
In today’s fast-paced and constantly changing world, it is essential to prioritize mental health and well-being. The brain, as the control center of our thoughts, emotions, and behaviors, plays a crucial role in maintaining our overall mental strength and flexibility. Fortunately, the concept of neuroplasticity has revealed that the brain has a remarkable ability to adapt and change throughout our lives.
Neuroplasticity, also known as brain plasticity, refers to the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections. This process allows the brain to compensate for injury or disease and adapt to new situations and experiences. By harnessing the power of neuroplasticity, we can actively build resilience and strengthen our mental health.
One of the key strategies for building brain resilience is through cognitive exercises and training. Engaging in activities that challenge our cognitive abilities, such as puzzles, memory games, and learning new skills, can help stimulate neuroplasticity. These activities force the brain to create new connections and pathways, enhancing its adaptability and overall functioning.
Additionally, practicing mindfulness and stress management techniques can also contribute to brain resilience. Mindfulness, which involves paying attention to the present moment without judgment, has been shown to promote neuroplasticity and improve mental well-being. By reducing stress and increasing self-awareness, mindfulness can help build a strong foundation for brain resilience.
Understanding Brain Resilience

The brain is an incredible organ with remarkable plasticity and strength. It has the ability to adapt and change in response to various challenges and experiences. This concept, known as neuroplasticity, is the foundation of brain resilience.
Brain resilience refers to the brain’s ability to bounce back from adversity and maintain optimal mental health. It involves the brain’s flexibility and capacity to recover and adapt to new situations, stressors, and traumas.
When faced with challenges, the brain undergoes a series of cognitive processes to promote resilience. These processes involve the activation of neural pathways, the release of neurotransmitters, and the restructuring of neuronal connections.
One key aspect of brain resilience is cognitive flexibility, which refers to the brain’s ability to adapt and switch between different cognitive strategies. This flexibility allows the brain to adjust its thinking patterns and behaviors in response to changing circumstances.
Another crucial factor in brain resilience is the ability to regulate emotions and manage stress. The brain’s capacity to process and regulate emotions plays a significant role in maintaining mental well-being and building resilience.
Understanding brain resilience is essential for strengthening mental health. By recognizing the brain’s capacity for adaptation and change, individuals can develop strategies to enhance their resilience and promote overall well-being.
Building brain resilience involves various practices such as mindfulness, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and stress management techniques. These practices can help individuals develop skills to cope with adversity, regulate emotions, and foster a positive mindset.
In conclusion, brain resilience is a fundamental aspect of mental health. It involves the brain’s plasticity, strength, and ability to adapt and recover from challenges. By understanding and nurturing brain resilience, individuals can cultivate their mental well-being and thrive in the face of adversity.
What is Brain Resilience?

Brain resilience refers to the ability of the brain to adapt and recover from challenges and setbacks. It is the cognitive strength that allows the brain to bounce back and maintain mental well-being in the face of adversity. Resilience is closely connected to the brain’s flexibility and plasticity, which are the brain’s ability to change and reorganize itself in response to new experiences and learning.
When the brain is resilient, it can effectively cope with stress, trauma, and other negative life events. It can quickly recover from setbacks and continue functioning at an optimal level. Resilience is not a fixed trait but can be developed and strengthened through various strategies and practices.
Building brain resilience involves cultivating positive mental habits, such as practicing mindfulness and gratitude. It also includes engaging in activities that promote cognitive health, such as regular exercise, healthy eating, and getting enough sleep. Additionally, having a strong support system and seeking help when needed are essential for enhancing brain resilience.
Brain resilience is crucial for maintaining good mental health and overall well-being. It enables individuals to adapt to changes, overcome challenges, and thrive in the face of adversity. By strengthening brain resilience, individuals can enhance their ability to handle stress, regulate emotions, and maintain a positive outlook on life.
Definition of Brain Resilience

