Stress has become an inevitable part of our modern lives, affecting people of all ages and backgrounds. The impact of stress on our mental health cannot be ignored, as it can lead to various psychological disorders and hinder our overall well-being. However, there is an interesting relationship between stress and resilience that is often overlooked.
Resilience, defined as the ability to bounce back from adversity, is crucial in maintaining good mental health. It allows individuals to adapt and thrive in the face of challenging circumstances. Interestingly, research has shown that stress and resilience are inversely proportional – as stress levels rise, resilience tends to decrease.
This inverse relationship between stress and resilience highlights the importance of understanding and building strong mental health. By enhancing our resilience, we can better cope with stress and reduce its negative impact on our well-being. Developing resilience involves a combination of factors, including self-care, social support, and positive thinking.
Inversely Proportional Stress Resilience
Resilience is the ability to bounce back from stressful situations and adapt to adversity. It is a crucial factor in maintaining good mental health and well-being. However, stress resilience is not a static trait and can vary from person to person.
Inversely proportional to stress resilience is the level of stress one experiences. When stress levels are high, resilience tends to be low, and vice versa. This means that individuals with low stress resilience may struggle more in managing and coping with stressors, while those with high stress resilience may be better equipped to handle and overcome challenges.
Building and strengthening stress resilience is essential for maintaining good mental health. It involves developing healthy coping mechanisms, such as practicing self-care, seeking support from others, and maintaining a positive mindset. Additionally, engaging in activities that promote relaxation, such as exercise, mindfulness, and hobbies, can also help enhance stress resilience.
It is important to note that stress resilience is not a measure of weakness or failure. It is a skill that can be developed and improved over time with practice and self-awareness. By understanding the inverse relationship between stress levels and resilience, individuals can take proactive steps to build their resilience and better manage stress in their lives.
In conclusion, stress resilience is inversely proportional to stress levels. The higher the stress levels, the lower the resilience, and vice versa. By actively working on building resilience and developing healthy coping mechanisms, individuals can enhance their ability to navigate and overcome stressful situations, ultimately promoting strong mental health and well-being.
What is stress resilience?
Stress resilience refers to an individual’s ability to adapt and cope with stress. It is the capacity to bounce back and recover from challenging or traumatic experiences. Resilience is not about avoiding stress or never experiencing it, but rather about how well we can handle and manage stress when it does occur.
Inversely related to stress, resilience acts as a protective factor, helping individuals maintain their mental health and well-being even in the face of adversity. It involves developing and utilizing a range of emotional, cognitive, and behavioral strategies to effectively navigate stressors and maintain a sense of balance and stability.
Resilience is not a fixed trait; it can be cultivated and strengthened through various practices and interventions. Building stress resilience involves developing self-awareness, fostering positive coping mechanisms, nurturing social support networks, and enhancing problem-solving skills.
Having high stress resilience can significantly impact our overall mental health and quality of life. It can help prevent the development of mental health disorders and contribute to greater emotional well-being, improved relationships, and increased productivity.
While everyone experiences stress differently, cultivating stress resilience is crucial for maintaining good mental health and thriving in the face of life’s challenges.
Why is stress resilience important?
Stress is a common part of life, and everyone experiences it to some degree. However, the ability to effectively cope with and bounce back from stress is crucial for maintaining good mental health. This is where stress resilience comes into play.
Resilience can be defined as the ability to adapt and recover in the face of adversity, including stress. When someone has high stress resilience, they are better equipped to handle the challenges and pressures that life throws at them. They are able to maintain a sense of balance, stay focused, and make rational decisions even in the midst of a stressful situation.
Inversely, individuals with low stress resilience may struggle to cope with stress. They may become overwhelmed, anxious, or even develop mental health issues such as depression. This is why stress resilience is so important – it acts as a protective factor against the negative effects of stress.
Building strong stress resilience is a process that involves various factors, such as having a support network, practicing self-care, and developing healthy coping mechanisms. By investing in stress resilience, individuals can improve their overall mental well-being and enhance their ability to navigate the challenges of life.
| Stress resilience helps: | Stress resilience doesn’t: |
| – Reduce the risk of developing mental health issues | – Eliminate stress completely |
| – Improve decision-making under pressure | – Make someone immune to stress |
| – Enhance overall well-being | – Guarantee a stress-free life |
Understanding the Relationship
When it comes to stress resilience, the relationship between stress and resilience is inversely proportional. In other words, as stress levels increase, resilience tends to decrease. This means that individuals who experience high levels of stress may struggle to maintain their mental health and cope with the challenges they face.
Resilience is the ability to bounce back from adversity and adapt to change. It is an important factor in maintaining good mental health and overall well-being. When individuals have high levels of resilience, they are better able to handle stress and recover from difficult experiences.
However, when stress levels become too high, it can overwhelm a person’s resilience and impact their mental health. Chronic stress can lead to symptoms of anxiety, depression, and other mental health disorders. It can also contribute to physical health problems such as high blood pressure and heart disease.
