
Stress is a common experience for individuals who identify as gender minorities. The Gender Minority Stress and Resilience Scale is a valuable tool for understanding the unique challenges faced by this population and assessing their resilience in the face of adversity.
This scale is designed to measure the stressors that gender minorities encounter on a daily basis, including discrimination, harassment, and stigma. By quantifying these stressors, researchers and mental health professionals can gain a deeper understanding of the impact they have on the well-being of gender minorities.
Resilience, on the other hand, refers to an individual’s ability to bounce back from adversity and maintain a positive sense of self. The Gender Minority Stress and Resilience Scale also assesses the resilience of gender minorities, highlighting their strengths and coping mechanisms.
By better understanding the stressors faced by gender minorities and their resilience in the face of these challenges, we can develop targeted interventions and support systems to promote their mental health and well-being. The Gender Minority Stress and Resilience Scale is a valuable tool in this process, providing a comprehensive assessment of the unique experiences and strengths of gender minorities.
What is Gender Minority Stress?
Gender minority stress refers to the unique stressors and challenges faced by individuals who identify as a gender minority. It encompasses the psychological, social, and environmental stressors that result from being part of a marginalized gender group.
The Gender Minority Stress and Resilience Scale is a tool used to measure the impact of these stressors on individuals’ well-being and mental health. It helps researchers and professionals better understand the specific experiences and needs of gender minorities.
Stressors related to gender minority status can include discrimination, prejudice, and stigma, as well as internalized negative beliefs and expectations. These stressors can lead to a range of negative outcomes, such as increased rates of mental health issues, substance abuse, and suicidality.
It is important to recognize and address gender minority stress in order to promote resilience and well-being among gender minority individuals. By understanding the unique challenges they face, we can work towards creating more inclusive and supportive environments that foster their strength and resilience.
Importance of Resilience in Gender Minority Individuals