Brain resilience refers to the ability of the brain to adapt and recover from difficult or challenging situations. It is a measure of the brain’s strength and flexibility in the face of adversity.
The brain is a highly complex organ that is constantly changing and adapting. This ability to change is known as neuroplasticity, and it plays a crucial role in brain resilience.
Neuroplasticity refers to the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections and pathways. This allows the brain to compensate for damage or changes in its structure, and enables it to continue functioning optimally.
Resilience is not just about bouncing back from difficult situations, but also about strengthening the brain’s ability to handle future challenges. Building brain resilience involves engaging in activities and practices that promote mental well-being and enhance the brain’s adaptive capabilities.
By actively working on building brain resilience, individuals can improve their mental health and enhance their overall well-being. This includes practicing stress management techniques, engaging in regular physical exercise, maintaining a healthy diet, getting enough sleep, and seeking support when needed.
In summary, brain resilience is the ability of the brain to adapt, recover, and maintain optimal functioning in the face of adversity. It is a result of the brain’s plasticity and its ability to form new connections and pathways. Building brain resilience involves taking proactive steps to enhance mental well-being and strengthen adaptive capabilities.
Importance of Brain Resilience
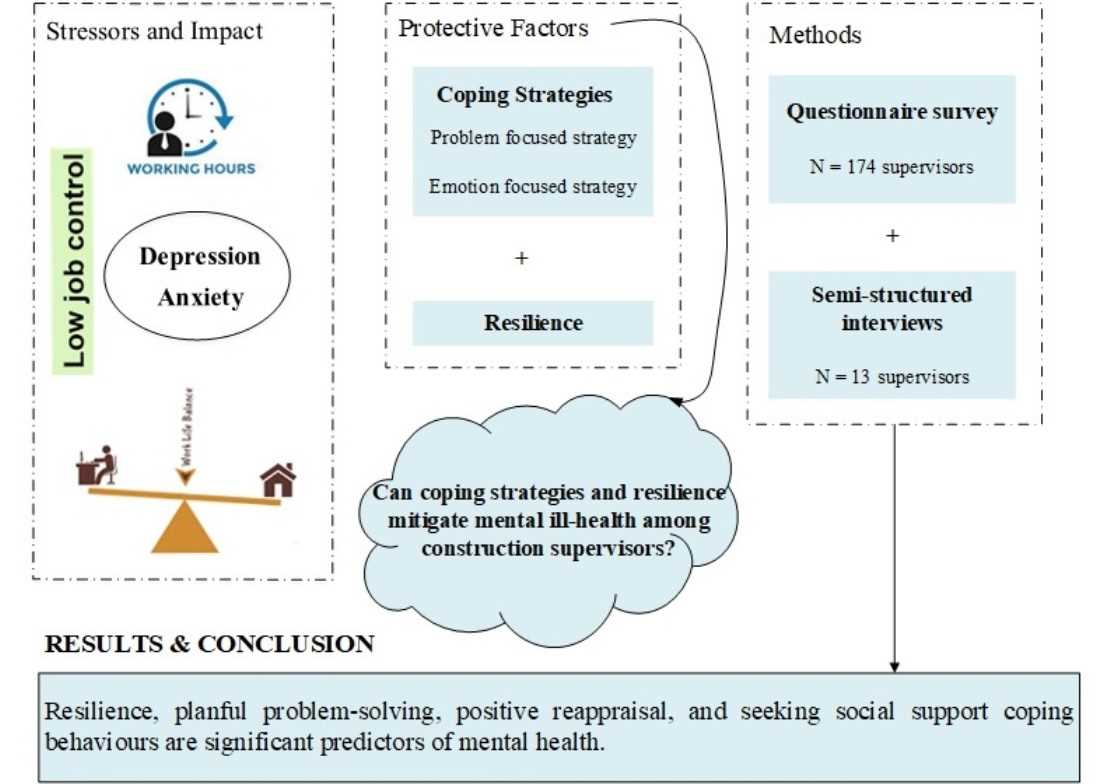
Brain resilience plays a crucial role in maintaining and strengthening mental health. The brain’s ability to adapt and change, known as neuroplasticity, is a key factor in building resilience. Neuroplasticity refers to the brain’s ability to reorganize itself, forming new neural connections and pathways.
Resilience is the strength and flexibility of the brain to bounce back from adversity, stress, and trauma. It allows individuals to cope with challenges, maintain emotional well-being, and recover from mental health issues. Building brain resilience helps individuals develop effective coping mechanisms, regulate emotions, and adapt to life’s challenges.
The plasticity of the brain enables it to adapt to new experiences, learn new skills, and recover from injuries or trauma. By promoting neuroplasticity, individuals can enhance their brain’s ability to rewire and reorganize itself, leading to improved cognitive function and mental well-being.
Resilience is especially important in today’s fast-paced and constantly changing world, where individuals face various stressors and challenges. By building brain resilience, individuals can better navigate these challenges and maintain their mental health.
Overall, the importance of brain resilience lies in its ability to promote mental well-being, enhance cognitive function, and facilitate adaptation to life’s challenges. By understanding and actively working on building brain resilience, individuals can strengthen their mental health and improve their overall quality of life.
Factors Affecting Brain Resilience

