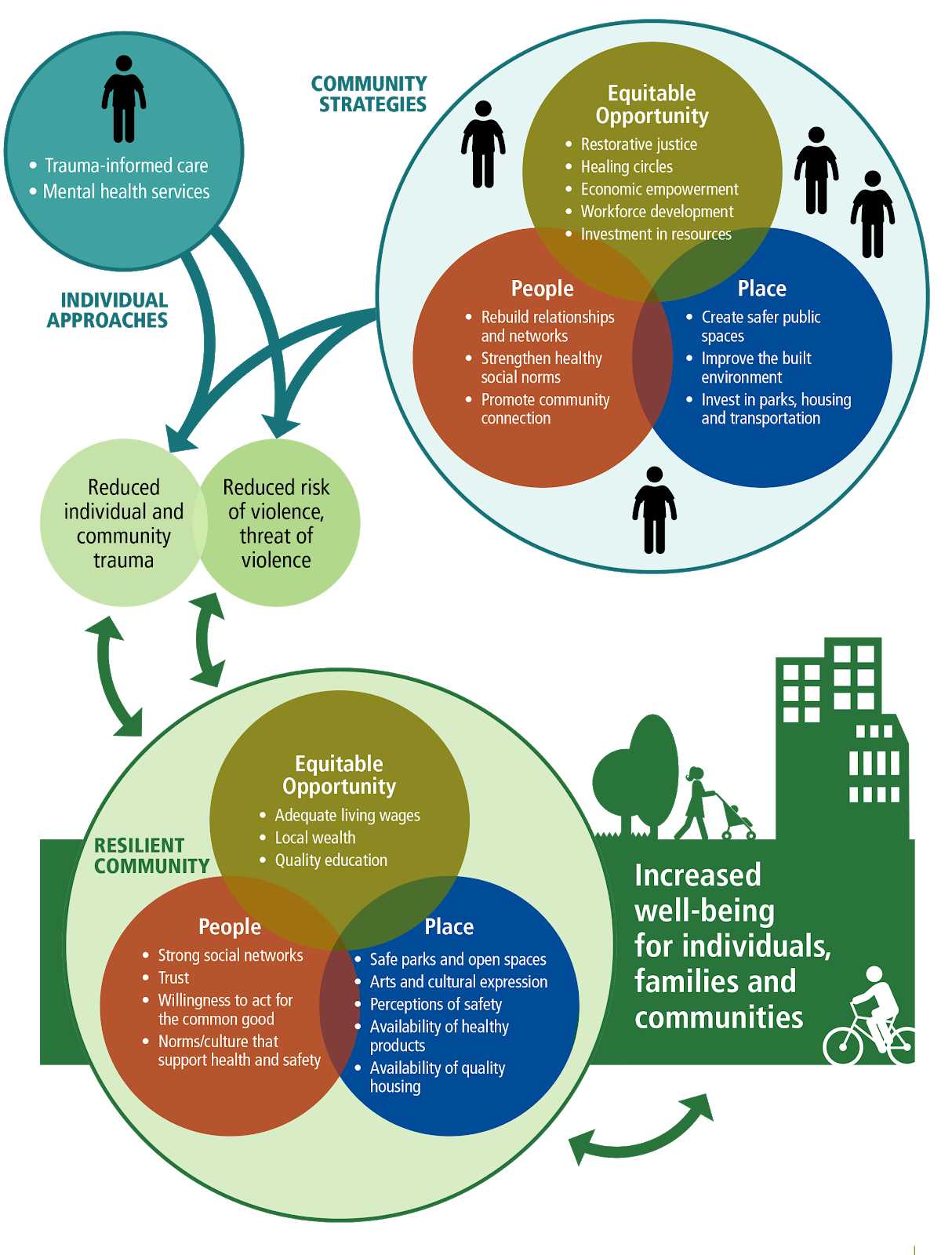
In today’s fast-paced and demanding world, it’s crucial to understand the impact of stress on our mental well-being. The Stress and Resilience Framework provides a comprehensive understanding of how individuals adapt and cope with the challenges they face. This framework offers valuable insights into the support systems and strategies that promote resilience and psychological well-being.
At its core, the Stress and Resilience Framework recognizes that stress is an inevitable part of life. Whether it’s work-related pressures, personal relationships, or unexpected life events, stress can have a significant impact on our mental health. However, this framework emphasizes that resilience is the key to navigating these challenges and bouncing back stronger.
