The back is an essential part of the human body, consisting of the spine, which is made up of a series of vertebrae. These vertebrae are divided into different regions, including the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and sacral regions. The spine plays a crucial role in providing support and protecting the spinal cord, which is a vital part of the central nervous system.
The thoracic region of the spine is located in the middle of the back and is responsible for protecting the vital organs in the chest, such as the heart and lungs. The lumbar region, on the other hand, is located in the lower back and provides support for the upper body and allows for movement. Both the thoracic and lumbar regions are crucial for maintaining proper posture and stability.
In addition to the spine, the back also includes other important structures, such as the intervertebral discs, which act as shock absorbers between the vertebrae. These discs help to cushion the spine and allow for flexibility. The dorsal region of the back, also known as the upper back, is responsible for providing support and stability to the upper body.
At the base of the spine, there are two additional structures known as the sacrum and coccyx. The sacrum is a triangular bone located at the base of the spine and connects the spine to the hip bones. The coccyx, commonly referred to as the tailbone, is a small, triangular bone located at the very bottom of the spine. These structures provide support and stability to the pelvis and help to distribute weight evenly.
In summary, the back is a complex structure that includes the spine, intervertebral discs, and other important bones and structures. It plays a crucial role in providing support, protecting vital organs, and allowing for movement and flexibility. Maintaining a healthy back is essential for overall well-being and quality of life.
Definition of Back

The back, also known as the spine or backbone, is the region of the body that extends from the top of the neck to the bottom of the pelvis. It is made up of a series of bones called vertebrae, which are connected to each other by joints and intervertebral discs.
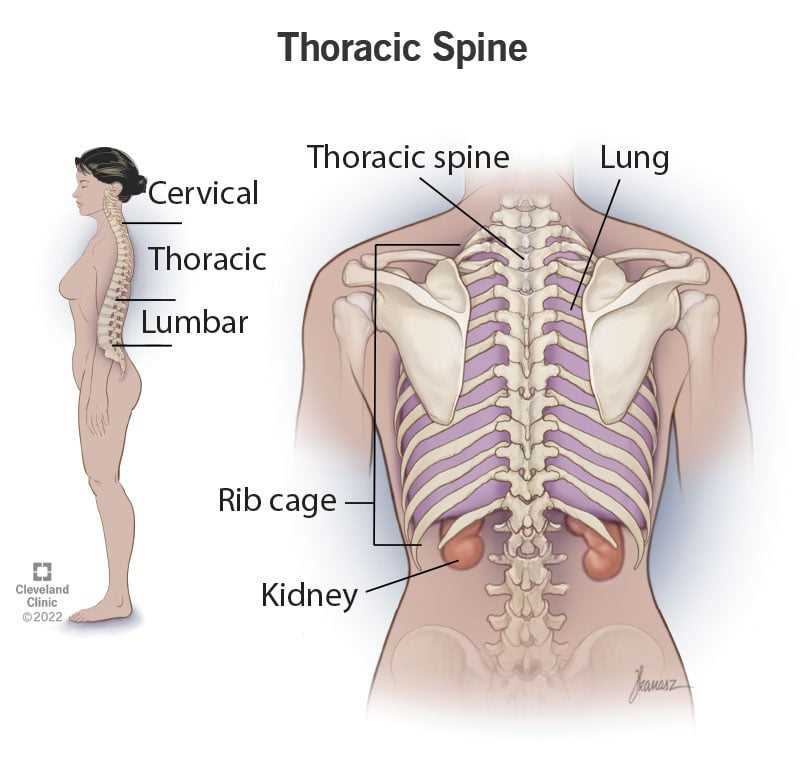
The back can be divided into different regions, including the cervical (neck), thoracic (upper back), lumbar (lower back), and sacrum and coccyx (tailbone). Each region has a specific number of vertebrae and plays a different role in supporting the body and allowing movement.
The cervical spine consists of seven vertebrae and is responsible for supporting the weight of the head and allowing for neck movement. The thoracic spine has twelve vertebrae and provides stability and protection for the organs of the chest. The lumbar spine, which is located in the lower back, consists of five vertebrae and bears the majority of the body’s weight. The sacrum and coccyx are fused bones at the base of the spine and provide support for the pelvis.