Brain resilience refers to the brain’s ability to adapt and recover from challenges and stressors. It is influenced by various factors, including:
| Neuroplasticity | The brain’s ability to change and reorganize itself, known as neuroplasticity, plays a crucial role in building resilience. Neuroplasticity allows the brain to form new neural connections, strengthen existing ones, and adapt to new situations. |
| Cognitive Strength | Mental resilience is closely linked to cognitive strength. Having strong cognitive abilities, such as problem-solving, decision-making, and critical thinking skills, can help individuals navigate challenges and bounce back from setbacks. |
| Adaptation | The ability to adapt to change is another essential factor in building brain resilience. Being able to adjust one’s thoughts, behaviors, and emotions in response to new situations or stressors can contribute to overall mental well-being. |
In conclusion, brain resilience is influenced by neuroplasticity, cognitive strength, and adaptation. By understanding and harnessing these factors, individuals can strengthen their mental health and better navigate the challenges of life.
Genetic Factors

Genetic factors play a crucial role in the development and functioning of the brain. They contribute to the neuroplasticity and resilience of the brain, which is the brain’s ability to adapt and change in response to experiences and challenges.
Studies have shown that certain genes are associated with cognitive and mental health outcomes. These genes influence various aspects of brain function, including synaptic plasticity, neurotransmitter regulation, and neurodevelopment.
One important genetic factor that affects brain resilience is the BDNF gene (brain-derived neurotrophic factor). BDNF plays a key role in promoting the growth and survival of neurons, as well as in modulating synaptic plasticity. Variations in the BDNF gene have been linked to differences in cognitive abilities, mood disorders, and response to stress.
Another genetic factor that contributes to brain resilience is the COMT gene (catechol-O-methyltransferase). COMT is involved in the regulation of dopamine, a neurotransmitter that is important for cognitive function and emotional regulation. Variations in the COMT gene have been associated with differences in cognitive flexibility and emotional processing.
Understanding the genetic factors that influence brain resilience can help in developing strategies to enhance mental health and well-being. By identifying individuals who may be more susceptible to certain mental health conditions, interventions and treatments can be tailored to their specific genetic profiles. Additionally, research into the genetic basis of brain resilience can lead to the development of new therapies and interventions that target specific genetic pathways and promote adaptive brain plasticity.
In conclusion, genetic factors play a significant role in brain resilience. They contribute to the cognitive and mental health outcomes by influencing various aspects of brain function such as synaptic plasticity, neurotransmitter regulation, and neurodevelopment. Understanding these genetic factors can help in developing personalized interventions and treatments for individuals to enhance their mental health and well-being.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors play a crucial role in building brain resilience and strengthening mental health. The brain’s neuroplasticity and cognitive flexibility allow it to adapt and respond to various environmental stimuli.
Resilience is the brain’s ability to bounce back from adversity and maintain mental well-being. Environmental factors can either enhance or hinder this resilience. Positive environments that foster growth, connection, and support can strengthen the brain’s plasticity and cognitive strength.
Exposure to diverse experiences and challenges can promote the development of new neural connections and enhance the brain’s adaptability. This can lead to increased resilience and the ability to cope with stress and adversity.
On the other hand, negative environments characterized by chronic stress, trauma, and lack of support can impair brain plasticity and hinder the development of resilience. Adverse childhood experiences, for example, can have long-lasting effects on mental health and well-being.
Creating a nurturing and supportive environment is essential for building brain resilience. This can include providing access to quality education, stable relationships, and a safe and stimulating living environment. Additionally, fostering a sense of belonging, promoting healthy social connections, and encouraging physical activity can all contribute to strengthening mental health.
Overall, environmental factors play a significant role in shaping brain resilience and mental well-being. By creating positive and supportive environments, individuals can enhance their neuroplasticity, cognitive flexibility, and adaptive abilities, ultimately strengthening their mental health and resilience.
Lifestyle Factors

