
Smoking has long been recognized as a major public health concern, with numerous studies highlighting its detrimental effects on both physical and mental well-being. One significant factor that has been found to contribute to smoking behavior is stress. High levels of stress are often associated with an increased likelihood of smoking initiation and continued smoking. However, not all individuals who experience high levels of stress turn to smoking as a coping mechanism.
Resilience, the ability to adapt and bounce back from adversity, may play a moderating role in the relationship between stress and smoking status. Individuals with higher levels of resilience may be better equipped to handle stress without resorting to smoking as a coping mechanism. They may have developed alternative strategies for managing stress, such as engaging in physical activity, seeking social support, or practicing mindfulness.
Understanding the moderating effect of resilience on the stress-smoking relationship is crucial for developing targeted interventions and prevention programs. By identifying individuals who are at a higher risk of smoking due to stress and low resilience, healthcare professionals can provide them with the necessary support and resources to build resilience and find healthier ways of managing stress. This research can also inform policies and initiatives aimed at reducing smoking rates and improving public health outcomes.
Overview of the Study

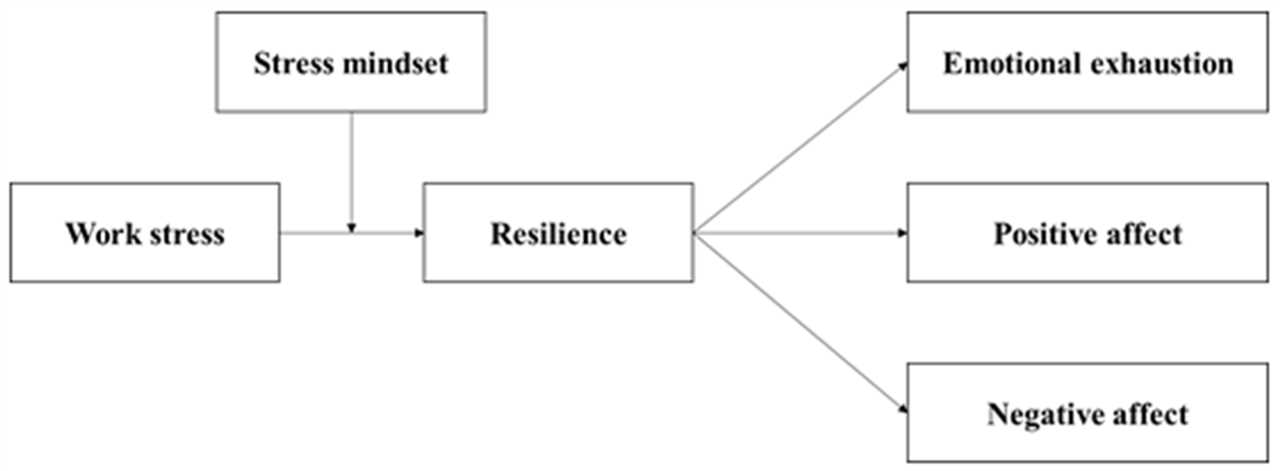
This study aims to examine whether resilience moderates the relationship between stress and smoking status. The main focus is on understanding how resilience, as a psychological trait, influences the association between stress levels and smoking behavior.
The study investigates the hypothesis that individuals with higher levels of resilience may be less likely to engage in smoking as a coping mechanism in response to stress. It seeks to explore whether resilience acts as a protective factor, buffering the negative impact of stress on smoking status.
To investigate this relationship, the study will gather data from a diverse sample of individuals, assessing their levels of stress, resilience, and smoking status. Various measures will be used to capture these constructs, including self-report questionnaires and objective smoking assessments.
The data collected will be analyzed using statistical methods, such as regression analysis, to determine the strength and direction of the relationships between stress, resilience, and smoking status. Additionally, moderation analysis will be conducted to examine whether resilience moderates the stress-smoking relationship.
The findings from this study may have implications for understanding the role of resilience in smoking behavior and provide insights into potential interventions to reduce smoking rates. By identifying the moderating effect of resilience, this research can contribute to the development of targeted interventions that promote resilience as a strategy for stress management and smoking cessation.
Importance of the Topic