The back also contains various muscles, ligaments, and tendons that help support and move the spine. These include the erector spinae muscles, which run along the length of the spine and help maintain proper posture, and the dorsal ligaments, which connect the vertebrae together.
In addition to its structural role, the back also houses the spinal cord, a bundle of nerves that transmits signals between the brain and the rest of the body. The spinal cord is protected by the vertebrae and plays a crucial role in controlling movement and sensation.
In summary, the back is the region of the body that includes the spine and its supporting structures. It is divided into different regions, each with its own set of vertebrae and functions. The back plays a vital role in supporting the body, allowing movement, and protecting the spinal cord.
The Back in Human Anatomy
The back is an essential part of the human anatomy, providing support and protection for the spinal cord, which is a crucial component of the central nervous system. The back consists of several key structures, including the thoracic vertebrae, intervertebral discs, and the dorsal spine.
The thoracic vertebrae are a series of 12 bones that make up the middle section of the backbone. These vertebrae are larger and stronger than the cervical vertebrae in the neck, and they provide support for the ribcage. Each thoracic vertebra has a specific shape and structure, allowing for flexibility and movement while still maintaining stability.
The intervertebral discs are located between each pair of vertebrae in the spine. These discs act as shock absorbers, cushioning the vertebrae and allowing for movement. Each disc consists of a tough outer layer called the annulus fibrosus and a gel-like center called the nucleus pulposus. The intervertebral discs play a crucial role in maintaining the overall health and function of the back.
The backbone, also known as the spinal column or vertebral column, is made up of a series of individual vertebrae. These vertebrae are stacked on top of each other and connected by joints, allowing for movement and flexibility. The backbone provides support for the body and protects the spinal cord, which runs through a central canal within the vertebrae.
The coccyx, also known as the tailbone, is a small triangular bone located at the bottom of the backbone. It consists of several fused vertebrae and serves as an attachment point for various muscles, ligaments, and tendons. While the coccyx has limited mobility, it still plays a role in providing support and stability to the back.
The dorsal spine, also known as the thoracic spine, refers to the region of the spine that runs along the back of the chest. This portion of the spine is connected to the ribcage and provides support and protection for the internal organs in the chest cavity. The dorsal spine consists of the thoracic vertebrae and is responsible for allowing movements such as bending, twisting, and rotating.
In conclusion, the back in human anatomy is a complex and vital structure that consists of the thoracic vertebrae, intervertebral discs, backbone, coccyx, and dorsal spine. These structures work together to provide support, protection, and flexibility, allowing for a wide range of movements and maintaining the overall health and function of the body.
The Back in Sports
The back plays a crucial role in sports, providing support, stability, and mobility to athletes. It is made up of several components, including the thoracic and dorsal regions of the spine, the sacrum, the coccyx, and the vertebrae.
The backbone, or spine, is composed of a series of vertebrae that are stacked on top of each other. These vertebrae protect the spinal cord and allow for movement and flexibility. The thoracic region of the spine is located in the upper back and is connected to the ribcage, providing stability and protection to the vital organs in the chest.
The dorsal region of the spine, also known as the lumbar region, is located in the lower back and is responsible for supporting the weight of the upper body. This region is particularly important in sports that involve lifting, such as weightlifting or powerlifting.
The sacrum is a triangular bone located at the base of the spine, between the two hip bones. It provides stability and connects the spine to the pelvis. The coccyx, also known as the tailbone, is located at the very bottom of the spine and provides support to the pelvic region.
The discs between the vertebrae act as shock absorbers, cushioning the spine and preventing it from rubbing against itself. These discs can be a common source of injury in sports, especially in high-impact activities like football or rugby.
Overall, a strong and healthy back is essential for athletes in order to perform at their best and avoid injury. Proper conditioning, stretching, and strengthening exercises can help maintain a strong back and prevent any potential issues.
Explanation of Back

The back is the dorsal side of the human body, extending from the base of the skull to the coccyx. It consists of the spine, which is made up of a series of vertebrae. The spine is divided into different regions, including the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacrum, and coccyx.
The backbone, or vertebral column, provides support and protection for the spinal cord. It is composed of individual vertebrae, which are connected by discs. These discs act as shock absorbers, allowing for flexibility and movement of the spine.
