
In today’s fast-paced and demanding world, stress has become an inevitable part of our lives. From work pressures to personal challenges, we all face situations that can overwhelm us. However, what sets individuals apart is their ability to bounce back from adversity and thrive despite the challenges. This ability is known as resilience.
Resilience can be defined as the capacity to adapt and recover from setbacks, trauma, or stress. It is not about avoiding or eliminating stress altogether, but rather about developing the skills and mindset to navigate through it successfully. Resilient individuals have a unique ability to buffer the impact of stress, allowing them to maintain their well-being and mental health.
Resilience is not an innate trait that some people are born with, but rather a skill that can be developed and strengthened over time. It involves a combination of factors, including genetics, personality traits, and life experiences. While some individuals may naturally possess a higher level of resilience, anyone can cultivate and enhance their ability to bounce back from adversity.
Resilience and its Importance

Resilience is the ability to bounce back and recover from adversity, setbacks, and stress. It acts as a buffer against the negative effects of stress and helps individuals maintain their mental and emotional well-being.
Having resilience allows individuals to adapt and cope with challenging situations, whether they are personal or professional. It provides the strength and determination to face obstacles head-on and find solutions, rather than being overwhelmed by stress.
Resilience is a crucial trait to develop because it helps individuals maintain a positive outlook, even in the face of adversity. It enables them to stay motivated and focused, despite setbacks and challenges. Resilient individuals are more likely to persevere and achieve their goals, as they have the ability to bounce back from failures and learn from them.
Moreover, resilience plays a significant role in maintaining good mental and emotional health. It helps individuals manage stress and prevent it from taking a toll on their well-being. Resilient individuals are better equipped to handle the pressures of daily life, as they have developed effective coping mechanisms.
Overall, resilience is an essential quality to cultivate, as it acts as a protective buffer against stress and adversity. It allows individuals to navigate through life’s challenges with strength and determination, maintaining their mental and emotional well-being along the way.
Definition of Resilience

Resilience is the ability to bounce back and adapt in the face of adversity, challenges, and stress. It is the capacity to recover quickly from difficult experiences and setbacks, and to maintain a positive outlook and sense of well-being.
The Role of Resilience in Mental Health

Resilience plays a crucial role in mental health as it has the ability to buffer the negative effects of stress and adversity. Individuals with high levels of resilience are better equipped to cope with and bounce back from challenging life events.
Resilience acts as a protective factor, helping individuals maintain their mental well-being in the face of adversity. It provides individuals with the ability to adapt and recover from difficult situations, reducing the risk of developing mental health disorders.
When faced with stressful situations, resilient individuals are more likely to maintain a positive outlook, problem-solving skills, and a sense of control over their lives. This allows them to effectively navigate through challenges and maintain their mental well-being.
Furthermore, resilience helps individuals build and maintain strong social support networks. Having a support system in place can provide individuals with the emotional and practical support needed during times of stress. This can help prevent feelings of isolation and loneliness, which are known risk factors for mental health issues.
Overall, the ability to bounce back from adversity and maintain mental well-being is crucial for overall mental health. Developing and strengthening resilience can help individuals better cope with life’s challenges and reduce the risk of developing mental health disorders.
Factors Influencing Resilience
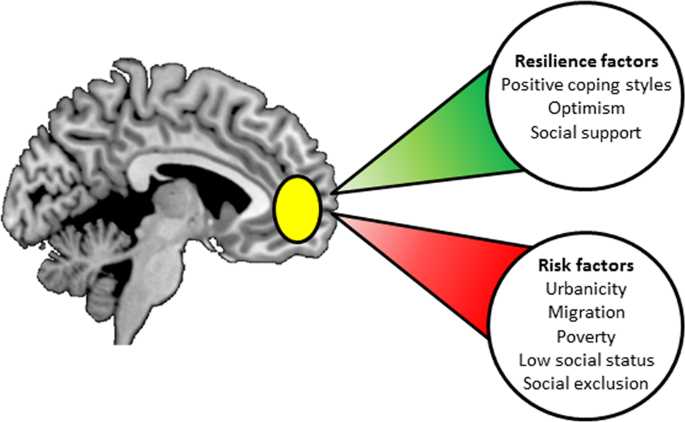
Resilience, the ability to bounce back from adversity and buffer against stress, is influenced by a variety of factors. These factors can have a significant impact on an individual’s ability to cope with and recover from difficult situations.
One factor that influences resilience is social support. Having a strong network of friends, family, and community members can provide emotional and practical support during challenging times. Social support can help individuals feel less alone and provide them with resources and guidance to navigate difficult circumstances.
Another factor that influences resilience is self-esteem. Individuals with higher levels of self-esteem tend to have greater resilience, as they have a positive sense of self-worth and confidence in their ability to overcome obstacles. This self-belief can help individuals persevere and maintain a positive outlook in the face of adversity.
Additionally, the presence of positive role models can influence resilience. Seeing others who have successfully overcome challenges can inspire individuals and provide them with hope and motivation. Role models can serve as examples of resilience and demonstrate that it is possible to overcome difficult circumstances.
Finally, personal characteristics and traits can also influence resilience. Traits such as optimism, flexibility, and adaptability can contribute to an individual’s ability to bounce back from adversity. These traits enable individuals to approach challenges with a positive attitude and find alternative solutions when faced with obstacles.
In conclusion, resilience is influenced by a variety of factors, including social support, self-esteem, positive role models, and personal characteristics. Understanding these factors can help individuals develop and strengthen their resilience, allowing them to better cope with and recover from stressful situations.
Genetic and Biological Factors