The study on the relationship between stress and smoking status is of great importance due to the significant health implications associated with both stress and smoking. Stress is a prevalent condition that affects individuals in various aspects of their lives, including their physical and mental well-being. On the other hand, smoking is a major public health concern, as it is a leading cause of preventable diseases and mortality worldwide.
Understanding the relationship between stress and smoking status can provide valuable insights into the factors that contribute to smoking initiation, maintenance, and cessation. It can help identify individuals who are more susceptible to smoking under stress and develop targeted interventions to reduce smoking rates among those at high risk.
Resilience, as a psychological construct, plays a crucial role in moderating the relationship between stress and smoking status. Resilience refers to an individual’s ability to adapt and bounce back from adversity or stress. It can act as a protective factor, buffering the negative effects of stress on smoking behavior.
By investigating how resilience moderates the relationship between stress and smoking status, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of the underlying mechanisms and develop effective interventions to promote smoking cessation and prevent relapse. This knowledge can contribute to the development of personalized approaches to smoking cessation, taking into account individuals’ resilience levels and stress coping strategies.
In conclusion, the study on the relationship between stress and smoking status, and the moderating role of resilience, is of significant importance in addressing the public health issue of smoking. It can inform the development of targeted interventions and strategies to reduce smoking rates and improve overall health outcomes. Understanding the interplay between stress, resilience, and smoking behavior is essential for designing effective interventions and policies that promote smoking cessation and support individuals in maintaining a smoke-free status.
Understanding Resilience

Resilience refers to an individual’s ability to adapt and bounce back from stressful situations. It is the capacity to maintain a positive mental outlook and cope with challenges, setbacks, and adversity. Resilience plays a crucial role in moderating the relationship between stress and smoking status.
Stress is a common experience in everyday life and can have a significant impact on an individual’s well-being. It can lead to various negative outcomes, including unhealthy coping mechanisms such as smoking. However, not everyone who experiences stress resorts to smoking as a means of dealing with it.
This is where resilience comes into play. Individuals with higher levels of resilience are better equipped to handle stress and are less likely to turn to smoking as a coping mechanism. Resilience acts as a buffer, moderating the relationship between stress and smoking status.
Research has shown that individuals with higher levels of resilience are more likely to engage in healthier coping strategies when faced with stress. They are better able to problem-solve, seek social support, and engage in self-care activities that promote well-being. These individuals are less susceptible to the negative effects of stress and less likely to resort to smoking as a way to cope.
Understanding resilience is crucial for developing effective interventions to prevent and reduce smoking behavior. By enhancing individuals’ resilience, interventions can help individuals develop healthier coping mechanisms and reduce their reliance on smoking as a means of dealing with stress.
| Status | Between | Resilience | Stress | Moderate | Smoking | Does |
|---|
Definition of Resilience

