetic and parasympathetic activity. The ratio of LF to HF power can provide insights into the balance between sympathetic and parasympathetic activity.
In summary, measuring heart rate variability is an important tool for assessing stress resilience. By analyzing HRV parameters, we can gain insights into the functioning of the autonomic nervous system and the body’s response to stress. This information can help individuals and healthcare professionals develop strategies to improve stress resilience and overall well-being.
Methods and Techniques
In this study, various methods and techniques were employed to explore the connection between heart rate variability (HRV) and stress resilience. The following approaches were used:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Collection | Participants’ heart rate variability data was collected using wearable devices that measured their heart rate and calculated the time intervals between consecutive heartbeats. |
| Stress Assessment | Participants’ stress levels were assessed using self-report questionnaires and physiological measures such as skin conductance and cortisol levels. |
| Data Analysis | The collected HRV data was analyzed using statistical techniques to identify patterns and correlations between HRV and stress resilience. |
| Machine Learning | Machine learning algorithms were employed to develop predictive models that could accurately classify individuals’ stress resilience based on their HRV patterns. |
| Intervention Techniques | Various intervention techniques, such as mindfulness meditation and breathing exercises, were used to train participants in stress management and improve their HRV. |
By utilizing these methods and techniques, the researchers were able to gain valuable insights into the relationship between HRV and stress resilience. The findings of this study contribute to a better understanding of how HRV can be used as a measure of stress and provide potential strategies for improving stress resilience.
Interpreting Heart Rate Variability Data

Heart rate variability (HRV) is a measure of the variability in the time interval between heartbeats. It is often used as an indicator of stress levels and overall health. HRV is influenced by a variety of factors, including stress, physical activity, and emotional state.
When interpreting HRV data, it is important to look at both the variability and the average heart rate. A higher HRV indicates a more resilient and adaptable cardiovascular system, while a lower HRV may suggest increased stress and a less flexible system.
One way to interpret HRV data is to look at the frequency domain analysis. This analysis breaks down the HRV data into different frequency bands, such as high frequency (HF) and low frequency (LF). The HF band is associated with parasympathetic activity, while the LF band is associated with sympathetic activity.
A higher HF power indicates a dominant parasympathetic influence, which is often associated with a relaxed and calm state. On the other hand, a higher LF power may suggest increased sympathetic activity, which is often associated with stress and arousal.
Another way to interpret HRV data is to look at the time domain analysis. This analysis looks at the overall variability in the heart rate over a given time period. A higher standard deviation of the RR intervals indicates a higher HRV and a more flexible cardiovascular system.
In addition to looking at the variability and average heart rate, it is also important to consider the context in which the HRV data was collected. Factors such as the individual’s age, gender, and physical fitness level can all influence HRV. It is also important to consider any medications or medical conditions that may affect HRV.
Overall, interpreting HRV data can provide valuable insights into an individual’s stress levels and overall health. By understanding the different factors that influence HRV, individuals can take steps to improve their stress resilience and promote a healthier cardiovascular system.
Stress Resilience and Heart Rate Variability
Stress is a common experience that affects individuals in various aspects of their lives. It can have negative effects on mental and physical health, leading to decreased well-being and increased risk of diseases. One way to measure and understand the impact of stress on the body is through heart rate variability (HRV).
Heart rate variability refers to the variation in the time interval between consecutive heartbeats. It is influenced by the autonomic nervous system, which regulates the body’s response to stress. When an individual is under stress, the sympathetic nervous system is activated, leading to an increase in heart rate and a decrease in HRV. On the other hand, when an individual is in a relaxed state, the parasympathetic nervous system is dominant, resulting in a decrease in heart rate and an increase in HRV.
Research has shown that individuals with higher HRV have greater resilience to stress. They are better able to regulate their emotions and recover from stressful situations. On the other hand, individuals with lower HRV are more vulnerable to the negative effects of stress and are at a higher risk of developing stress-related disorders.
Improving stress resilience can be achieved through various techniques, such as mindfulness meditation, exercise, and biofeedback training. These techniques have been shown to increase HRV and promote a state of relaxation, allowing individuals to better cope with stress. By improving HRV, individuals can enhance their stress resilience and protect their mental and physical well-being.
In conclusion, there is a strong connection between stress resilience and heart rate variability. By understanding and improving HRV, individuals can better manage stress and promote their overall well-being. It is important to prioritize stress management techniques that enhance HRV to build resilience and protect against the negative effects of stress.

I am Patrina de Silva, a psychologist and mental health blogger in Sri Lanka. After obtaining psychology degrees from the University of Colombo and Monash University, I returned home to work as a counselor while also starting the popular blog “Pressy but Happy” to provide advice on psychological issues. Over the past decade, my empathetic articles have made my blog a leading mental health resource in the country. In addition to writing, I maintain a private therapy practice, frequently volunteer counseling time, and conduct seminars, driven by my passion for destigmatizing mental illness and educating the public on the mind-body connection. I strive to be an influential voice in my field through my compassionate approach.