Resilience plays a crucial role in the lives of gender minority individuals, who often face unique stressors and challenges due to their minority status. The Gender Minority Stress and Resilience Scale is a valuable tool for understanding and assessing the impact of stress on this population and identifying sources of resilience.
Gender minority individuals, including transgender, non-binary, and gender nonconforming individuals, often experience higher levels of stress compared to cisgender individuals. This stress can stem from various sources, such as discrimination, prejudice, and social rejection. These individuals may face challenges in their personal relationships, education, employment, and healthcare, which can further contribute to their stress levels.
The Gender Minority Stress and Resilience Scale provides a comprehensive framework for measuring the stress experienced by gender minority individuals. It assesses various dimensions of stress, including minority stressors, internalized transphobia, and experiences of discrimination. By quantifying these stressors, the scale helps researchers and healthcare professionals gain a better understanding of the unique challenges faced by this population.
Resilience, on the other hand, refers to an individual’s ability to adapt and bounce back from adversity. It is an essential factor for gender minority individuals in coping with stress and maintaining their mental health. Resilience enables individuals to develop effective coping strategies, seek support, and maintain a positive outlook despite the challenges they face.
Understanding the importance of resilience in gender minority individuals is crucial for developing interventions and support systems that promote their well-being. By identifying the factors that contribute to resilience, healthcare professionals can tailor their approaches to better support this population. The Gender Minority Stress and Resilience Scale serves as a valuable tool for assessing and enhancing resilience in gender minority individuals, ultimately improving their overall mental health and quality of life.
| Stressors | Internalized Transphobia | Experiences of Discrimination |
|---|---|---|
| Discrimination | Self-blame | Verbal abuse |
| Prejudice | Shame | Physical assault |
| Social rejection | Isolation | Harassment |
Understanding the Impact of Gender Minority Stress
Gender minority individuals often face unique challenges and stressors that can have a significant impact on their well-being and mental health. This stress, known as gender minority stress, refers to the adverse experiences and discrimination that individuals who identify as a gender minority face due to their gender identity or expression.
Resilience, or the ability to bounce back from adversity, plays a crucial role in how gender minority individuals cope with and navigate the stress they face. Understanding the impact of gender minority stress is essential in developing strategies and interventions to support the resilience and well-being of these individuals.
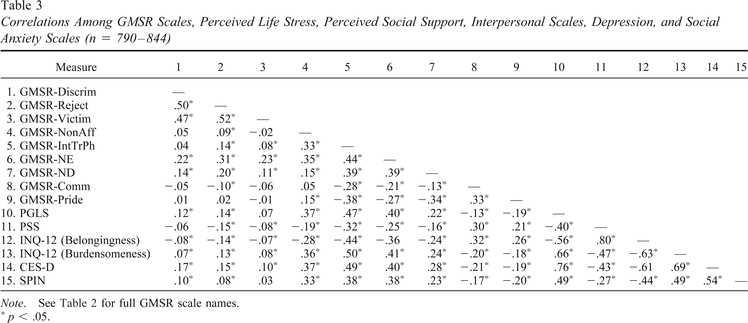
Gender minority stress encompasses a range of experiences, including external stressors such as discrimination, harassment, and violence, as well as internal stressors such as internalized transphobia or self-stigma. These stressors can have profound effects on mental health, contributing to higher rates of anxiety, depression, and suicidal ideation among gender minority individuals.
Research has shown that gender minority individuals often experience higher levels of stress and discrimination compared to cisgender individuals. This stress can manifest in various domains of life, including healthcare, employment, education, and interpersonal relationships. The cumulative effect of these stressors can lead to chronic stress and a decreased sense of well-being.
Understanding the impact of gender minority stress is not only important for identifying the challenges these individuals face but also for developing strategies to promote resilience and support their mental health. Building resilience can involve developing coping strategies, fostering social support networks, and advocating for inclusive policies and practices.
| External Stressors | Internal Stressors |
|---|---|
| – Discrimination | – Internalized transphobia |
| – Harassment | – Self-stigma |
| – Violence |
Addressing gender minority stress requires a comprehensive approach that includes both individual and systemic interventions. By understanding the impact of gender minority stress and promoting resilience, we can create a more inclusive and supportive society for gender minority individuals.
Mental Health Consequences of Gender Minority Stress
Gender minority individuals often face unique challenges and stressors due to their minority status. These stressors can have significant impacts on their mental health and well-being. Research has shown that gender minority individuals are at a higher risk for developing mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, and substance abuse.
The experience of gender minority stress, which includes discrimination, prejudice, and social rejection, can lead to feelings of isolation, low self-esteem, and internalized transphobia. These negative experiences can contribute to the development of mental health issues and can make it difficult for gender minority individuals to cope with everyday stressors.
However, it is important to note that not all gender minority individuals experience negative mental health outcomes. Resilience plays a significant role in determining how individuals are able to navigate and cope with gender minority stress. Resilience refers to the ability to bounce back from adversity and maintain mental well-being.
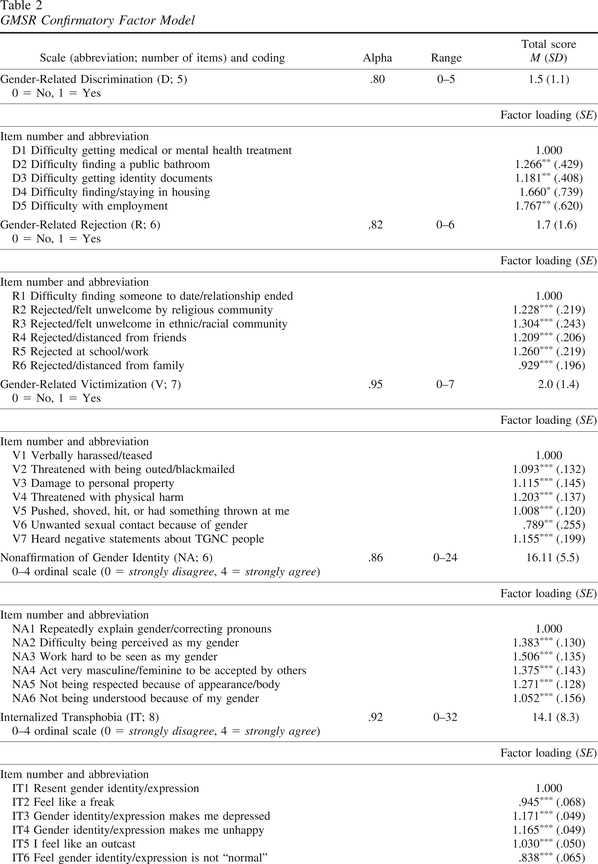
The Gender Minority Stress and Resilience Scale is a tool that can help researchers and clinicians better understand the impact of gender minority stress on mental health outcomes. This scale measures various dimensions of gender minority stress, including experiences of discrimination, internalized transphobia, and social support. By assessing these factors, the scale can provide valuable insights into the specific stressors that contribute to mental health issues in gender minority individuals.
Understanding the mental health consequences of gender minority stress is crucial for developing effective interventions and support systems for this population. By recognizing the unique challenges faced by gender minority individuals and promoting resilience, we can work towards creating a more inclusive and supportive society for all.
Social and Emotional Impact of Gender Minority Stress
Gender minority individuals face unique challenges and stressors that can have a profound impact on their social and emotional well-being. The Gender Minority Stress and Resilience Scale (GMRS) is a tool that helps to assess the specific stressors experienced by gender minority individuals and their ability to cope with these stressors.
Gender minority stress refers to the chronic stress and discrimination that individuals who identify outside of traditional gender norms may experience. This stress can come from various sources, including societal prejudice, stigma, and lack of acceptance. It can manifest in different ways, such as microaggressions, verbal and physical abuse, and exclusion from social networks.
The social impact of gender minority stress is significant. It can lead to feelings of isolation and loneliness, as individuals may struggle to find acceptance and support from their families, friends, and communities. This social rejection can have a detrimental effect on mental health and overall well-being.
Emotionally, gender minority stress can result in heightened anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem. The constant pressure to conform to societal expectations and the fear of judgment can take a toll on one’s emotional resilience. Additionally, the internalized stigma and negative beliefs about oneself can further contribute to emotional distress.
The Gender Minority Stress and Resilience Scale is designed to measure the impact of these stressors and assess an individual’s ability to cope with them. It takes into account various domains, including social support, personal resilience, and self-acceptance. By understanding the specific stressors faced by gender minority individuals and their resilience levels, interventions and support systems can be developed to promote their well-being.
In conclusion, gender minority stress has a significant social and emotional impact on individuals. The Gender Minority Stress and Resilience Scale provides a valuable tool for assessing and understanding these stressors and can guide the development of targeted interventions to support the well-being of gender minority individuals.
Physical Health Effects of Gender Minority Stress