Understanding the relationship between stress and resilience is crucial for building strong mental health. By recognizing the impact of stress on resilience, individuals can take steps to manage stress and enhance their resilience. This may involve practicing stress management techniques, seeking support from others, and engaging in self-care activities.
By building resilience, individuals can develop the skills and resources needed to navigate through challenging times and maintain their mental well-being. This can lead to improved stress management, better overall health, and a higher quality of life.
The concept of inversely proportional
When it comes to stress and resilience, the concept of inversely proportional is an important one to understand. In simple terms, it means that as stress levels increase, resilience levels decrease, and vice versa. This relationship is crucial in understanding how to build strong mental health and effectively manage stress.
Stress is a natural response to challenging or demanding situations. It can come from various sources, such as work, relationships, or financial pressures. When we experience stress, our bodies release hormones like cortisol, which can have negative effects on our mental and physical well-being.
Resilience, on the other hand, refers to our ability to bounce back from adversity and cope with stress. It is the capacity to adapt and recover quickly from difficult situations. Resilient individuals are better equipped to handle stress and are more likely to maintain good mental health.
The relationship between stress and resilience is inversely proportional. As stress levels increase, our resilience levels tend to decrease. This means that when we are under high levels of stress, we may find it more challenging to cope and recover from difficult situations.
Understanding this relationship is vital for building strong mental health. By recognizing the impact of stress on our resilience, we can take steps to manage stress effectively and enhance our ability to bounce back from adversity.
There are various strategies to build resilience and reduce stress levels. These include practicing self-care, engaging in stress-reducing activities like exercise or meditation, seeking support from friends or professionals, and developing healthy coping mechanisms.
In conclusion, the concept of inversely proportional stress resilience highlights the importance of managing stress effectively to build strong mental health. By understanding this relationship and implementing strategies to reduce stress and enhance resilience, we can improve our overall well-being and ability to cope with life’s challenges.
How stress resilience and mental health are related?
Stress and mental health are closely intertwined, and understanding the relationship between the two is crucial for building strong mental health. Stress is a natural response to challenging or threatening situations, and it can have both positive and negative effects on our well-being. Resilience, on the other hand, refers to our ability to bounce back from adversity and maintain positive mental health.
Research has shown that individuals with high levels of stress resilience are more likely to have better mental health outcomes. When we are resilient to stress, we are better equipped to handle life’s challenges and are less likely to experience negative psychological effects. This is because resilience helps us adapt and cope with stress in a healthy way, reducing the impact it has on our mental well-being.
Inversely, individuals with low levels of stress resilience may be more susceptible to developing mental health problems. When we are unable to effectively cope with stress, it can accumulate and lead to chronic stress, which has been linked to a variety of mental health issues such as anxiety and depression. Chronic stress can also weaken our immune system and increase the risk of physical health problems.
Building stress resilience is therefore crucial for maintaining good mental health. This can be done through various strategies such as practicing self-care, engaging in stress-reducing activities like exercise or mindfulness, and seeking support from others. By developing resilience to stress, we can protect our mental health and improve our overall well-being.
| Key Points: |
|---|
| – Stress and mental health are closely related. |
| – Stress resilience is the ability to bounce back from adversity. |
| – High stress resilience is associated with better mental health outcomes. |
| – Low stress resilience may increase the risk of mental health problems. |
| – Building stress resilience is important for maintaining good mental health. |
Factors that influence stress resilience
Stress resilience refers to an individual’s ability to adapt and cope with stressful situations. It is influenced by various factors, including but not limited to:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Proportional Factors | These are factors that are directly related to stress resilience. They include social support, self-esteem, and problem-solving skills. Having a strong support system, a positive self-image, and the ability to effectively solve problems can enhance an individual’s stress resilience. |
| Stress Factors | These are factors that contribute to the experience of stress. They include work-related demands, financial difficulties, relationship problems, and traumatic events. High levels of stress can negatively impact an individual’s stress resilience, making it more difficult to cope with future stressors. |
| Inversely Proportional Factors | These are factors that are inversely related to stress resilience. They include chronic health conditions, lack of social support, negative thinking patterns, and poor coping mechanisms. These factors can decrease an individual’s stress resilience, making them more vulnerable to the negative effects of stress. |
| Protective Factors | These are factors that buffer against the negative effects of stress. They include healthy coping mechanisms, positive relationships, optimism, and a sense of purpose. Having these protective factors can enhance an individual’s stress resilience, allowing them to bounce back more easily from stressful situations. |
Understanding the various factors that influence stress resilience is crucial for building strong mental health. By identifying and addressing these factors, individuals can enhance their ability to cope with stress and improve their overall well-being.