The lumbar region of the back is located in the lower back, consisting of five vertebrae. This region is responsible for supporting the weight of the upper body and providing stability during movement.
The thoracic region of the back is located in the middle and upper back, consisting of twelve vertebrae. This region is connected to the rib cage and provides support for the chest and upper body.
The sacrum is a triangular bone located at the base of the spine, between the two pelvic bones. It provides support for the spine and connects the spine to the pelvis.
Overall, the back plays a crucial role in supporting the body, protecting the spinal cord, and allowing for movement and flexibility.
Importance of a Strong Back
A strong back is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. The back is composed of various structures, including the discs, lumbar region, sacrum, spine, coccyx, vertebrae, thoracic region, and dorsal region. These structures work together to provide support, stability, and flexibility to the body.
One of the main functions of the back is to protect the spinal cord, which is responsible for transmitting signals between the brain and the rest of the body. A strong back helps to ensure that the spinal cord is properly protected and prevents injuries that can result in pain, numbness, and loss of function.
In addition to protecting the spinal cord, a strong back also helps to maintain good posture. Poor posture can lead to muscle imbalances, joint dysfunction, and increased risk of injury. By strengthening the muscles of the back, individuals can improve their posture and reduce the risk of developing chronic pain and musculoskeletal problems.
A strong back also plays a key role in maintaining a healthy and active lifestyle. Strong back muscles provide the necessary support and stability for everyday activities, such as lifting, carrying, and bending. Without a strong back, individuals may experience difficulty performing these tasks, which can limit their independence and quality of life.
Regular exercise and strength training are essential for developing a strong back. Exercises that target the back muscles, such as rows, lat pulldowns, and deadlifts, can help to strengthen and tone the muscles in the back. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or qualified trainer before starting any exercise program to ensure proper form and technique.
In conclusion, a strong back is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. It provides support, stability, and flexibility to the body, protects the spinal cord, maintains good posture, and enables individuals to perform everyday activities with ease. By incorporating regular exercise and strength training into their routine, individuals can develop a strong back and enjoy the numerous benefits it offers.
Common Back Problems
Back problems can be caused by various issues affecting the backbone, which is made up of the sacrum, vertebrae, and discs. These problems can occur in different regions of the back, including the dorsal, thoracic, and lumbar spine.
One common back problem is a herniated disc, which occurs when the soft cushion-like discs between the vertebrae become damaged or bulge out of place. This can cause pain, numbness, and tingling in the back and legs.
Another common issue is lower back pain, also known as lumbar pain. This can be caused by muscle strain, poor posture, or injury to the muscles, ligaments, or discs in the lower back. It can range from mild discomfort to severe pain that affects daily activities.
Scoliosis is a condition that affects the curvature of the spine, causing it to curve sideways. This can lead to back pain, uneven shoulders or hips, and difficulty breathing in severe cases.
Spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the spinal canal, which can put pressure on the spinal cord and nerves. This can cause pain, numbness, and weakness in the back and legs.
Other common back problems include degenerative disc disease, osteoarthritis, and sciatica. These conditions can cause chronic pain and discomfort in the back, making it difficult to perform daily tasks.
| Back Problem | Description |
|---|---|
| Herniated Disc | Damage or bulging of the discs between the vertebrae |
| Lower Back Pain | Pain in the muscles, ligaments, or discs in the lower back |
| Scoliosis | Curvature of the spine, causing sideways curvature |
| Spinal Stenosis | Narrowing of the spinal canal, putting pressure on the spinal cord and nerves |
| Degenerative Disc Disease | Breakdown of the discs in the spine |
| Osteoarthritis | Wear and tear of the joints in the spine |
| Sciatica | Compression of the sciatic nerve, causing pain in the back and legs |

I am Patrina de Silva, a psychologist and mental health blogger in Sri Lanka. After obtaining psychology degrees from the University of Colombo and Monash University, I returned home to work as a counselor while also starting the popular blog “Pressy but Happy” to provide advice on psychological issues. Over the past decade, my empathetic articles have made my blog a leading mental health resource in the country. In addition to writing, I maintain a private therapy practice, frequently volunteer counseling time, and conduct seminars, driven by my passion for destigmatizing mental illness and educating the public on the mind-body connection. I strive to be an influential voice in my field through my compassionate approach.