Resilience refers to an individual’s ability to adapt and thrive in the face of adversity. It involves psychological, emotional, and social aspects that contribute to one’s ability to cope with stress. By understanding the factors that promote resilience, individuals can develop effective coping strategies and build a solid foundation for their mental well-being.
The Stress and Resilience Framework highlights the importance of social support in fostering resilience. Strong social connections, such as family, friends, and community, provide a crucial source of emotional and practical support during times of stress. Additionally, this framework emphasizes the significance of self-care practices, such as exercise, mindfulness, and self-reflection, in promoting resilience and mental well-being.
By embracing the Stress and Resilience Framework, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the factors that contribute to stress and resilience. This comprehensive guide will explore the various components of the framework, providing practical tips and strategies to enhance coping skills and promote psychological well-being. Whether you’re facing a major life transition or simply seeking ways to better manage daily stressors, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to navigate the challenges and build resilience.
The Importance of Understanding Stress and Resilience
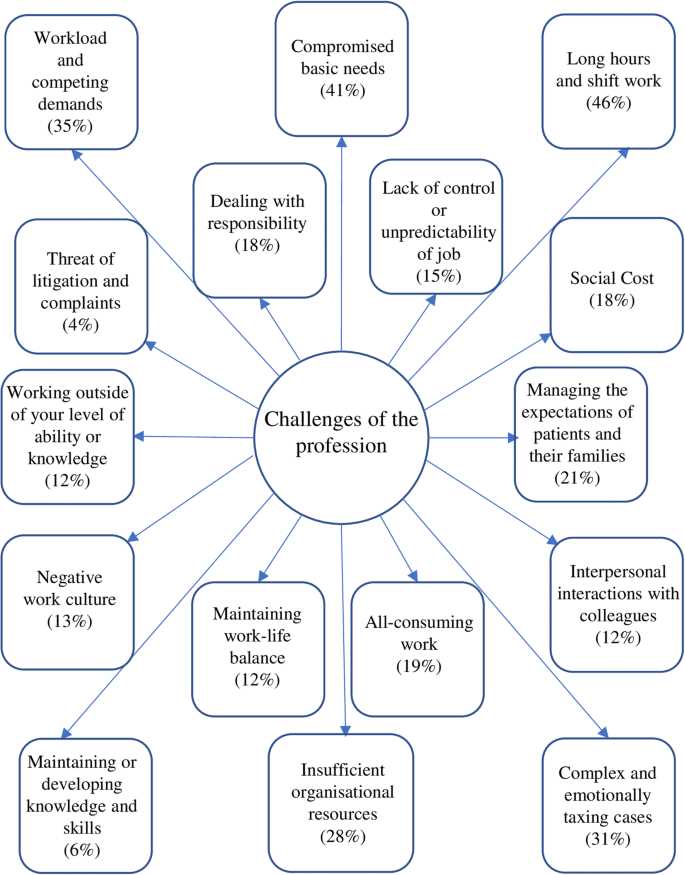
Understanding stress and resilience is crucial for maintaining good health and well-being. In today’s fast-paced world, individuals are constantly faced with various stressors that can have a negative impact on their mental and physical health.
Stress is a natural response to the demands and challenges of daily life. It can come from various sources, such as work, relationships, or financial difficulties. When individuals are exposed to chronic stress, it can lead to a range of negative outcomes, including mental health problems, such as anxiety and depression, as well as physical health problems, such as cardiovascular disease and weakened immune function.
However, it is important to note that not everyone responds to stress in the same way. Resilience refers to an individual’s ability to adapt and bounce back from stressful situations. Some individuals may be more resilient than others, and this can have a significant impact on their overall well-being.
Understanding the stress and resilience framework can help individuals better manage and cope with stress. It involves recognizing stressors, identifying coping strategies, and seeking support when needed. By developing resilience skills, individuals can enhance their ability to handle stress and maintain good mental and physical health.
Moreover, understanding stress and resilience can also help individuals support others who may be experiencing high levels of stress. By recognizing signs of stress and offering support, individuals can contribute to the well-being of their friends, family members, and colleagues.