Resilience, the ability to buffer and bounce back from stress, is influenced by a combination of genetic and biological factors. Research has shown that certain genetic variations can affect an individual’s response to stress and their ability to cope with adversity.
One key biological factor that contributes to resilience is the functioning of the stress response system. This system, which includes the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, plays a crucial role in regulating the body’s response to stress. Individuals with a more efficient stress response system may be better equipped to handle and recover from stressful situations.
Additionally, research has identified specific genes that may be associated with resilience. For example, the BDNF gene, which is involved in the growth and survival of neurons, has been linked to resilience. Variations in this gene may impact an individual’s ability to adapt and recover from stress.
Understanding the genetic and biological factors that contribute to resilience can help inform interventions and treatments aimed at enhancing resilience. By targeting these factors, researchers and clinicians can develop strategies to promote resilience and improve mental health outcomes.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors play a crucial role in buffering stress and enhancing one’s ability to bounce back from adversity. The physical environment in which we live can have a significant impact on our overall well-being and resilience.
One important environmental factor is social support. Having a strong network of family, friends, and colleagues can provide a buffer against the negative effects of stress. Social support can offer emotional support, practical assistance, and a sense of belonging, all of which contribute to an individual’s ability to cope with and recover from challenging situations.
Another environmental factor that can influence resilience is access to resources. This includes access to healthcare, education, and employment opportunities. Having access to these resources can provide individuals with the tools and skills necessary to navigate and overcome stressors. Additionally, living in a safe and stable neighborhood can contribute to a sense of security and reduce the likelihood of exposure to additional stressors.
The physical environment itself can also impact resilience. Natural environments, such as parks and green spaces, have been shown to have a positive effect on mental health and well-being. Spending time in nature can reduce stress levels, improve mood, and enhance overall resilience. On the other hand, living in environments with high levels of pollution, noise, or overcrowding can increase stress and decrease resilience.
Overall, environmental factors play a significant role in shaping an individual’s ability to buffer stress and develop resilience. By creating supportive social networks, providing access to resources, and promoting a healthy physical environment, communities can help individuals build the skills and resources necessary to thrive in the face of adversity.
Psychological Factors