Resilience refers to an individual’s ability to adapt and bounce back from stressful situations. It is a dynamic process that involves the relationship between stress and an individual’s ability to cope effectively. Resilience can moderate the relationship between stress and smoking status, as individuals with higher levels of resilience are more likely to engage in healthier coping mechanisms rather than turning to smoking as a way to deal with stress.
Resilience is not a fixed trait, but rather a set of skills and qualities that can be developed and strengthened over time. It involves the ability to maintain a positive outlook, manage emotions, and problem-solve effectively. Resilient individuals are able to navigate through difficult situations without resorting to harmful behaviors such as smoking.
Research has shown that individuals with higher levels of resilience are less likely to succumb to the negative effects of stress and are more likely to maintain a non-smoking status. This suggests that resilience plays a crucial role in moderating the relationship between stress and smoking, as it helps individuals find healthier ways to cope with stressors.
Overall, resilience is an important factor to consider when examining the relationship between stress and smoking status. By understanding and promoting resilience, interventions can be developed to help individuals build their resilience skills and reduce their reliance on smoking as a coping mechanism.
Factors Influencing Resilience
Resilience, the ability to bounce back from stress and adversity, is influenced by a variety of factors. One key factor is the level of stress an individual experiences. High levels of stress can challenge a person’s resilience and make it more difficult to cope with difficult situations.
Another factor that influences resilience is the presence of social support. Having a strong support network of family, friends, and other loved ones can provide emotional support, practical assistance, and a sense of belonging, all of which contribute to resilience.
Personal characteristics, such as self-esteem and optimism, also play a role in resilience. Individuals with higher levels of self-esteem and optimism tend to be more resilient in the face of stress and adversity.
Additionally, the relationship between stress and resilience is complex. While high levels of stress can challenge resilience, moderate levels of stress can actually enhance resilience by providing opportunities for growth and adaptation.
Smoking status can also impact resilience. Research has shown that smokers may have lower levels of resilience compared to non-smokers, which may be due to the negative impact of smoking on physical health and overall well-being.
In conclusion, resilience is influenced by factors such as stress, social support, personal characteristics, and smoking status. Understanding these factors can help individuals and healthcare professionals develop strategies to enhance resilience and promote well-being.
Role of Resilience in Coping with Stress
Resilience plays a crucial role in moderating the relationship between stress and smoking status. Stress is a common experience in our daily lives, and it can have a significant impact on our overall well-being. It is well-known that stress can contribute to the development and maintenance of unhealthy behaviors, such as smoking.
However, not everyone who experiences stress turns to smoking as a coping mechanism. This is where resilience comes into play. Resilience can be defined as the ability to bounce back from adversity and adapt positively to challenging situations. Individuals with high levels of resilience are better equipped to cope with stress and are less likely to engage in unhealthy behaviors like smoking.
Research has shown that individuals with high levels of resilience are more likely to employ effective coping strategies when faced with stress. They are better able to regulate their emotions, seek social support, and find alternative ways to manage stress without resorting to smoking. Resilient individuals are also more likely to have a positive outlook on life and possess a sense of self-efficacy, which further enhances their ability to cope with stress.
Furthermore, resilience can act as a buffer against the negative effects of stress. It can help individuals maintain their smoking cessation efforts even when faced with challenging situations or triggers. Resilient individuals are more likely to persevere through difficult times and stay committed to their goal of quitting smoking.
In conclusion, resilience plays a vital role in moderating the relationship between stress and smoking status. It acts as a protective factor, enabling individuals to cope with stress in healthier ways and resist the temptation to smoke. Understanding the role of resilience in coping with stress can inform interventions and strategies aimed at promoting smoking cessation and overall well-being.
Stress and Smoking Status

The relationship between stress and smoking status is a complex one, with various factors at play. Stress can have a significant impact on smoking behavior, and smoking status can also influence an individual’s response to stress. Resilience, as a moderating factor, plays a crucial role in this relationship.
Stress, whether it is caused by external factors such as work pressure or internal factors such as personal conflicts, can lead individuals to engage in smoking as a coping mechanism. Smoking is often seen as a way to relieve stress and provide temporary relaxation. However, this relationship between stress and smoking status is not straightforward.
Resilience, the ability to bounce back from adversity and cope with stress effectively, moderates the relationship between stress and smoking status. Individuals with high levels of resilience are more likely to find healthier ways to cope with stress, such as through exercise or social support, rather than turning to smoking. On the other hand, individuals with low resilience may be more prone to using smoking as a coping mechanism.
Understanding the relationship between stress and smoking status is crucial for developing effective interventions to reduce smoking prevalence. By focusing on enhancing resilience and providing alternative coping strategies for individuals experiencing stress, it may be possible to reduce the reliance on smoking as a stress management tool. This, in turn, could lead to improved smoking cessation rates and better overall health outcomes.
Effects of Stress on Smoking