In conclusion, understanding stress and resilience is essential for maintaining good mental and physical health. By recognizing the impact of stress and developing resilience skills, individuals can better manage and cope with stressors. Additionally, understanding stress and resilience can help individuals provide support to others who may be experiencing high levels of stress. Overall, this knowledge is vital for promoting well-being and fostering a healthier society.
Overview of the Stress and Resilience Framework

The Stress and Resilience Framework is a comprehensive mental health framework that aims to understand and address the psychological impact of stress and promote resilience in individuals. It provides a systematic approach to understanding how stress affects mental health and the factors that contribute to resilience.
Stress is a natural response to challenging or demanding situations, and it can have a significant impact on an individual’s mental well-being. The Stress and Resilience Framework recognizes that stress is a normal part of life but also highlights the importance of managing and adapting to stress in a healthy way.
The framework emphasizes the role of resilience in promoting mental health and well-being. Resilience refers to an individual’s ability to bounce back from adversity and adapt to stressful situations. It involves the development of coping mechanisms, social support networks, and the utilization of personal strengths and resources.
Within the Stress and Resilience Framework, various factors are considered to influence an individual’s response to stress and their ability to adapt. These factors include biological, psychological, and social determinants. Biological factors may include genetic predispositions or physiological responses to stress. Psychological factors may include cognitive processes, emotions, and personality traits. Social determinants may include social support networks, socioeconomic status, and cultural influences.
The framework also recognizes the importance of support systems in promoting resilience and mental health. Support can come from various sources, such as family, friends, healthcare professionals, and community organizations. These support systems play a crucial role in providing individuals with the resources and assistance they need to cope with stress and build resilience.
| Key Concepts | Definition |
|---|---|
| Stress | A natural response to challenging or demanding situations |
| Resilience | An individual’s ability to bounce back from adversity and adapt to stressful situations |
| Support | Assistance and resources provided by family, friends, healthcare professionals, and community organizations |
In conclusion, the Stress and Resilience Framework provides a comprehensive understanding of the mental health impact of stress and the factors that contribute to resilience. By recognizing the importance of support systems and promoting healthy adaptation to stress, the framework aims to improve the overall well-being of individuals.
Key Concepts and Definitions
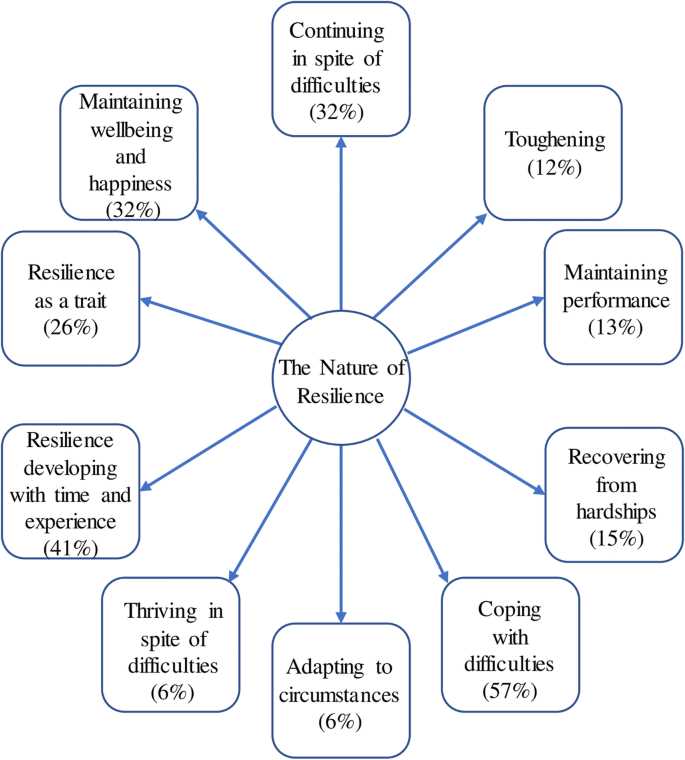
In order to understand the Stress and Resilience Framework, it is important to familiarize oneself with key concepts and definitions related to stress, health, coping, adaptation, psychological resilience, and support.
- Stress: Stress refers to the psychological and physical response of an individual to external pressures or demands, also known as stressors. It can have both positive (eustress) and negative (distress) effects on an individual’s well-being.
- Health: Health encompasses the overall well-being of an individual, including physical, mental, and social aspects. It is influenced by various factors, including genetics, lifestyle choices, and environmental factors.