Gender minority stress refers to the unique stressors and discrimination faced by individuals whose gender identity does not align with societal norms. This stress can have significant negative effects on physical health.
Resilience, or the ability to cope with and bounce back from adversity, plays a crucial role in mitigating the physical health effects of gender minority stress. Research has shown that individuals with higher levels of resilience are better equipped to handle the stressors associated with being a gender minority.
The Gender Minority Stress and Resilience Scale is a tool that measures the impact of gender minority stress and assesses an individual’s level of resilience. By understanding the specific stressors and their impact on physical health, interventions and support systems can be developed to improve the well-being of gender minority individuals.
Physical health effects of gender minority stress can manifest in various ways. Chronic stress can lead to increased blood pressure, heart disease, and other cardiovascular problems. It can also weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to illnesses and infections.
Additionally, gender minority stress can contribute to mental health issues such as depression, anxiety, and substance abuse, which can further impact physical health. The chronic activation of the body’s stress response can lead to inflammation, which has been linked to a range of physical health problems, including chronic pain and autoimmune disorders.
Addressing the physical health effects of gender minority stress requires a multi-faceted approach. It involves not only addressing the external stressors and discrimination faced by gender minority individuals but also providing support and resources to build resilience. This can include access to affirming healthcare, mental health services, support groups, and community resources.
By recognizing and addressing the physical health effects of gender minority stress, we can work towards creating a more inclusive and supportive society for all individuals, regardless of their gender identity.
Building Strength and Resilience

Building strength and resilience is crucial for individuals who identify as a gender minority, as they often face unique challenges and stressors related to their gender identity. The Gender Minority Stress and Resilience Scale is a valuable tool that can help individuals understand and measure the impact of these stressors on their mental health and well-being.
One way to build strength and resilience is by fostering a supportive and inclusive community. Connecting with others who share similar experiences can provide a sense of belonging and validation, which can help alleviate the stress and isolation that gender minority individuals may feel. This can be achieved through support groups, online communities, or LGBTQ+ organizations.
Developing coping strategies and self-care practices is another important aspect of building resilience. This can involve engaging in activities that promote self-care, such as mindfulness exercises, journaling, or engaging in hobbies and interests. It’s also important to prioritize self-care and set boundaries to avoid burnout.
Seeking professional support and therapy can also be beneficial in building strength and resilience. Mental health professionals who specialize in working with gender minority individuals can provide the necessary support and guidance in navigating the unique challenges and stressors that they may face.
Education and awareness are key in building strength and resilience. Learning about the experiences and challenges faced by gender minority individuals can help promote empathy and understanding, both within the gender minority community and in society at large. This can be achieved through workshops, training, and educational resources.
Ultimately, building strength and resilience is an ongoing process that requires self-reflection, self-compassion, and a commitment to personal growth. By acknowledging and addressing the stressors faced by gender minority individuals, and by actively working towards building strength and resilience, individuals can cultivate a sense of empowerment and well-being.
Supportive Communities and Networks