The relationship between stress and smoking status has been extensively studied in recent years. Stress has been found to have a significant impact on smoking behaviors, with many individuals turning to smoking as a way to cope with stress.
Research has shown that stress can increase the likelihood of smoking initiation and make it more difficult for individuals to quit smoking. This is due to the fact that smoking can provide temporary relief from stress, leading to a cycle of dependence and continued smoking.
Furthermore, stress can also influence smoking status by affecting the level of resilience in individuals. Resilience refers to an individual’s ability to bounce back from stressful situations. Those with higher levels of resilience may be less likely to turn to smoking as a coping mechanism.
However, the relationship between stress and smoking status can be moderated by resilience. Some individuals may have a higher level of resilience, which can buffer the effects of stress and reduce the likelihood of smoking initiation or relapse.
| Relationship | Stress | Status | Moderate | Resilience | Does | Between |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smoking | Can increase | Initiation and make it more difficult to quit | By affecting resilience | Higher levels can reduce likelihood | Resilience can buffer effects | Stress and smoking status |
Factors Influencing Smoking Status
In the study “Does Resilience Moderate the Relationship Between Stress and Smoking Status”, the researchers aimed to investigate the factors that influence smoking status. The main focus was on the role of resilience in moderating the relationship between stress and smoking.
Resilience, defined as the ability to adapt and bounce back from adversity, has been found to play a significant role in various health behaviors, including smoking. Individuals with higher levels of resilience are more likely to resist the temptation to smoke and maintain a non-smoking status even in the face of stress.
Smoking status, whether being a smoker or a non-smoker, is influenced by various factors such as stress levels, coping mechanisms, and personal characteristics. The relationship between stress and smoking status is complex, as stress can both contribute to smoking initiation and hinder smoking cessation.
The study aimed to explore whether resilience acts as a moderator in this relationship. It hypothesized that individuals with higher levels of resilience would be less likely to start smoking or more likely to quit smoking, even in the presence of high levels of stress.
| Factors | Influence on Smoking Status |
|---|---|
| Resilience | Higher levels of resilience are associated with a lower likelihood of smoking initiation and a higher likelihood of smoking cessation, even in the presence of stress. |
| Stress | High levels of stress can contribute to smoking initiation and hinder smoking cessation. |
| Coping Mechanisms | The ability to effectively cope with stressors can influence smoking status, as individuals with healthier coping mechanisms are less likely to turn to smoking as a means of stress relief. |
| Personal Characteristics | Individual characteristics such as age, gender, socioeconomic status, and education level can also influence smoking status. These factors may interact with stress and resilience to further shape smoking behavior. |
Understanding the factors that influence smoking status, particularly the role of resilience in moderating the relationship between stress and smoking, can inform the development of targeted interventions and prevention strategies. By promoting resilience and providing effective stress management techniques, it may be possible to reduce smoking rates and improve overall health outcomes.
Link between Stress and Smoking Status

The relationship between stress and smoking status has been a topic of interest in recent research. Stress is known to be a significant factor in the initiation and maintenance of smoking behavior. It has been observed that individuals who experience high levels of stress are more likely to be smokers compared to those who experience lower levels of stress.
However, the relationship between stress and smoking status is not straightforward. It is influenced by various factors, one of which is resilience. Resilience refers to an individual’s ability to adapt and bounce back from stressful situations.
Research suggests that resilience may moderate the relationship between stress and smoking status. Individuals with higher levels of resilience may be less likely to take up smoking or continue smoking in response to stress. This is because they have better coping mechanisms and are able to handle stress in healthier ways, such as engaging in exercise or seeking social support.
On the other hand, individuals with lower levels of resilience may be more vulnerable to the negative effects of stress and may turn to smoking as a way to cope. Smoking can provide temporary relief from stress, as nicotine has been found to have mood-altering effects. However, it is important to note that smoking is not an effective long-term coping strategy and can have detrimental health effects.
Understanding the link between stress and smoking status, as well as the role of resilience, is crucial for developing effective interventions and prevention strategies. By promoting resilience and providing alternative coping mechanisms for stress, it may be possible to reduce smoking rates and improve overall health outcomes.

I am Patrina de Silva, a psychologist and mental health blogger in Sri Lanka. After obtaining psychology degrees from the University of Colombo and Monash University, I returned home to work as a counselor while also starting the popular blog “Pressy but Happy” to provide advice on psychological issues. Over the past decade, my empathetic articles have made my blog a leading mental health resource in the country. In addition to writing, I maintain a private therapy practice, frequently volunteer counseling time, and conduct seminars, driven by my passion for destigmatizing mental illness and educating the public on the mind-body connection. I strive to be an influential voice in my field through my compassionate approach.