- Mental Health: Mental health refers to an individual’s emotional, psychological, and social well-being. It affects how people think, feel, and act, and it also helps determine how individuals handle stress, relate to others, and make choices.
- Coping: Coping refers to the cognitive and behavioral efforts individuals make to manage or adapt to stressful situations. It involves the use of various strategies, such as problem-solving, seeking social support, or engaging in relaxation techniques, to reduce stress and promote well-being.
- Adaptation: Adaptation refers to the process of adjusting to changes in the environment or circumstances. It involves modifying one’s thoughts, behaviors, or emotions to better fit the new situation and maintain well-being.
- Psychological Resilience: Psychological resilience is the ability to bounce back and recover from adversity, trauma, or stress. It involves the capacity to adapt and maintain mental well-being in the face of challenging circumstances.
- Support: Support refers to the assistance, encouragement, or resources provided to individuals in times of need. It can be emotional, instrumental, or informational in nature and is crucial for promoting resilience and well-being.
By understanding these key concepts and definitions, one can gain a deeper insight into the Stress and Resilience Framework and its application in promoting mental health and well-being.
Section 2: The Impact of Stress on Mental and Physical Health
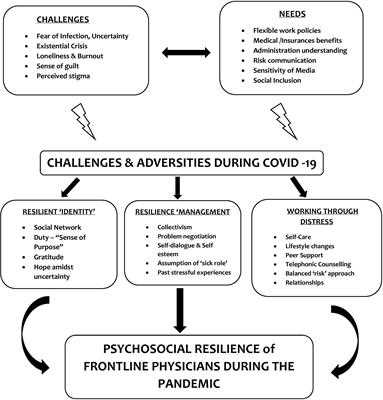
Stress can have a significant impact on both mental and physical health. When individuals experience high levels of stress, it can affect their overall well-being and functioning. The effects of stress on mental health can be particularly detrimental, leading to increased symptoms of anxiety, depression, and other psychological disorders. These mental health issues can then further exacerbate stress levels, creating a cycle of negative impact on overall health.
On a physical level, stress can manifest in a variety of ways. It can lead to increased blood pressure, heart rate, and other physiological responses that can have long-term implications for health. Chronic stress has been linked to a higher risk of developing cardiovascular disease, obesity, and other chronic health conditions.
However, it is important to note that not all individuals experience the same level of negative impact from stress. Some individuals are more resilient and able to cope with stress in a healthy way. Resilience refers to an individual’s ability to adapt and bounce back from stressful situations. Those with higher levels of resilience are better equipped to handle stress and may experience fewer negative effects on their mental and physical health.
Support systems and coping mechanisms also play a significant role in how individuals are affected by stress. Having a strong support system, whether it be friends, family, or professional help, can provide individuals with the resources and assistance they need to navigate stressful situations. Additionally, having healthy coping mechanisms, such as exercise, meditation, or therapy, can help individuals manage stress and reduce its negative impact on their health.
In conclusion, stress can have a profound impact on both mental and physical health. The effects of stress can range from increased symptoms of anxiety and depression to physiological responses that increase the risk of chronic health conditions. However, individuals who are resilient and have strong support systems and coping mechanisms are better equipped to handle stress and minimize its negative effects on their overall health.
Understanding the Stress Response
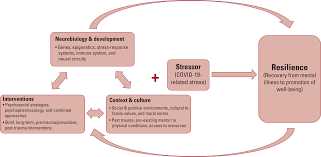
The stress response is a natural and automatic reaction that occurs when an individual is faced with a challenging or threatening situation. It is a complex framework that involves various physiological, psychological, and behavioral changes. When a person experiences stress, their body releases stress hormones, such as cortisol, which triggers a series of responses to help the individual cope with the perceived threat or challenge.
The stress response can have both positive and negative effects on an individual’s mental and physical health. In the short term, stress can provide the motivation and energy needed to overcome a difficult situation. However, chronic or excessive stress can have detrimental effects on a person’s well-being, leading to a range of physical and psychological health problems.
Coping with stress is an essential part of building resilience and maintaining good mental health. Effective coping strategies can help individuals manage stress and minimize its negative impact. These strategies may include seeking social support, engaging in relaxation techniques, practicing mindfulness, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits.