When it comes to building brain resilience and strengthening mental health, lifestyle factors play a crucial role. The brain has an incredible ability to adapt and change, known as neuroplasticity. This means that our brain is not fixed or static, but rather it has the capacity to change and reorganize itself throughout our lives.
One of the key lifestyle factors that can enhance brain resilience is cognitive stimulation. Engaging in activities that challenge and stimulate our cognitive abilities can help to improve brain function and enhance neuroplasticity. This can include activities such as reading, puzzles, learning a new skill, or participating in mentally stimulating hobbies.
Another important lifestyle factor is physical exercise. Regular exercise has been shown to have numerous benefits for brain health and resilience. It can help to improve blood flow to the brain, increase the production of growth factors that promote brain cell growth and survival, and enhance cognitive function.
Additionally, maintaining a healthy diet is essential for brain resilience. Consuming a balanced diet that is rich in nutrients, antioxidants, and omega-3 fatty acids can provide the necessary fuel and building blocks for optimal brain function and neuroplasticity.
Lastly, managing stress and practicing relaxation techniques can also contribute to brain resilience. Chronic stress can have detrimental effects on the brain, impairing cognitive function and increasing the risk of mental health disorders. By engaging in stress-reducing activities such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or practicing mindfulness, individuals can strengthen their mental resilience and enhance their overall well-being.
In conclusion, lifestyle factors such as cognitive stimulation, physical exercise, a healthy diet, and stress management all play a crucial role in building brain resilience and strengthening mental health. By incorporating these strategies into our daily lives, we can harness the power of neuroplasticity and enhance our cognitive strength and resilience.
Strategies for Building Brain Resilience
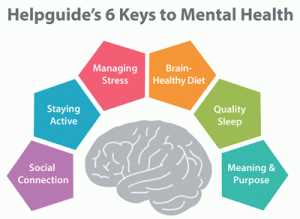
Mental health is closely linked to the strength and adaptability of the brain. The concept of brain plasticity, also known as neuroplasticity, refers to the brain’s ability to change and reorganize itself throughout life. This flexibility allows the brain to adapt to new experiences, learn new skills, and recover from trauma or injury.
Building brain resilience involves implementing strategies that promote cognitive health and enhance neuroplasticity. Here are some effective strategies:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Exercise | Regular physical exercise improves blood flow to the brain, stimulates the release of growth factors, and enhances neuroplasticity. |
| Healthy Diet | A nutrient-rich diet, including omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins, provides the necessary building blocks for brain health and promotes cognitive function. |
| Quality Sleep | Adequate sleep is crucial for brain health and resilience. It allows the brain to consolidate memories, repair and regenerate cells, and regulate emotions. |
| Mental Stimulation | Engaging in activities that challenge the brain, such as puzzles, reading, learning a new skill, or playing a musical instrument, promotes neuroplasticity and cognitive function. |
| Stress Management | Chronic stress can negatively impact brain health and resilience. Implementing stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, meditation, or deep breathing exercises, can help reduce stress and improve brain function. |
| Social Connections | Maintaining strong social connections and engaging in meaningful relationships has been linked to improved brain health and resilience. Social interaction stimulates the brain and promotes emotional well-being. |
By incorporating these strategies into your daily routine, you can strengthen your brain’s resilience, enhance neuroplasticity, and promote mental well-being.
Physical Exercise

Physical exercise plays a crucial role in building brain resilience and strengthening mental health. The brain is a highly adaptable organ with the ability to change and reorganize itself, known as neuroplasticity. Regular physical exercise promotes neuroplasticity by increasing brain plasticity and flexibility.
Engaging in physical exercise has been shown to have numerous mental health benefits. It helps reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety, improves mood, and enhances cognitive function. Physical exercise also increases the production of endorphins, which are natural chemicals in the brain that promote feelings of happiness and well-being.
Furthermore, physical exercise improves brain function by increasing blood flow and oxygen delivery to the brain. This enhances cognitive abilities such as memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. Regular exercise also stimulates the growth of new neurons and strengthens existing connections, leading to improved cognitive function and mental strength.
Adaptation is a key aspect of physical exercise. When the body is subjected to physical stress, such as during exercise, it undergoes various adaptations to become stronger and more resilient. Similarly, the brain adapts to physical exercise by becoming more efficient and better equipped to handle mental challenges.
Incorporating physical exercise into one’s daily routine is essential for building brain resilience and promoting mental well-being. Whether it’s going for a brisk walk, jogging, cycling, or participating in a sport, any form of physical activity can have a positive impact on the brain and mental health.
In conclusion, physical exercise is a powerful tool for strengthening mental health and building brain resilience. It promotes neuroplasticity, enhances cognitive function, and improves overall mental well-being. By incorporating regular physical exercise into our lives, we can reap the numerous benefits it offers and cultivate a resilient and healthy brain.

I am Patrina de Silva, a psychologist and mental health blogger in Sri Lanka. After obtaining psychology degrees from the University of Colombo and Monash University, I returned home to work as a counselor while also starting the popular blog “Pressy but Happy” to provide advice on psychological issues. Over the past decade, my empathetic articles have made my blog a leading mental health resource in the country. In addition to writing, I maintain a private therapy practice, frequently volunteer counseling time, and conduct seminars, driven by my passion for destigmatizing mental illness and educating the public on the mind-body connection. I strive to be an influential voice in my field through my compassionate approach.