Psychological factors play a crucial role in buffering stress and enhancing resilience. The ability to cope with adversity and bounce back from difficult situations is influenced by various psychological factors.
One important psychological factor is the individual’s cognitive appraisal of stress. How a person perceives and interprets stressful events can significantly impact their ability to cope. Those who have a positive outlook and view stress as a challenge rather than a threat are more likely to have higher levels of resilience.
Another psychological factor that influences resilience is self-efficacy, which refers to an individual’s belief in their ability to successfully handle difficult situations. People with higher levels of self-efficacy are more likely to approach challenges with confidence and are better equipped to overcome obstacles.
Emotional intelligence is also a crucial psychological factor in resilience. The ability to understand and manage one’s emotions, as well as effectively navigate social interactions, can help individuals maintain their composure and adapt to stressful situations more effectively.
Lastly, social support is a psychological factor that can significantly impact resilience. Having a strong support network of family, friends, and other individuals who provide emotional and practical support can act as a buffer against stress and enhance an individual’s ability to bounce back from adversity.
| Psychological Factors |
|---|
| Cognitive appraisal of stress |
| Self-efficacy |
| Emotional intelligence |
| Social support |
Building Resilience

Resilience refers to the ability to bounce back from stress and adversity. It is the capacity to adapt and recover quickly when facing challenges. Building resilience is crucial in today’s fast-paced and demanding world, where stressors are abundant.
Resilience acts as a buffer against stress, helping individuals maintain their mental and emotional well-being. It allows them to cope with difficult situations, setbacks, and disappointments without being overwhelmed. Resilient individuals are more likely to view challenges as opportunities for growth rather than insurmountable obstacles.
To build resilience, it is important to develop certain skills and habits. One key aspect is cultivating a positive mindset. This involves focusing on one’s strengths and abilities, practicing self-compassion, and reframing negative thoughts into more positive and constructive ones.
Another important factor in building resilience is fostering strong social connections. Having a support network of friends, family, and colleagues can provide emotional support, practical assistance, and different perspectives. These relationships can also help individuals gain new insights and learn from others’ experiences.
Additionally, taking care of one’s physical health plays a crucial role in resilience. Engaging in regular exercise, getting enough sleep, and maintaining a healthy diet can enhance one’s ability to cope with stress. Physical well-being is closely linked to mental and emotional well-being, and taking care of the body can positively impact overall resilience.
Lastly, practicing self-care and stress management techniques is vital. This may include engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation, such as hobbies, meditation, or spending time in nature. Learning how to set boundaries, manage time effectively, and prioritize self-care can help individuals build resilience and prevent burnout.
In conclusion, building resilience is essential in navigating through life’s challenges. It is the ability to bounce back and adapt in the face of stress and adversity. By cultivating a positive mindset, fostering social connections, taking care of physical health, and practicing self-care, individuals can enhance their resilience and build a strong buffer against stress.
Developing Strong Support Systems
In order to effectively buffer stress and build resilience, it is crucial to develop strong support systems. These support systems can provide the necessary resources, guidance, and emotional support to help individuals navigate through challenging times.
One way to develop a strong support system is to cultivate and maintain healthy relationships. Building connections with family, friends, and peers can provide a network of individuals who can offer encouragement, advice, and a listening ear. These relationships can create a sense of belonging and provide a safe space for individuals to express their thoughts and feelings.
Another important aspect of developing a strong support system is seeking professional help when needed. Mental health professionals, such as therapists or counselors, can offer specialized guidance and support to help individuals manage stress and build resilience. They can provide tools and strategies to cope with challenges and develop a resilient mindset.
Additionally, participating in support groups or community organizations can be beneficial in developing a strong support system. These groups can provide a sense of community and understanding, as individuals with similar experiences come together to share their stories and support one another. It can be empowering to connect with others who have faced similar challenges and learn from their resilience.
Lastly, it is important to prioritize self-care as a part of developing a strong support system. Taking care of one’s physical, emotional, and mental well-being is essential in building resilience. This can involve engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation, practicing mindfulness and self-reflection, and seeking out resources and information to support personal growth.
By developing strong support systems, individuals can enhance their ability to buffer stress and build resilience. These support systems provide a foundation of support and resources that can help individuals face challenges with resilience and strength.
Practicing Self-Care and Stress Management