Resilience plays a crucial role in the stress response. Resilient individuals are better able to adapt to and recover from stressful situations. They have the ability to bounce back and maintain their psychological well-being even in the face of adversity. Building resilience involves developing a strong support network, cultivating positive thinking patterns, and engaging in self-care activities.
Understanding the stress response and how it affects individuals’ mental and physical health is essential for promoting overall well-being. By recognizing the signs of stress and implementing effective coping strategies, individuals can better manage stress and enhance their resilience. Seeking professional help and support when needed is also crucial for maintaining optimal psychological health.
| Key Points: |
|---|
| – The stress response is a natural and automatic reaction to challenging or threatening situations. |
| – Stress can have both positive and negative effects on mental and physical health. |
| – Coping strategies are essential for managing stress and promoting resilience. |
| – Resilience plays a crucial role in the stress response and overall well-being. |
| – Seeking professional help and support is important for maintaining psychological health. |
The Effects of Chronic Stress on Mental Health
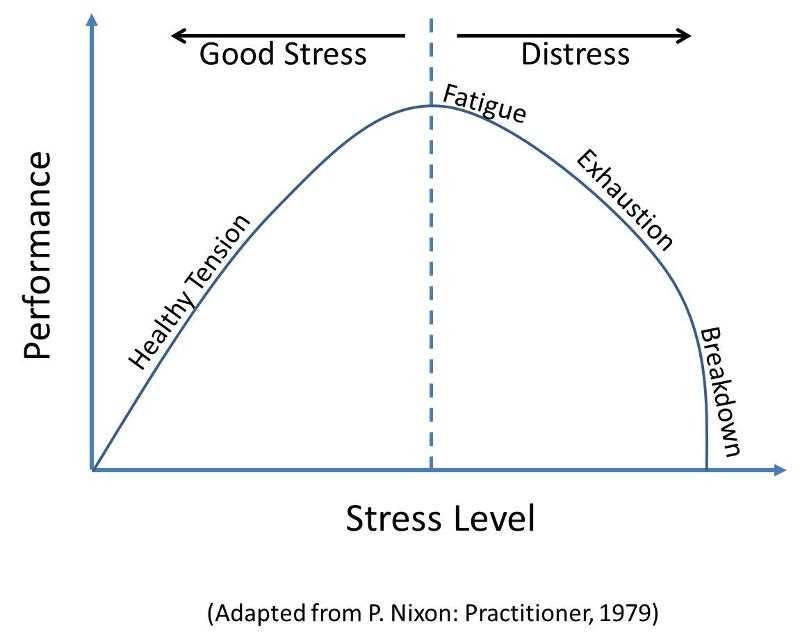
Chronic stress can have a significant impact on mental health. The human mind and body are designed to adapt and cope with stress, but when stress becomes chronic, it can overwhelm the psychological and physiological systems that are responsible for maintaining mental well-being.
According to the stress and resilience framework, chronic stress can lead to a variety of mental health issues. One of the primary effects is an increased risk of developing psychological disorders such as anxiety and depression. The constant activation of the stress response can disrupt the normal functioning of the brain, leading to changes in mood, cognition, and behavior.
Chronic stress can also impair cognitive function and memory. The prolonged release of stress hormones like cortisol can interfere with the formation and retrieval of memories, making it difficult to concentrate, learn new information, and recall past experiences. This can further contribute to feelings of frustration, helplessness, and decreased self-esteem.
In addition to these cognitive effects, chronic stress can also impact physical health, leading to a range of symptoms such as headaches, digestive issues, and sleep disturbances. These physical symptoms can further exacerbate mental health problems, creating a vicious cycle of stress and poor well-being.
However, it is important to note that not everyone who experiences chronic stress will develop mental health issues. The concept of resilience, which is a key component of the stress and resilience framework, suggests that individuals vary in their ability to adapt and cope with stress. Some people may be more resilient and able to bounce back from stressful situations, while others may be more vulnerable and susceptible to the negative effects of stress.
Understanding the effects of chronic stress on mental health is crucial for developing effective strategies and interventions to promote resilience and well-being. By recognizing the impact of chronic stress on mental health, individuals can take steps to manage and reduce stress levels, seek support when needed, and engage in self-care practices that promote psychological well-being.
| Effects of Chronic Stress on Mental Health: |
|---|
| – Increased risk of psychological disorders |
| – Impaired cognitive function and memory |
| – Physical symptoms and health issues |
| – Variations in resilience and coping mechanisms |
| – Importance of stress management and self-care |
The Effects of Chronic Stress on Physical Health
Chronic stress can have a significant impact on a person’s physical health. When the body is under constant stress, it can lead to a variety of negative health outcomes. The stress response is designed to support short-term adaptation and coping, but when stress becomes chronic, it can take a toll on the body.