Being a gender minority can be a challenging experience, often leading to increased stress levels and decreased resilience. However, one key factor that can significantly impact the well-being of gender minorities is the presence of supportive communities and networks.
Supportive communities and networks provide a sense of belonging, acceptance, and understanding, which can help mitigate the stressors and challenges that gender minorities face on a daily basis. These communities can consist of friends, family, peers, or even online support groups.
Having access to a supportive community allows gender minorities to share their experiences, seek advice, and find comfort in knowing that they are not alone in their struggles. This sense of connection can be a powerful source of resilience, helping individuals navigate through difficult times and build the strength to overcome adversity.
Furthermore, supportive communities and networks can also provide gender minorities with opportunities for empowerment and advocacy. By coming together, individuals can collectively work towards creating change and challenging societal norms and stereotypes that perpetuate gender-based stress and discrimination.
It is important to recognize the value of supportive communities and networks in promoting the well-being of gender minorities. By fostering these connections and creating safe spaces, we can help individuals build resilience and navigate the stressors that come with being a gender minority.
Therapeutic Interventions for Gender Minority Individuals

Gender minority individuals often face unique challenges and stressors related to their gender identity. The Gender Minority Stress and Resilience Scale (GMSRS) has been developed to measure the impact of these stressors and assess individual resilience. However, it is also important to explore therapeutic interventions that can help gender minority individuals cope with and overcome these challenges.
Therapeutic interventions for gender minority individuals should aim to address both the external stressors they face, such as discrimination and stigma, as well as the internal stressors related to their gender identity. These interventions can include individual therapy, support groups, and educational programs.
Individual therapy can provide a safe and supportive space for gender minority individuals to explore their feelings, experiences, and identity. Therapists can help individuals develop coping strategies, build resilience, and navigate the challenges they face. Additionally, therapists can address any mental health concerns that may arise as a result of gender minority stress.
Support groups can be particularly beneficial for gender minority individuals as they provide a sense of community and connection. These groups offer a space for individuals to share their experiences, receive support, and learn from others who may have faced similar challenges. Support groups can also provide a platform for advocacy and empowerment.
Educational programs can play a crucial role in reducing discrimination and promoting understanding of gender minority issues. These programs can be targeted towards healthcare professionals, educators, employers, and the general public. By increasing knowledge and awareness, educational programs can help create more inclusive and supportive environments for gender minority individuals.
In conclusion, therapeutic interventions for gender minority individuals are essential for addressing the stressors they face and building resilience. Individual therapy, support groups, and educational programs can all contribute to the well-being and empowerment of gender minority individuals. By providing these interventions, we can work towards reducing the impact of gender minority stress and creating a more inclusive society.
Self-Care Strategies to Enhance Resilience

Resilience is a crucial factor in the well-being and mental health of gender minority individuals. It refers to the ability to bounce back from adversity and cope with stressors effectively. Building resilience can help individuals navigate the challenges they face and maintain their mental and emotional well-being.
Here are some self-care strategies that can enhance resilience:
- Practice self-compassion: Being kind to oneself and acknowledging one’s own worth and value is essential for resilience. Engage in self-care activities that promote self-compassion, such as journaling, practicing mindfulness, or engaging in hobbies.
- Seek support: Building a strong support network is crucial for resilience. Connect with friends, family, or support groups who can provide understanding and empathy. Consider seeking therapy or counseling to talk about your experiences and challenges.
- Engage in self-reflection: Take time to reflect on your experiences, thoughts, and emotions. Self-reflection can help you gain insight into your strengths and weaknesses and identify areas for personal growth.
- Set boundaries: Establishing clear boundaries is important for self-care and resilience. Learn to say no when needed and prioritize your own well-being. Setting boundaries can help protect your energy and prevent burnout.
- Practice self-care activities: Engage in activities that promote self-care and well-being. This can include exercise, meditation, practicing a hobby, or spending time in nature. Find what activities bring you joy and make time for them regularly.
- Develop coping strategies: Identify healthy coping strategies that work for you. This can include deep breathing exercises, positive self-talk, or engaging in creative outlets. Having effective coping strategies can help you navigate stressors and challenges more effectively.
- Celebrate small victories: Acknowledge and celebrate your achievements, no matter how small. Recognizing your progress and successes can boost your self-confidence and resilience.
- Practice gratitude: Cultivate a sense of gratitude by focusing on the positive aspects of your life. Take time each day to reflect on what you are grateful for. Gratitude can help shift your mindset and enhance resilience.
By incorporating these self-care strategies into your life, you can enhance your resilience and better navigate the challenges and stressors that come with being a gender minority individual.

I am Patrina de Silva, a psychologist and mental health blogger in Sri Lanka. After obtaining psychology degrees from the University of Colombo and Monash University, I returned home to work as a counselor while also starting the popular blog “Pressy but Happy” to provide advice on psychological issues. Over the past decade, my empathetic articles have made my blog a leading mental health resource in the country. In addition to writing, I maintain a private therapy practice, frequently volunteer counseling time, and conduct seminars, driven by my passion for destigmatizing mental illness and educating the public on the mind-body connection. I strive to be an influential voice in my field through my compassionate approach.