Building Strong Mental Health
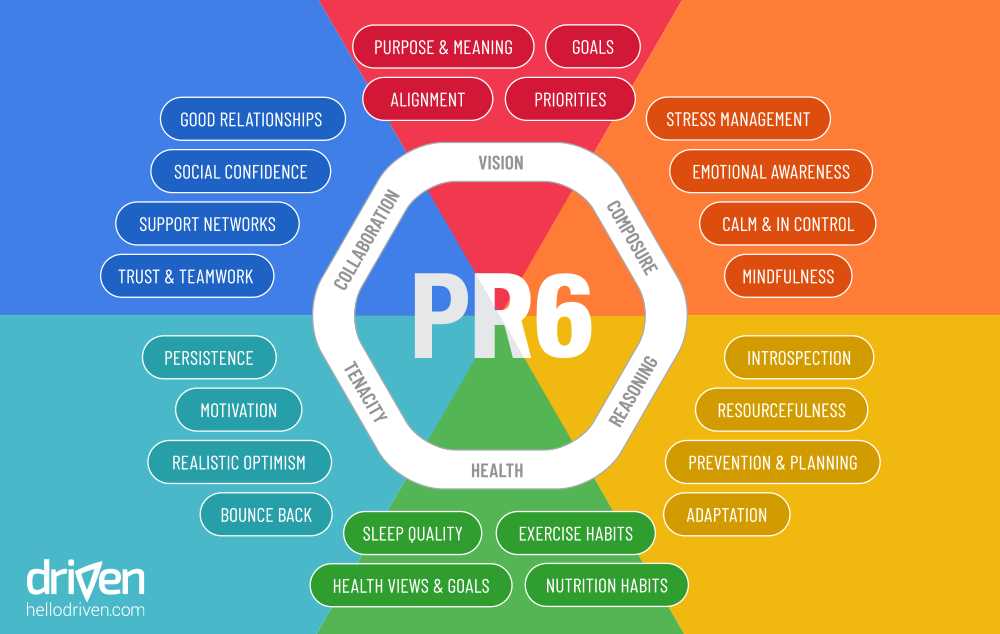
Building strong mental health is essential in managing stress and developing resilience. Stress and mental health are inversely related, meaning that as stress levels increase, mental health may decline. Therefore, it is important to prioritize mental well-being and take proactive steps to build resilience.
Here are some strategies to help build strong mental health:
- Practice self-care: Taking care of oneself is crucial in maintaining good mental health. This includes getting enough sleep, eating a balanced diet, and engaging in regular physical activity.
- Seek support: It is important to reach out to friends, family, or mental health professionals for support. Talking about one’s feelings and experiences can help in processing emotions and finding solutions.
- Develop coping mechanisms: Building resilience involves developing healthy coping mechanisms to deal with stress. This can include practicing mindfulness, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies and activities that bring joy.
- Set boundaries: Learning to set boundaries and say no when necessary can help reduce stress levels. It is important to prioritize one’s own needs and not overextend oneself.
- Practice gratitude: Cultivating a gratitude practice can shift focus towards the positive aspects of life and improve overall mental well-being. This can be done through journaling, expressing gratitude to others, or simply taking time to appreciate the present moment.
By implementing these strategies, individuals can work towards building strong mental health and improving their ability to cope with stress. Remember, mental health is a journey, and it is important to be patient and kind to oneself throughout the process.
Developing coping mechanisms
Inversely proportional to stress, resilience is the ability to adapt and bounce back from difficult experiences. Developing coping mechanisms is essential in building strong mental health and increasing stress resilience. Coping mechanisms are strategies or tools that individuals use to manage and reduce stress.
There are various coping mechanisms that can be developed to enhance stress resilience. These include:
| 1. Self-care: | Taking care of oneself is crucial in managing stress. Engaging in activities that promote relaxation and well-being, such as exercise, meditation, and hobbies, can help reduce stress levels and improve resilience. |
| 2. Social support: | Building a strong support network of friends, family, or support groups can provide emotional support and a sense of belonging, which can help individuals better cope with stress and adversity. |
| 3. Cognitive reframing: | Changing negative thought patterns and reframing stressful situations in a more positive and constructive way can help reduce stress and increase resilience. This can involve practicing gratitude, positive self-talk, and focusing on solutions rather than problems. |
| 4. Time management: | Effectively managing time and prioritizing tasks can help reduce feelings of overwhelm and stress. Breaking tasks into smaller, more manageable steps and setting realistic goals can improve stress resilience. |
| 5. Seeking professional help: | When stress becomes overwhelming or difficult to manage, seeking professional help from a therapist or counselor can provide individuals with the necessary tools and support to develop effective coping mechanisms and enhance stress resilience. |
By actively developing and practicing coping mechanisms, individuals can strengthen their mental health and increase their ability to handle stress. It is important to remember that everyone’s coping mechanisms may be different, and it may take time to find the strategies that work best for each individual.

I am Patrina de Silva, a psychologist and mental health blogger in Sri Lanka. After obtaining psychology degrees from the University of Colombo and Monash University, I returned home to work as a counselor while also starting the popular blog “Pressy but Happy” to provide advice on psychological issues. Over the past decade, my empathetic articles have made my blog a leading mental health resource in the country. In addition to writing, I maintain a private therapy practice, frequently volunteer counseling time, and conduct seminars, driven by my passion for destigmatizing mental illness and educating the public on the mind-body connection. I strive to be an influential voice in my field through my compassionate approach.