One of the main ways that chronic stress affects physical health is through the activation of the body’s stress response system. This system, also known as the fight-or-flight response, is designed to help the body respond to perceived threats. However, when stress is chronic, this response system can become overactive, leading to a range of physical symptoms and health issues.
Research has shown that chronic stress can contribute to the development or exacerbation of various health conditions. These can include cardiovascular problems such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke. Chronic stress can also weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and illnesses.
In addition to these physical health issues, chronic stress can also have a significant impact on mental health. The stress and resilience framework recognizes the interconnectedness of psychological and physical well-being. Chronic stress can contribute to the development of mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression.
It is important to note that the effects of chronic stress on physical health can vary from person to person. Some individuals may be more resilient and able to cope with stress, while others may be more susceptible to its negative effects. Understanding the individual factors that contribute to stress and resilience can help in developing appropriate interventions and support mechanisms.
In conclusion, chronic stress can have a profound impact on physical health. It can lead to a range of health issues, including cardiovascular problems, weakened immune system, and mental health conditions. By recognizing the effects of chronic stress and implementing appropriate support and coping mechanisms, individuals can better manage their stress levels and promote overall health and well-being.
Section 3: Building Resilience in the Face of Stress
Building resilience is an essential part of the stress and resilience framework. Resilience refers to the ability to adapt and bounce back from stressful situations, maintaining mental health and well-being. It involves developing coping strategies and psychological resources to navigate through challenging circumstances.
Resilience is not a fixed trait, but rather a skill that can be cultivated and strengthened over time. Research has shown that individuals who possess higher levels of resilience are better equipped to handle stress and adversity, experiencing less negative impact on their mental and physical health.
There are several key factors that contribute to building resilience. One important aspect is the development of healthy coping mechanisms. These can include engaging in activities that promote relaxation and self-care, such as exercise, meditation, or spending time with loved ones. Building a support network of friends, family, or professionals can also provide valuable resources for managing stress.
Another crucial factor in building resilience is fostering a positive mindset. This involves cultivating optimism, gratitude, and self-compassion. By reframing negative thoughts and focusing on strengths and successes, individuals can enhance their ability to cope with stress and bounce back from setbacks.
Additionally, developing problem-solving skills and effective communication strategies can contribute to resilience. Being able to identify and address challenges, as well as effectively communicate one’s needs and boundaries, can help individuals navigate stressful situations with greater ease.
Furthermore, maintaining physical health is an important component of building resilience. Engaging in regular exercise, eating a balanced diet, and getting enough sleep can provide the necessary energy and stamina to cope with stress.
Overall, building resilience is a multifaceted process that involves developing coping strategies, fostering a positive mindset, cultivating problem-solving skills, and maintaining physical health. By actively working on these aspects, individuals can enhance their ability to adapt and thrive in the face of stress.
| Key Points: |
|---|
| – Resilience is the ability to adapt and bounce back from stressful situations |
| – Building resilience involves developing coping strategies and psychological resources |
| – Healthy coping mechanisms, a positive mindset, problem-solving skills, and physical health are important factors |
| – Building resilience is an ongoing process that can be cultivated and strengthened over time |
Understanding Resilience and its Benefits
Resilience is a psychological trait that allows individuals to adapt and bounce back from difficult and challenging situations. It is the ability to cope with stress and adversity, and to maintain mental health and well-being. Resilience is not about avoiding or eliminating stress, but rather about effectively managing and responding to it.
One of the key benefits of resilience is improved mental health. Resilient individuals are better equipped to handle the pressures and demands of daily life, and are less likely to experience symptoms of anxiety, depression, or other mental health disorders. They have a greater sense of control over their emotions and thoughts, and are able to maintain a positive outlook even in the face of adversity.
Resilience also has physical health benefits. Research has shown that resilient individuals have lower levels of stress hormones, such as cortisol, which can have a negative impact on the body. They also have stronger immune systems and are less likely to develop chronic illnesses or experience physical symptoms related to stress.