When it comes to dealing with stress, practicing self-care and stress management techniques can greatly enhance your ability to buffer the negative effects. Self-care involves taking deliberate actions to prioritize your physical, mental, and emotional well-being. By making self-care a priority, you can build resilience and strengthen your ability to cope with stress.
One effective way to practice self-care is to engage in activities that help you relax and unwind. This can include hobbies such as reading, listening to music, or practicing mindfulness and meditation. Taking time for yourself and doing things that bring you joy and peace can help reduce stress and promote a sense of calm.
In addition to engaging in relaxing activities, it is important to prioritize your physical health. This can involve getting regular exercise, eating a balanced diet, and getting enough sleep. Physical activity releases endorphins, which are natural stress-fighting chemicals in the body. Eating well and getting enough rest can also help boost your energy levels and improve your ability to handle stress.
Another crucial aspect of self-care is maintaining a strong support system. Surrounding yourself with positive and supportive people can provide a buffer against stress. Reach out to friends, family, or a therapist who can offer guidance and support during challenging times. Connecting with others and sharing your feelings can help alleviate stress and provide a sense of belonging and validation.
Lastly, it is important to develop effective stress management techniques. This can involve learning how to identify and challenge negative thought patterns, practicing relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation, and setting realistic goals and priorities. By actively managing stress, you can reduce its impact on your overall well-being and enhance your ability to bounce back from challenging situations.
Overall, practicing self-care and stress management techniques is essential for building resilience and buffering the negative effects of stress. By prioritizing your well-being, engaging in activities that promote relaxation, taking care of your physical health, maintaining a strong support system, and developing effective stress management strategies, you can enhance your ability to cope with stress and lead a more balanced and fulfilling life.
Resilience in Different Life Stages

Resilience is an individual’s ability to bounce back and adapt in the face of adversity and stress. It acts as a buffer, protecting individuals from the negative effects of life challenges. Resilience is not a fixed trait, but rather a skill that can be developed and strengthened throughout different life stages.
In childhood, resilience plays a crucial role in helping children navigate the challenges they encounter, such as academic pressure, family conflicts, or bullying. Children who develop resilience skills are better equipped to handle these challenges, cope with stress, and maintain a positive outlook on life.
During adolescence, resilience becomes even more important as young people face numerous physical, emotional, and social changes. The ability to bounce back from setbacks, manage peer pressure, and make healthy choices is essential for their overall well-being. Resilience allows teenagers to develop a sense of self-confidence and autonomy, enabling them to navigate the transition into adulthood.
In adulthood, resilience continues to be a valuable asset. It helps individuals navigate the ups and downs of careers, relationships, and personal challenges. Resilient adults are better able to cope with job loss, financial difficulties, or relationship breakdowns. They have the ability to adapt to new situations, learn from failures, and maintain a positive mindset.
As individuals enter older age, resilience becomes crucial in maintaining physical and mental health. The ability to adapt to age-related changes, cope with loss, and maintain social connections is vital for overall well-being. Resilient older adults are better able to face the challenges of aging, such as chronic illness or the loss of loved ones, and maintain a sense of purpose and fulfillment.
Overall, resilience is a dynamic skill that evolves and develops throughout different life stages. It acts as a buffer, helping individuals navigate the challenges and stressors they encounter. By fostering resilience, individuals can enhance their ability to bounce back, adapt, and thrive in the face of adversity.

I am Patrina de Silva, a psychologist and mental health blogger in Sri Lanka. After obtaining psychology degrees from the University of Colombo and Monash University, I returned home to work as a counselor while also starting the popular blog “Pressy but Happy” to provide advice on psychological issues. Over the past decade, my empathetic articles have made my blog a leading mental health resource in the country. In addition to writing, I maintain a private therapy practice, frequently volunteer counseling time, and conduct seminars, driven by my passion for destigmatizing mental illness and educating the public on the mind-body connection. I strive to be an influential voice in my field through my compassionate approach.