Another benefit of resilience is improved coping skills. Resilient individuals are better able to problem solve and find solutions to difficult situations. They have a greater ability to adapt to change and are more flexible in their thinking. This allows them to effectively navigate through challenges and setbacks, and to bounce back more quickly.
Support is an important factor in building resilience. Having a strong support network of family, friends, and professionals can provide emotional and practical assistance during times of stress and adversity. Support can also help individuals develop and strengthen their coping skills, and provide a sense of belonging and connection.
In conclusion, resilience is a valuable trait that can have numerous benefits for an individual’s psychological and physical health. It allows individuals to adapt and bounce back from difficult situations, maintain mental well-being, and effectively cope with stress. Building resilience requires support and the development of coping skills, but the rewards are well worth the effort.
Factors that Contribute to Resilience
Resilience is a psychological trait that allows individuals to cope with and adapt to challenging situations. It plays a crucial role in promoting mental health and well-being, especially in the face of stress. Understanding the factors that contribute to resilience can help individuals build and strengthen this important trait.
One key factor that contributes to resilience is social support. Having a strong support network of family, friends, and community members can provide individuals with the emotional and practical assistance they need during difficult times. Social support can help buffer the negative effects of stress and provide a sense of belonging and connection.
Another important factor is self-efficacy, which refers to an individual’s belief in their ability to successfully navigate and overcome challenges. Those with high levels of self-efficacy are more likely to approach stressful situations with a positive mindset and actively seek solutions. Developing a sense of self-efficacy can be achieved through setting and achieving goals, learning new skills, and reflecting on past successes.
Additionally, having good problem-solving skills is crucial for resilience. Being able to identify and assess problems, generate effective solutions, and implement them can help individuals overcome adversity and reduce stress. Problem-solving skills can be improved through practice and seeking feedback from others.
Furthermore, maintaining a healthy lifestyle is essential for resilience. Engaging in regular physical exercise, eating a balanced diet, getting enough sleep, and managing stress can all contribute to overall well-being and enhance resilience. Taking care of one’s physical health can provide a solid foundation for coping with and recovering from stressful situations.
In conclusion, resilience is a multifaceted trait that is influenced by various factors. Social support, self-efficacy, problem-solving skills, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle all contribute to an individual’s ability to cope with and adapt to stress. By understanding and nurturing these factors, individuals can enhance their resilience and promote their mental health and well-being.
Strategies for Building Resilience
Building resilience is crucial in today’s fast-paced and stressful world. Resilience refers to the ability to bounce back from adversity and overcome challenges. It is a mental framework that allows individuals to adapt and thrive in the face of stress.
Here are some strategies for building resilience:
- Develop a strong support network: Surround yourself with positive and supportive people who can provide emotional support and guidance during difficult times.
- Practice self-care: Take care of your mental and physical health by engaging in activities that promote relaxation, such as exercise, meditation, or hobbies.
- Learn effective coping skills: Develop healthy coping mechanisms to deal with stress, such as problem-solving, positive self-talk, and seeking professional help when needed.
- Build psychological flexibility: Cultivate the ability to adapt to new situations and perspectives, and embrace change as an opportunity for growth.
- Set realistic goals: Break down larger goals into smaller, achievable tasks to avoid feeling overwhelmed and increase your sense of accomplishment.
- Practice gratitude: Focus on the positive aspects of your life and express gratitude for the things you have. This can help shift your mindset and build resilience.
- Develop problem-solving skills: Take a proactive approach to problem-solving by identifying challenges and finding creative solutions.
- Seek professional support: If you are struggling with stress or mental health issues, don’t hesitate to seek help from a therapist or counselor who can provide guidance and support.
By implementing these strategies, individuals can build resilience and improve their mental health, allowing them to better navigate the challenges and stressors of daily life.

I am Patrina de Silva, a psychologist and mental health blogger in Sri Lanka. After obtaining psychology degrees from the University of Colombo and Monash University, I returned home to work as a counselor while also starting the popular blog “Pressy but Happy” to provide advice on psychological issues. Over the past decade, my empathetic articles have made my blog a leading mental health resource in the country. In addition to writing, I maintain a private therapy practice, frequently volunteer counseling time, and conduct seminars, driven by my passion for destigmatizing mental illness and educating the public on the mind-body connection. I strive to be an influential voice in my field through my compassionate approach.
